 |
 |
- Search
| Psychiatry Investig > Volume 17(9); 2020 > Article |
|
Abstract
Objective
To evaluate the associative role of depression and apolipoprotein E epsilon 4 allele (APOEε4) in subjective cognitive decline (SCD) and its progression to objective cognitive decline.
Methods
After literature search in electronic databases, studies were selected by following precise eligibility criteria. Meta-analyses were performed to examine the role of APOEε4 and depression in SCD or its progression to mild cognitive impairment (MCI) or dementia.
Results
APOEε4 positivity was not different between SCD and normal individuals but was significantly higher in individuals with SCD plus than in normal individuals [odds ratio: 2.39 (95% CI: 1.87, 3.05); p<0.00001] and in SCD converters than in non-converters [odds ratio: 5.19 (95% CI: 2.36, 11.42); p<0.00001]. Depression was significantly higher in individuals with SCD [standardized mean difference: 0.63 (0.45, 0.82); p<0.00001] and SCD plus [standardized mean difference: 0.83 (0.43, 1.22); p<0.0001] than in normal individuals. However, depression was not different between SCD and MCI or between SCD converters and non-converters. Age of SCD converters was higher than non-converters [mean difference: 2.95 years (0.58, 5.31)].
Subjective cognitive decline (SCD) is a self-perceived persistently declining cognitive function when compared to the individual’s previous state of normal cognitive performance on a standardized cognitive test score adjusted for age, sex, and education. SCD plus is a higher category of SCD that increases the likelihood of preclinical Alzheimer’s disease [1]. Presenting symptoms of SCD such as subjective memory complaints (individual informed memory problems) have a prevalence of 25% to 50% in community-dwelling elderly [2]. Individuals with SCD are at a greater risk of progression to any form of objective cognitive decline such as mild cognitive impairment (MCI) or Alzheimer’s disease [3-5]. The predictability is greater when a SCD-related complaint made by the individual is also endorsed by an informant (an individual who knows the patient well). A study of a multicenter cohort of elderly found that individuals were at a 4-fold risk of developing MCI or dementia if the SCD complaint was made by both the individual and the informant, whereas either the individual’s or the informant’s complaint posed 2-fold risk of progression [6].
Pathological changes associated with SCD and its progression include changes in both brain anatomy and biomarkers. In community-dwelling elderly, the severity of white matter lesions has been found to be associated with SCD and its worsening in the last five years [7]. The presence of thinner parietal and temporal cortices in individuals with SCD is associated with the later progression of SCD to dementia [8]. Increased amyloid beta deposition in the brain is also reported in older individuals with SCD [9]. Although, a significant proportion of older adults who report cognitive problems progress to objective cognitive impairment, the predictability is not straight forward and the link between SCD and objective cognitive impairment may be affected by the affective symptoms [10]. Moreover, the predictability of SCD for future objective cognitive impairment may also be confounded by many factors like depression, anxiety, physical health, and somatic problems [11,12].
The relationship between depression and SCD is not clear. Studies involving individuals with SCD have found associations of SCD with apolipoprotein E epsilon 4 allele (APOEε4) or with depression but the outcomes are not always consistent. In the present study, we undertake this issue by conducting a systematic review of these studies to perform a meta-analysis of important indices in order to seek a refined evidence of the relationship between APOEε4, depression and SCD.
A study was included if it 1) investigated cohorts of individuals with SCD or surveyed community-dwelling individuals; 2) reported APOEε4 status and the prevalence of depression in individuals with SCD; and 3) reported an association between SCD and APOEε4, and/or between SCD and depression, and/or between SCD and depression in APOEε4 positive individuals. A study was excluded if it 1) reported the relationships between APOEε4 and/or depression in individuals with MCI or dementia but not in individuals with SCD; 2) or reported the outcomes of either APOEε4 status or depression prevalence but not both in individuals with SCD; or 3) reported the outcomes without differentiating stages/forms of cognitive impairment.
A comprehensive literature search was conducted in Google Scholar, PubMed, and Science Direct electronic databases by using the most relevant key terms including subjective cognitive decline, SCD, memory complaints, dementia risk, preclinical Alzheimer’s disease, apolipoprotein E ε4, APOEε4, depression, and depressive symptoms. The search strategy is given in the supporting information file (Supplementary Table 1 in the online-only Data Supplement). Additional searches included screening the bibliographic sections of important research and review articles as well as the software suggested records. The literature search was restricted to research articles published in English before November 2019.
Data pertaining to demographics, study design, cognitive status/measures, APOEε4 positivity, depression prevalence and scale, SCD progression rates, and associational outcomes were extracted from the identified research articles. SCD was defined as the individual’s complaint of worsened cognitive function (not related to an acute event) in comparison with a previously normal state, where SCD plus was considered a higher category of SCD as identified by the authors of individual studies. SCD converters were defined as the individuals who progressed to objective cognitive decline (MCI, Alzheimer’s disease or any other type of dementia) during study followup period.
To attain overall estimates of the prevalence of APOEε4 or depression, meta-analyses of proportions were performed under a random-effects model with Stata software (Stata Corporation, TX, USA) using dichotomous data of individual studies. Meta-analyses of odds ratios (ORs) were performed to estimate the differences in the prevalence of APOEε4 between normal individuals and in individuals with SCD, SCD plus, or MCI. In a separate meta-analysis, the ORs reported by the included studies were pooled to obtain overall estimates.
To estimate the significance of difference between normal individuals and individuals with SCD or MCI in depression scores, age, and formal education, random-effects meta-analyses of mean differences (MD) or standardized MD (SMD) were performed with RevMan software (Nordic Cochrane Centre, Cochrane Community). The between-studies inconsistency in outcomes was estimated with the I2 index.
Twenty-five studies published in twenty-eight research articles were included in the meta-analysis (Figure 1) [13-40]. From these studies, data were available for 6247 individuals with SCD {55% [95% confidence interval (CI): 51, 59] females}, 10087 normal (cognitively) individuals [56% (95% CI: 51, 60) females], and 1165 individuals with MCI [58% (95% CI: 49, 68) females]. Of these, 13 were cross-sectional and 13 were longitudinal studies. The average follow-up duration of the longitudinal studies was 5.8 years (95% CI: 4.8, 6.9). Important characteristics of the included studies are presented in Supplementary Table 1 (in the online-only Data Supplement).
The percent positivity of APOEε4 (homozygote or heterozygote) was 23% (95% CI: 19, 27) in normal, 28% (95% CI: 23, 33) in SCD, 31% (95% CI: 16, 49) in SCD plus, and 39% (95% CI: 29, 49) in MCI individual. The odds of APOEε4 positivity were not different between individuals with SCD and normal individuals [OR: 1.03 (95% CI: 0.79, 1.35); p=0.52]. However, the odds of APOEε4 positivity were significantly higher for individuals with SCD plus than for normal individuals [OR: 2.39 (95% CI: 1.87, 3.05); p<0.00001]. The odds of APOEε4 positivity were also significantly higher for SCD converters than for non-converters [OR: 5.19 (95% CI: 2.36, 11.42); p<0.00001) (Figure 2).
A pooled analysis of ORs reported by the individual studies also showed similar outcomes. In this meta-analysis, 1) the prevalence of APOEε4 was not different between SCD and normal individuals [pooled OR: 1.13 (95% CI: 0.86, 1.40)]; 2) the prevalence of depression was higher in individuals with SCD [pooled OR: 1.79 (95% CI: 0.33, 3.25)]; 3) the co-existence of APOEε4 and depression was also higher in individuals with SCD [pooled OR: 3.32 (95% CI: 0.04, 6.61)]; and 4) the risk of progression in individuals with SCD was higher in APOEε4 carriers [pooled OR: 1.94 (95% CI: 1.04, 2.84)] (Supplementary Figure 1 in the online-only Data Supplement).
A meta-analysis of depression scores indicated that depression was significantly higher in individuals with SCD [SMD: 0.63 (95% CI: 0.45, 0.82); p<0.00001] and SCD plus [SMD: 0.83 (95% CI: 0.43, 1.22); p<0.0001] in comparison with normal individuals. However, depression was not statistically significantly different between individuals with SCD and individuals with MCI [SMD: 0.12 (95% CI: -0.31, 0.54); p=0.70] or between SCD converters and non-converters [SMD: 0.21 (95% CI: -0.09, 0.51; p=0.17] (Figure 3).
The age of individuals with SCD or SCD plus were not different from those of normal individuals [mean difference (MD): 0.25 years (95% CI: 0.03, 0.46) and 1.07 years (95% CI: -1.55, 3.69) respectively]. However, the age of SCD converters was approximately 3 years higher than that of non-converters [MD: 2.95 years (95% CI: 0.58, 5.31); p=0.01] (Supplementary Figure 2 in the online-only Data Supplement). Formal education was not different between the groups (Supplementary Figure 3 in the online-only Data Supplement).
In this meta-analysis we found that, in comparison with normal individuals, APOEε4 prevalence was not significantly higher in individuals with SCD but was significantly higher in individuals with SCD plus than in normal individuals and in SCD converters than in non-converters. On the other hand, the level of depression was significantly higher in individuals with SCD or SCD plus than in normal individuals but was not significantly different between individuals with SCD and individuals with MCI or between SCD converters and non-converters.
In older adults, depression is found to be associated with altered cognitive function including attention deficits, memory impairment, decreased information processing speed, poor responsiveness, problems in visual and spatial performance and lower performance in complex mental tasks [41-44]. In addition to the outcomes of the present study, a review of 47 crosssectional studies found depressive symptoms to be positively associated with SCD [45]. In a study of more than 13000 cognitively normal individuals over 50-years old of which 10% had depression and 27% had SCD at baseline, 11% developed MCI or dementia during 7 years of follow-up. The risk of developing MCI or dementia was significant with SCD (hazard ratio; HR: 2) as well as with depression (HR: 1.4) but the risk was highest when both depression and SCD (HR: 2.8) coexisted at baseline [46]. Thus, at least some of the SCD symptoms may stem from depression or depression may substantiate the symptoms of cognitive worsening arising from neurodegenerative processes.
In a longitudinal community-based study of elderly, a positive association was observed between APOEε4 and depression during 5 years of follow-up. This relationship persisted even after the exclusion of individuals who developed dementia within 9 years of follow-up and after controlling for the Mini-Mental State Examination score which showed that depression was not a prodromal symptom of dementia [47]. A meta-analysis of 9 studies also found that APOEε4 was positively associated with depression in individuals aged 23 to 83 years [48]. In the present study, we found that the odds of the coincidence of APOEε4 and depression were also higher in individuals with SCD. A study that used data of 11453 cognitively asymptomatic individuals from the National Alzheimer’s Coordinating Center, found that the hazard of developing Alzheimer’s disease was 10 times higher (HR: 10.1) among APOEε4 carriers with clinician-verified depression [49].
In the present study, the expression of APOEε4 increased from 23% in normal to 28% in SCD, 31% in SCD plus, and 39% MCI individuals. Our prevalence estimate resembles that of Zhang et al. [50] who reported the prevalence of APOEε4 at 32% in individuals with SCD after reviewing 28 studies. Moreover, in our study, APOEε4 positivity was significantly higher in SCD converters than in non-converters. A study of individuals with MCI found that the expression of APOEε4 was 62% in individuals who progressed from MCI to Alzheimer’s dementia [51]. Homozygous carriers of APOEε4 are reported to have a faster rate of cognitive decline between the age of 40 and 70 years [52]. Moreover, whereas heterozygous APOEε4 poses 3-fold risk of sporadic Alzheimer’s disease, APOEε4 homozygosity poses a 14-fold risk [53]. A probable mechanism of APOEε4 action appears to be related to amyloid beta clearance from the brain. It has been demonstrated that whereas APOEε2 enhances amyloid beta clearance from the brain, APOEε4 remains inefficient in this clearance [53].
Although the present study and the literature cited above indicate a relationship between depression and SCD, several caveats need to be addressed in future research. Whether depression develops because of persistent cognitive problems in individuals with SCD or whether depression causes, coexists, or worsens cognitive decline should be delineated. The relationship between APOEε4 and SCD can be better understood in SCD plus individuals but the relationship with depression in manifesting objective cognitive decline is not as clear. This study and some others suggest that the presence of both depression and APOEε4 increases the risk of progression among individuals with SCD more than either factor alone.
Some limitations of the present study should be noted. Firstly, less data were available with regards to the prevalence or measures of depression in APOEε4 positive vs APOEε4 negative individuals with SCD which could better portray a relationship between depression and SCD or its progression. Secondly, less binary data were available in individual studies pertaining to the prevalence of depression which could further clarify the outcomes of the present study. Thirdly, although in most of the analyses I2 remained moderate, statistical heterogeneity was high in some meta-analyses which represented high between-studies inconsistency in the outcomes. The use of various scales to measure depression, and study design features could have contributed to the heterogeneity.
Supplementary Materials
The online-only Data Supplement is available with this article at https://doi.org/10.30773/pi.2019.0324.
The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: Yue-ping Huang, Ju-jun Xue. Data curation: Chao Li, Xi Chen. Formal analysis: Chao Li, Xi Chen. Funding acquisition: Peng-xiang Bi. Investigation: Hong-juan Fu. Methodology: Teng Fei. Project administration: Peng-xiang Bi. Resources: Peng-xiang Bi. Sofware: Chao Li, Xi Chen. Supervision: Peng-xiang Bi. Validation: Peng-xiang Bi. Visualization: Peng-xiang Bi. Writing—original draf: Yue-ping Huang, Ju-jun Xue. Writing—review & editing: Peng-xiang Bi.
Figure 1.
A flowchart of the study screening and selection process. SCD: subjective cognitive decline
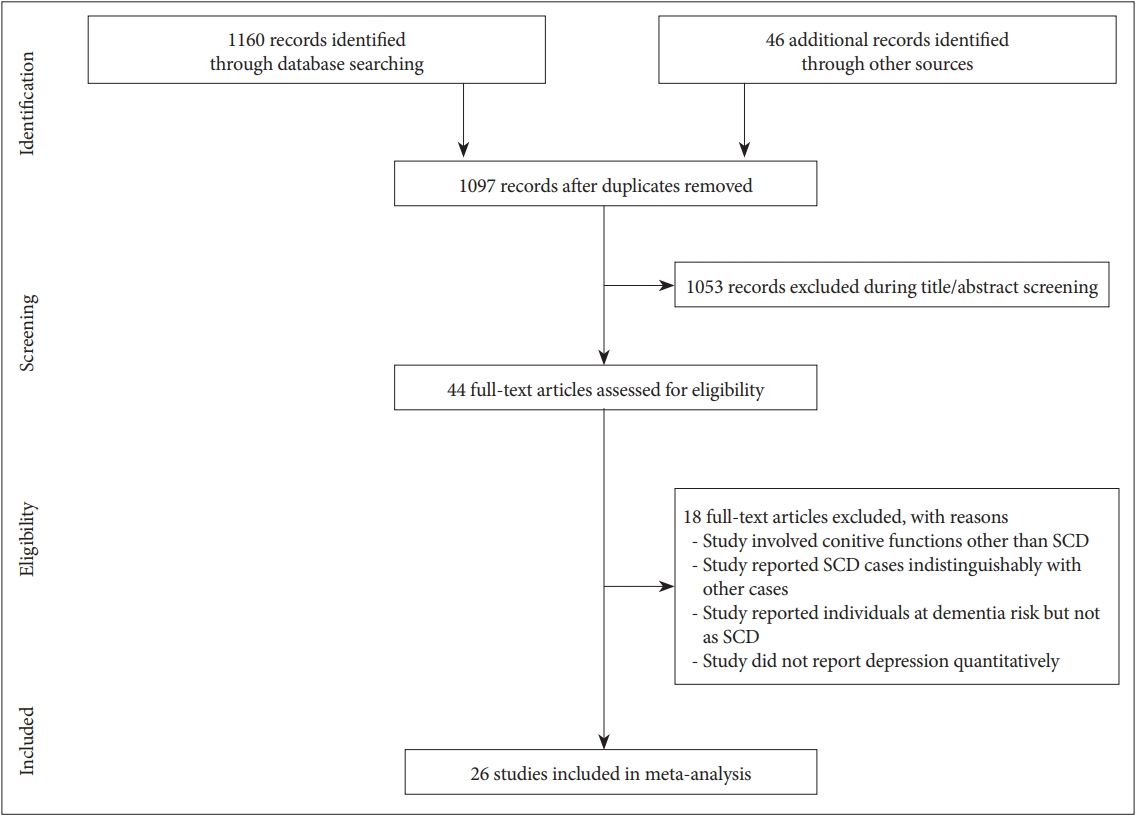
Figure 2.
A forest graph showing the ORs between SCD and normal/MCI individuals or between converters and non-converters from SCD to MCI in the presence of APOEε4. Diamonds show the overall ORs where the thicknesses represent summary point and the spread shows the 95% CI of the summary point. For individual studies, the central box represents the OR and lines show the 95% CI. The size of the box represents the weight of the study relative to other studies. BDI: Beck Depression Inventory, GDS: Geriatric Depression Scale, HDRS: Hamilton Depression Rating Scale, Met: methionine allele carriers, Val: valine allele carriers, OR: odds ratios, SCD: subjective cognitive decline, MCI: mild cognitive impairment, CI: confidence interval.

Figure 3.
A forest graph showing the SMDs between SCD and normal/MCI individuals or between converters and non-converters from SCD to MCI in the levels of depression measured with validated tools. SCD: subjective cognitive decline, MCI: mild cognitive impairment, CI: confidence interval, SMD: standardized mean difference.

REFERENCES
1. Jessen F, Amariglio RE, van Boxtel M, Breteler M, Ceccaldi M, Chetelat G, et al. A conceptual framework for research on subjective cognitive decline in preclinical Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement 2014;10:844-852.



2. Lee MJ, Varadaraj V, Ramulu PY, Whitson HE, Deal JA, Swenor BK. Memory and confusion complaints in visually impaired older adults: an understudied aspect of well-being. Gerontol Geriatr Med 2019;5:2333721418818944



3. Dufouil C, Fuhrer R, Alperovitch A. Subjective cognitive complaints and cognitive decline: consequence or predictor? The epidemiology of vascular aging study. J Am Geriatr Soc 2005;53:616-621.


4. Reisberg B, Shulman MB, Torossian C, Leng L, Zhu W. Outcome over seven years of healthy adults with and without subjective cognitive impairment. Alzheimers Dement 2010;6:11-24.


5. Mitchell AJ, Beaumont H, Ferguson D, Yadegarfar M, Stubbs B. Risk of dementia and mild cognitive impairment in older people with subjective memory complaints: meta-analysis. Acta Psychiatr Scand 2014;130:439-451.


6. Gifford KA, Liu D, Lu Z, Tripodis Y, Cantwell NG, Palmisano J, et al. The source of cognitive complaints predicts diagnostic conversion differentially among nondemented older adults. Alzheimers Dement 2014;10:319-327.


7. de Groot JC, de Leeuw FE, Oudkerk M, Hofman A, Jolles J, Breteler MM. Cerebral white matter lesions and subjective cognitive dysfunction: the Rotterdam Scan Study. Neurology 2001;56:1539-1545.


8. Verfaillie SC, Tijms B, Versteeg A, Benedictus MR, Bouwman FH, Scheltens P, et al. Thinner temporal and parietal cortex is related to incident clinical progression to dementia in patients with subjective cognitive decline. Alzheimers Dement (Amst) 2016;5:43-52.



9. Snitz BE, Lopez OL, McDade E, Becker JT, Cohen AD, Price JC, et al. Amyloid-beta imaging in older adults presenting to a memory clinic with subjective cognitive decline: a pilot study. J Alzheimers Dis 2015;48(Suppl 1):S151-S159.



10. Hanninen T, Reinikainen KJ, Helkala EL, Koivisto K, Mykkanen L, Laakso M, et al. Subjective memory complaints and personality traits in normal elderly subjects. J Am Geriatr Soc 1994;42:1-4.


11. Cooper C, Bebbington P, Lindesay J, Meltzer H, McManus S, Jenkins R, et al. The meaning of reporting forgetfulness: a cross-sectional study of adults in the English 2007 Adult Psychiatric Morbidity Survey. Age Ageing 2011;40:711-717.



12. Balash Y, Mordechovich M, Shabtai H, Giladi N, Gurevich T, Korczyn AD. Subjective memory complaints in elders: depression, anxiety, or cognitive decline? Acta Neurol Scand 2013;127:344-350.


13. Bessi V, Mazzeo S, Bagnoli S, Padiglioni S, Carraro M, Piaceri I, et al. The implication of BDNF Val66Met polymorphism in progression from subjective cognitive decline to mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease: a 9-year follow-up study. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 2020;270:471-482.



14. Buckley RF, Maruff P, Ames D, Bourgeat P, Martins RN, Masters CL, et al. Subjective memory decline predicts greater rates of clinical progression in preclinical Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement 2016;12:796-804.


15. Caselli RJ, Chen K, Locke DE, Lee W, Roontiva A, Bandy D, et al. Subjective cognitive decline: self and informant comparisons. Alzheimers Dement 2014;10:93-98.


16. Choe YM, Byun MS, Lee JH, Sohn BK, Lee DY, Kim JW. Subjective memory complaint as a useful tool for the early detection of Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 2018;14:2451-2460.



17. Chu CS, Sun IW, Begum A, Liu SI, Chang CJ, Chiu WC, et al. The association between subjective memory complaint and objective cognitive function in older people with previous major depression. PLoS One 2017;12:e0173027



18. Dik MG, Jonker C, Comijs HC, Bouter LM, Twisk JW, van Kamp GJ, et al. Memory complaints and APOE-epsilon4 accelerate cognitive decline in cognitively normal elderly. Neurology 2001;57:2217-2222.


19. Fernandez-Blazquez MA, Avila-Villanueva M, Maestu F, Medina M. Specific features of subjective cognitive decline predict faster conversion to mild cognitive impairment. J Alzheimers Dis 2016;52:271-281.


20. Grambaite R, Hessen E, Auning E, Aarsland D, Selnes P, Fladby T. Correlates of subjective and mild cognitive impairment: depressive symptoms and CSF biomarkers. Dement Geriatr Cogn Dis Extra 2013;3:291-300.



21. Hong YJ, Yoon B, Shim YS, Kim SO, Kim HJ, Choi SH, et al. Predictors of clinical progression of subjective memory impairment in elderly subjects: data from the Clinical Research Centers for Dementia of South Korea (CREDOS). Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 2015;40:158-165.


22. Jessen F, Wiese B, Cvetanovska G, Fuchs A, Kaduszkiewicz H, Kolsch H, et al. Patterns of subjective memory impairment in the elderly: association with memory performance. Psychol Med 2007;37:1753-1762.


23. Jessen F, Wiese B, Bachmann C, Eifflaender-Gorfer S, Haller F, Kolsch H, et al. Prediction of dementia by subjective memory impairment: effects of severity and temporal association with cognitive impairment. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2010;67:414-422.


24. Jessen F, Wolfsgruber S, Wiese B, Bickel H, Mosch E, Kaduszkiewicz H, et al. AD dementia risk in late MCI, in early MCI, and in subjective memory impairment. Alzheimers Dement 2014;10:76-83.


25. Jorm AF, Butterworth P, Anstey KJ, Christensen H, Easteal S, Maller J, et al. Memory complaints in a community sample aged 60-64 years: associations with cognitive functioning, psychiatric symptoms, medical conditions, APOE genotype, hippocampus and amygdala volumes, and white-matter hyperintensities. Psychol Med 2004;34:1495-1506.


26. Kim JM, Stewart R, Shin IS, Choi SK, Yoon JS. Subjective memory impairment, cognitive function and depression--a community study in older Koreans. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 2003;15:218-225.


27. Merrill DA, Siddarth P, Raji CA, Emerson ND, Rueda F, Ercoli LM, et al. Modifiable risk factors and brain positron emission tomography measures of amyloid and tau in nondemented adults with memory complaints. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry 2016;24:729-737.



28. Miebach L, Wolfsgruber S, Polcher A, Peters O, Menne F, Luther K, et al. Which features of subjective cognitive decline are related to amyloid pathology? Findings from the DELCODE study. Alzheimers Res Ther 2019;11:66




29. Muller-Gerards D, Weimar C, Abramowski J, Tebrugge S, Jokisch M, Dragano N, et al. Subjective cognitive decline, APOE epsilon4, and incident mild cognitive impairment in men and women. Alzheimers Dement (Amst) 2019;11:221-230.



30. Niti M. APOE-epsilon4, depressive symptoms, and cognitive decline in Chinese older adults: Singapore Longitudinal Aging Studies. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 2009;64:306-311.



31. Risacher SL, Kim S, Nho K, Foroud T, Shen L, Petersen RC, et al. APOE effect on Alzheimer’s disease biomarkers in older adults with significant memory concern. Alzheimers Dement 2015;11:1417-1429.



32. Roehr S, Luck T, Heser K, Fuchs A, Ernst A, Wiese B, et al. Incident subjective cognitive decline does not predict mortality in the elderly--Results from the Longitudinal German Study on Ageing, Cognition, and Dementia (AgeCoDe). PLoS One 2016;11:e0147050



33. Sanchez-Benavides G, Grau-Rivera O, Suarez-Calvet M, Minguillon C, Cacciaglia R, Gramunt N, et al. Brain and cognitive correlates of subjective cognitive decline-plus features in a population-based cohort. Alzheimers Res Ther 2018;10:123




34. Scheef L, Grothe MJ, Koppara A, Daamen M, Boecker H, Biersack H, et al. Subregional volume reduction of the cholinergic forebrain in subjective cognitive decline (SCD). Neuroimage Clin 2019;21:101612


35. Sohrabi HR, Bates KA, Rodrigues M, Taddei K, Martins G, Laws SM, et al. The relationship between memory complaints, perceived quality of life and mental health in apolipoprotein Eepsilon4 carriers and non-carriers. J Alzheimers Dis 2009;17:69-79.


36. Slot RER, Verfaillie SCJ, Overbeek JM, Timmers T, Wesselman LMP, Teunissen CE, et al. Subjective Cognitive Impairment Cohort (SCIENCe): study design and first results. Alzheimers Res Ther 2018;10:76




37. Stewart R, Russ C, Richards M, Brayne C, Lovestone S, Mann A. Depression, APOE genotype and subjective memory impairment: a crosssectional study in an African-Caribbean population. Psychol Med 2001;31:431-440.


38. Striepens N, Scheef L, Wind A, Meiberth D, Popp J, Spottke A, et al. Interaction effects of subjective memory impairment and ApoE4 genotype on episodic memory and hippocampal volume. Psychol Med 2011;41:1997-2006.


39. Visser PJ, Verhey F, Knol DL, Scheltens P, Wahlund LO, Freund-Levi Y, et al. Prevalence and prognostic value of CSF markers of Alzheimer’s disease pathology in patients with subjective cognitive impairment or mild cognitive impairment in the DESCRIPA study: a prospective cohort study. Lancet Neurol 2009;8:619-627.


40. Wang L, van Belle G, Crane PK, Kukull WA, Bowen JD, McCormick WC, et al. Subjective memory deterioration and future dementia in people aged 65 and older. J Am Geriatr Soc 2004;52:2045-2051.


41. Weisenbach SL, Boore LA, Kales HC. Depression and cognitive impairment in older adults. Curr Psychiatry Rep 2012;14:280-288.



42. Lockwood KA, Alexopoulos GS, van Gorp WG. Executive dysfunction in geriatric depression. Am J Psychiatry 2002;159:1119-1126.


43. Butters MA, Whyte EM, Nebes RD, Begley AE, Dew MA, Mulsant BH, et al. The nature and determinants of neuropsychological functioning in late-life depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2004;61:587-595.


44. Kohler S, Thomas AJ, Barnett NA, O’Brien JT. The pattern and course of cognitive impairment in late-life depression. Psychol Med 2010;40:591-602.


45. Hill NL, Mogle J, Wion R, Munoz E, DePasquale N, Yevchak AM, Parisi JM. Subjective cognitive impairment and affective symptoms: a systematic review. Gerontologist 2016;56:e109-e127.




46. Liew TM. Depression, subjective cognitive decline, and the risk of neurocognitive disorders. Alzheimers Res Ther 2019;11:70




47. Skoog I, Waern M, Duberstein P, Blennow K, Zetterberg H, Borjesson-Hanson A, et al. A 9-year prospective population-based study on the association between the APOE*E4 allele and late-life depression in Sweden. Biol Psychiatry 2015;78:730-736.


48. Wang WW, Liu XL, Ruan Y, Wang L, Bao TH. Depression was associated with apolipoprotein E ε4 allele polymorphism: a meta-analysis. Iran J Basic Med Sci 2019;22:112-117.


49. Burke SL, Maramaldi P, Cadet T, Kukull W. Associations between depression, sleep disturbance, and apolipoprotein E in the development of Alzheimer’s disease: dementia. Int Psychogeriatr 2016;28:1409-1424.



50. Zhang T, Liu S, Zhang Y, Guan Y, Wang X, Zhao L, et al. Apolipoprotein E e4 Allele is associated with subjective cognitive decline: a meta-analysis. Neuroepidemiology 2017;49:165-173.


51. Xu J, Li Q, Qin W, Jun Li M, Zhuo C, Liu H, et al. Neurobiological substrates underlying the effect of genomic risk for depression on the conversion of amnestic mild cognitive impairment. Brain 2018;141:3457-3471.











