 |
 |
- Search
| Psychiatry Investig > Volume 18(3); 2021 > Article |
|
Abstract
Objective
This study investigated the types of daily life stressors associated with social media use in adolescents with problematic Internet/smartphone use in a city in Korea.
Methods
Data from 2,997 Internet and smartphone users who participated in a survey about the actual use of smart digital media in Korea were included. The measurement tools included questionnaires on Internet and smartphone usage patterns and types of daily life stressors as well as the Internet Gaming Use-Elicited Symptom Screen and a smartphone addiction scale. The subjects were divided into a problematic Internet/smartphone use group and a control group. We compared the types of daily life stressors associated with social media use for each group.
Results
All types of daily life stressors were more prevalent in the problematic Internet use group than in the control group. In the problematic Internet/smartphone use group, the types of daily life stressors that were positively associated with social media use were sibling rivalry and physical health. In the control group, social media use was negatively associated with daily life stressors related to appearance and heterosexual relationships.
Recently, the problematic use of the Internet and smartphones has become a major issue in relation to behavioral problems in adolescents worldwide. The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5), and the International Statistical Classification of Disease, Eleventh Revision, were recently revised, and problematic Internet and smartphone use has been classified as Internet gaming disorder or gaming disorder [1,2]. Recently, it has been emphasized that excessive use of social media as well as games should be included in the problematic use of the Internet/smartphone. This indicates that the use of social media is an issue among youth with problematic Internet/smartphone use [3].
In South Korea, information technology is highly developed; 91.5% (50,393,000) of the population aged 3 years or older uses the Internet, and 91.0% of the population aged 6 years or older owned a smartphone in 2018 [4]. Adolescents in South Korea have easy access to the Internet and smartphones. In a previous study of Swiss students, indiscriminate accessibility increased the risk of problematic Internet/smartphone use by approximately 3 to 18 times in adolescents [5]. In a study of Internet and smartphone use among Korean youth, the prevalence of problematic Internet/smartphone use requiring psychiatric attention was approximately 3-33% [6,7]. In particular, if the Internet or a smartphone was used to access social media for longer periods of time than it was used for other purposes, such as information retrieval, media viewing, games, or telephone conversations, the risk of problematic Internet/smartphone use was higher [5,8].
Globally, adolescents use social media for diverse purposes, and social media are part of youth culture [9,10]. Anonymity can easily lead to criticism, blame, or cyber bullying against others on social media [11]. A high number of anonymous relationships online can lead to social isolation in real life [12]. Furthermore, stress associated with social media use can increase the risk of psychiatric problems, such as depression and anxiety disorder, in adolescents [13,14]. Because of the ubiquity of social media, users of social media have both instant and delayed reactions as a result of their social media usage. Therefore, predicting the effect of social media use on adolescents is difficult [15]. The impact of social media on adolescents is determined by the intensity of online technology usage, such as the Internet or smartphones [15].
Previous studies have reported that adolescents with behavioral problems such as problematic Internet/smartphone use are vulnerable to stress and use social media for long periods of time due to an inadequate ability to cope with stress [16,17]. In the context of mental illness prevention, it is important to understand daily life stressors. Adolescents with symptoms of problematic Internet/smartphone use are particularly vulnerable to mental illness and more likely to have behavioral problems [16,17]. In adolescents, the relationship between social media usage and daily life stressors is affected by the time and intensity of Internet/smartphone use. According to Goffman’s presentation of self as one of the archetypical theories attempting to understand social media usage, social media is about self-presentation [18,19]. Goffman suggested that an individual’s self-presentation could be analyzed through the observation of interpersonal interaction in his or her everyday life [18,19]. Current techniques for the observation of interpersonal interaction are different than those used in the past when Goffman’s theory was suggested. However, several researchers have suggested that Goffman’s theory is applicable in computer-mediated communication [20-22]. Currently, social media is a major context in which adolescents’ social interactions are reflected.
In adolescents with addictive behavior (problematic Internet/smartphone use), psychological and physical problems affect low self-esteem. Since experiences in daily life are reflected in self-presentation on social media, daily life stressors can be experienced differently adolescents with problematic Internet/smartphone use than by normal adolescents due to low self-esteem. Therefore, we hypothesized that there may be a difference in the relationship between daily life stressors and social media usage depending on whether or not adolescents exhibit problematic Internet/smartphone use. If there are differences in the types of daily life stressors experienced by the general population and the group with Internet addiction issues, it may be important to understand these differences and to suggest ways to deal with stress. Therefore, this study compared the types of stressors that are related to social media use in adolescents with and without problematic Internet/smartphone use in Korea.
From March to October 2017, the researchers surveyed 3,937 youth in one area (Nowon-gu) of Seoul, South Korea, about their actual use of smart digital media as part of a national mental health project. The survey was conducted on students from 4th grade in elementary school to 2nd grade in high school in Nowon-gu in Seoul. The survey was designed in multistage cluster sampling. In the first stage of sampling, schools located in Nowon-gu were extracted, and in the second stage, the classes were selected from the schools extracted in the first stage. In the last three stages, the subjects were selected from the classes. Among the surveyed data, data with errors or inaccurate information were excluded. This study conducted a second analysis using data from 2,997 Internet and smartphone users who participated in the survey. The survey included sociodemographic variables such as age, sex, number of family members, economic status of family members, academic achievement, main purpose of Internet and smartphone usage, a questionnaire regarding the types of stressors, the Internet Gaming Use-Elicited Symptom Screen (IGUESS), and a smartphone addiction scale. The subjects were divided into a control group and a problematic Internet/smartphone use risk group; subjects in the problematic use group scored ≥10 on IGUESS or ≥23 on the smartphone addiction scale [23,24]. This study was approved by the Institutional Ethics Review Committee of Eulji University Hospital (IRB No. EMCS 2018-06-014).
The questionnaires included nine items, and the subjects could choose from a variety of types of Internet and smartphone use. The question was, “Mark all types of ways that you mainly use the Internet or a smartphone (multiple responses available)”. The possible answers were as follows: online gaming, mobile messenger, media content, searching, community, social media, academic education, Internet shopping, and finance. In the questionnaire about social media, Facebook, Instagram, KaKaostory, blog, and Band were used as examples.
IGUESS is a self-report scale that was developed by Jo et al. [23] to screen for Internet game use disorders among adolescents in Korea based on the DSM-5. It consists of 9 items and evaluates symptoms during the last 12 months. Each item is rated on a 4-point Likert scale (1 to 4). The cutoff for this scale was 10 points, and the sensitivity (79%) and specificity (87%) were appropriate for screening Internet gaming problems [23]. The reliability and validity of this tool have been confirmed (Cronbach’s alpha=0.94) [23]. We used the smartphone addiction scale developed by the National Information Society Agency (2016), and it is a self-report questionnaire to screen for smartphone addiction. This scale integrated the previous individual scales, the Korean Scale for Internet Addiction (K-Scale) and the Smartphone Scale for Smartphone Addiction (S-Scale), from national survey data. This scale consists of 10 items, including 3 items on self-control failure, 3 items about salience, and 4 items related to serious consequences, each of which is rated on a 4-point Likert scale (1-4). The higher the score, the higher the tendency is toward smartphone addiction. The cutoff of this scale is 23 points for youth, which can be considered probable or high risk for smartphone addiction [24]. This scale has been validated (Cronbach’s α=0.81) [24]. In this study, the problematic Internet/smartphone use group included subjects whose scores were ≥10 on IGUESS or ≥23 on the smartphone addiction scale.
The questionnaire on the types of daily life stressors used in this study was developed by the National Youth Policy Institute in Korea in 2013. This questionnaire was used in a survey of elementary, middle and high school students nationwide in Korea in 2013, and the Cronbach’s α was 0.876. It consists of a total of 12 items, and each item is rated on a 4-point Likert scale (“not at all”=1-“very much”=4). The items are as follows: relationship with parents, sibling rivalry, appearance, physical health, psychological health, economic problems, peer relationships, heterosexual relationships, hierarchical relationships, relationship with teachers, career concerns, and academic difficulties. For each item, less than two points (“I do not have much”) indicates a nonstressful factor, and three points (“I have a little”) or more indicates a stressful factor.
A t-test and χ2 test were performed to compare the sociodemographic variables, Internet and smartphone usage patterns, and the types of daily life stressors between the problematic Internet/smartphone use group and the control group in all subjects (n=2,997). For each of the two groups, binary logistic regression analyses (enter method) were performed to assess the associations of the types of daily life stressor with social media use. For the dependent variable, the control and problematic Internet/smartphone use groups were subdivided into the presence of social media use and the absence of social media use. These analyses included the presence or absence of the use of social media (“yes” or “no”) as a dependent variable and 12 items about types of daily life stressors (categorical variables) as independent variables. Age, sex, number of family members, economic status, and academic achievement were included as covariates. In total, we performed a binary logistic regression analysis for each group. The effect sizes of the binary logistic regression analyses were determined using Cohen’s f2 values. Cohen’s f2 value was calculated by using the R2 value of each binary regression analysis. Statistical analyses were performed using IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, version 25.0 (IBM Corp, Armonk, NY, USA), and the fifer package in R (version 4.0.2, R Core Team 2020) is used for post-hoc analysis of chi-squared test. A p value of 0.05 was set for statistical significance. A p-value of 0.05 was set for statistical significance.
The subjects with problematic Internet/smartphone use (14.8±2.2 years) were significantly older than the subjects in the control group (13.7±2.2 years) (p<0.001, t=9.867). The sex proportion was not significantly different between the groups (p=0.881, χ2 =0.033). There were 33 (6.7%) subjects with high academic achievement in the problematic Internet/smartphone use group and 330 (13.3%) in the control group. The number of family members, economic status, and academic achievement were significantly different between the groups (p=0.005, χ2=16.710; p=0.001, χ2=18.291; p<0.001, χ2=121.289, respectively). In the results of the post hoc analysis (Bonferroni method), the control group had a higher number of family members (adjusted p=0.016), higher economic status (adjusted p: high vs. middle low=0.048; upper middle vs. middle low=0.012), higher academic achievement (adjusted p: high vs. middle=0.007, middle-low=<0.001, and low= <0.001; upper-middle vs. middle=0.002, middle-low=<0.001, and low=<0.001; middle vs. middle low=0.002 and low=<0.001; and middle low vs. low=0.012).
Among the subjects whose main purpose for using the Internet and smartphone was accessing social media, 346 (68.5%) were in the problematic Internet/smartphone use group, and 1,217 (48.8%) were in the control group (p<0.001, χ2=65.164). The mean duration of social media use was longer in the problematic Internet/smartphone use group than in the control group, with significant differences between groups (p<0.001, t=6.557). Table 1 shows the socioeconomic variables with significant differences between the two groups.
In a comparison of the daily life stressors between the two groups, a significantly higher percentage of the problematic Internet/smartphone use group than the control group reported experiencing each of the stressors. Figure 1 shows the results for the comparisons of the types of daily life stressors between groups.
There were differences in the types of daily life stressors between the problematic Internet/smartphone use group and the control group in the results of the binary logistic regression analyses. In the problematic Internet/smartphone use group, the significant daily life stressors were sibling rivalry [B=0.680, S.E.=0.297, p=0.022, odds ratio (OR)=1.974] and physical health (B=0.980, S.E.=0.358, p=0.006, OR=2.688). Among the covariates, age and female sex were significantly associated with social media usage (B=0.358, S.E.=0.080, p<0.001, OR=1.431; B=1.216, S.E.=0.289, p<0.001, OR=3.375). The Cohen’s f2 of this binary logistic regression was 0.812. In the control group, appearance (B=-0.338, S.E.=0.126, p=0.007, OR=0.713) and heterosexual relationships (B=-0.516, S.E.=0.227, p=0.023, OR=0.597) were negatively associated with social media usage. Among the covariates, age, female sex, and academic achievement were associated with social media usage (B=0.499, S.E.=0.032, p<0.001, OR=1.647; B=0.610, S.E.=0.102, p<0.001, OR=1.840, B=-1.082, S.E.=0.307, p<0.001). The Cohen’s f2 of this binary logistic regression was 0.541 (Table 2).
The main finding of this study is that the types of stressors associated with the main use of social media differed between the problematic Internet/smartphone use group and the control group. Consistent with Goffman’s theory on presentation of self, the problematic Internet/smartphone use group used social media for self-presentation, for improving deficits in real life such as low self-esteem due to sibling rivalry, and for addressing physical health problems. In the control group, self-presentation on social media was better than that in the real world, and the individuals wanted to share their better self with others [18,19]. The types of daily life stressors in adolescents with problematic Internet/smartphone use were sibling rivalry and physical health. In adolescents without problematic Internet/smartphone use, social media use was negatively associated with the types of daily life stressors, including appearance and heterosexual relationships. In the results of this study, the type of daily stressor related to social media and its associations were different between the problematic use of Internet/smartphone group and the control group. Adolescents with problematic Internet/smartphone use used social media as they became more stressed about sibling rivalry and physical health. In contrast, the control group used social media, as they were less stressed about appearance and heterosexual relationships. In a previous study, social media use was associated with psychiatric symptoms, such as problematic use of information technologies [25]. According to Goffman’s theory, which suggested social media to be one of means of self-presentation, users present a better self on social media than the self in real life, and users engage in imaginative performance for better self-presentation [18,19]. Social media presents a modified situation that reflects self-presentation that is affected by the user’s experiences in real world [18,19]. As shown in previous studies and this study, adolescents with problematic Internet and smartphone use are more stressed in daily life than controls, and improper prolonged use causes low self-esteem and worsens mental health and physical conditions [16,17,26]. Long-term use of social media in adolescents in the problematic Internet/smartphone use group disturbed their active ability to cope with stress, decreased activity, or interfered with positive communication. Adolescents are likely to be disturbed by negative feedback from unknown individuals on social media because of the anonymity of social media. If adolescents with problematic Internet/smartphone use are inappropriately exposed to social media for a long time, they become vulnerable to stress [5,25]. The self-presentation of adolescents who are frequently exposed to negative feedback is expressed as a negative self-image with low self-esteem on social media; these adolescents try to find a solution for what afflicts them rather than actively introducing themselves on social media. Problematic Internet/smartphone use constitutes addictive behavior that has a reward effect because it allows users to escape from discomfort in daily life [27]; thus, self-presentation related to daily negative experiences, including sibling rivalry and physical health problems, can be reflected in social media use. On the other hand, adolescents without problematic Internet/smartphone use can use social media for positive self-presentation, as they are less stressed by their appearance and heterosexual relationships. Self-presentation differed between those in the problematic Internet/smartphone group, who had low self-esteem and were prone to stress, and normal controls, and different types of daily life stress that reflect differently in self-presentation were associated with social media use.
The results indicate that adolescents with problematic Internet/smartphone use were more likely to use social media when they experienced severe stress from sibling rivalry. This result is related to the social role of the sibling relationship. In adolescence, sibling relationships are an important component of family dynamics; in addition, adolescence can have a direct impact on social role performance. Moreover, sibling relationships affect social role formation in adolescents [28,29]. The sibling relationship is considered a source of everyday social relations or a mutual role model of interpersonal relationships. Adolescents have an opportunity to adapt their social emotional development and competitive systems and to understand peer emotions through sibling relationships [29]. Sibling conflicts in childhood lead to impulse control problems. At the same time, internalizing symptoms, such as depressive mood and loneliness, can increase the risk of bullying and make peer relationships difficult. These psychiatric problems increase the risk of addictive behavior in adolescents and obstruct social adaptation [30,31]. Therefore, adolescents with a high level of stress from sibling rivalry are at high risk of being isolated from the real world, and adolescents with problematic Internet/smartphone use, who are more easily engaged in the Internet, may use social media for long periods of time to easily and immediately form relationships in virtual reality [15,28,29,32].
In adolescents with problematic Internet/smartphone use, stress related to physical health was associated with social media use. Long-term use of the Internet or smartphones causes physical health problems in adolescents. Adolescents with problematic Internet/smartphone use are at higher risk of physical health problems such as musculoskeletal disease and blurred vision compared with other adolescents [26]. Adolescents with problematic Internet/smartphone use have more physical discomfort than control subjects and may use social media to find information about solutions or to resolve concerns. Social media via the Internet or a smartphone are used as a tool to receive reassurance about health concerns or to exchange medical information. However, in individuals with problematic Internet use, this excess of information is associated with cyberchondria, which causes excessive worry about health [33,34]. Adolescents with problematic Internet/smartphone use seek health information on social media to alleviate their concerns and anxieties about individual health problems. However, this search cannot ameliorate the symptoms; rather, it reinforces the use of social media for medical information and increases anxiety, leading adolescents to become more stressed [33,34].
In the results for the control group, adolescents who were less stressed about appearance and heterosexual relationships mainly used social media via the Internet or smartphones. In these results, attention to nonphysical characteristics and amicable heterosexual relationships affected the positive use of social media. Unlike adolescents with problematic Internet/smartphone use who are immersed in the limited community’s social media, adolescents who have courage and temperance, which are known protective factors against problematic Internet/smartphone use, find pleasure in forming positive relationships through positive self-expression and appropriate social media use [35,36]. Recently, adolescents have used social media, through which they can fully show themselves to each other, to form heterosexual relationships. The formation of relationships through intimacy and trust plays an important role in psychological stability. Since self-disclosure is relatively open in social media, self-expression can easily be demonstrated [37]. In online communication, there is no association between the formation and maintenance of smooth social relations and physical characteristics such as appearance, and it is important for individuals to self-disclose to share their identities and psychological similarities [37,38]. In this regard, adolescents who are able to express themselves with less emphasis on their physical characteristics, such as appearance, may use social media to an appropriate degree.
There are several limitations of this study. First, the range of activity of individuals using social media could not be accurately evaluated. Second, we identified only the types of daily life stressors associated with the use of social media and could not confirm a causal relationship. Third, the results of this study cannot be generalized to the general youth population because the youth who participated in this study lived in a rural area in Korea. Further studies are needed to investigate how temperaments affect the relationship between social media use and daily stress in adolescents.
Despite these limitations, this study found that the types of daily life stressors related to social media use differed between Korean adolescents with problematic Internet/smartphone use and those without. This study suggests that the daily life stressors related to social media in problematic Internet/smartphone use could be an important issue. There is a need to provide personalized stress management for problematic Internet/smartphone use in adolescents experiencing stress related to social media use, which is different from the stress experienced by other adolescents.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This study was supported by a grant from the Korea Mental Health Technology R&D Project, Ministry of Health & Welfare, Republic of Korea (HM15C1058).
The authors would like to thank Seung-Chan Kim for consultancy regarding the data analysis.
The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Authors’ contribution
Ceptualization: Dongyun Lee, Cheol-Soon Lee. Data curation: Soo-Young Bhang. Formal analysis: Dongyun Lee. Investigation: Soo-Young Bhang. Methodology: Soo-Young Bhang. Software: Young-Ji Lee. Validation: Dongyun Lee, Jiyeong Seo. Writing—Original draft preparation: Dongyun Lee. Writing—review & editing: Jiyeong Seo, Soo-Young Bhang.
Figure 1.
The results of the comparison of the stress factors between the two groups by chi-squared test. The number of subjects who were stressed for all 12 items was significantly higher in the problematic Internet/smartphone use group than in the control group. *p<0.001, values of χ2 were as follows from left to right: 120.9, 13.6, 123.0, 93.6, 151.9, 79.3, 66.6, 96.7, 14.9, 35.5, 132.7, 146.
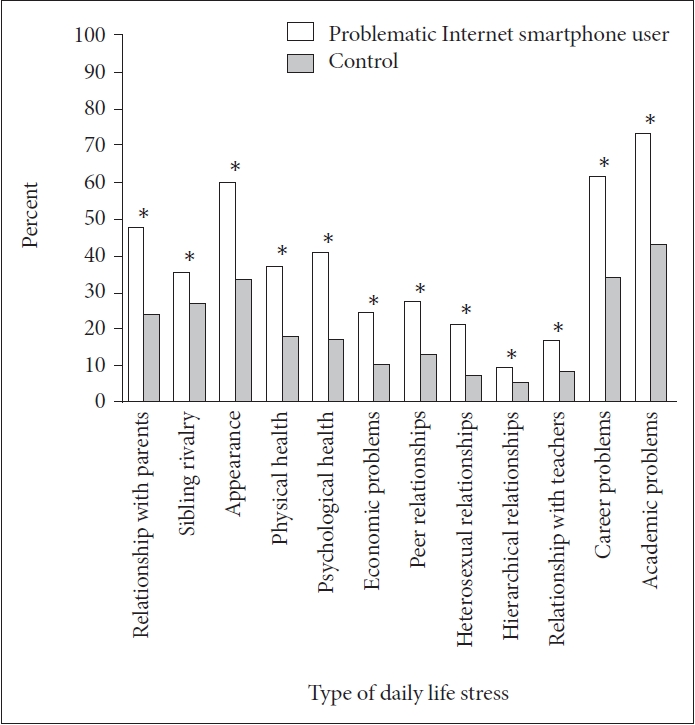
Table 1.
Sociodemographic characteristics between the problematic Internet/smartphone use group and the control group
| Problematic Internet/smartphone use (N=505) | Control (N=2,492) | p | t or χ2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years)* | 14.8±2.2 | 13.7±2.2 | <0.001 | 9.867 |
| Sex (male)** | 199 (39.9) | 995 (40.3) | 0.881 | 0.033 |
| 1Number of family members** | 0.005 | 16.710 | ||
| 0 | 4 (0.8) | 11 (0.4) | ||
| 1 | 26 (5.3) | 86 (3.4) | ||
| 2† | 293 (59.4) | 1680 (67.4) | ||
| 3 | 108 (21.9) | 408 (16.5) | ||
| 4 | 46 (9.3) | 201 (8.1) | ||
| 5 or more | 16 (3.2) | 84 (3.5) | ||
| A significant difference in the number of family members between groups by post hoc analysis (Bonferroni method) was as follow: †vs. 3 | ||||
| 2Economic status** | 0.001 | 18.291 | ||
| High† | 24 (4.9) | 181 (7.3) | ||
| Upper middle† | 112 (22.7) | 717 (29.1) | ||
| Middle | 285 (57.8) | 1315 (53.3) | ||
| Middle low | 57 (11.6) | 200 (8.1) | ||
| Low | 15 (3.0) | 52 (2.1) | ||
| A significant differences in economic status between groups by post hoc analysis (Bonferroni method) was as follows: †vs. middle low | ||||
| 3Academic achievement** | <0.001 | 121.289 | ||
| High†‡§ | 33 (6.7) | 330 (13.3) | ||
| Upper middle†‡§ | 92 (18.6) | 780 (31.5) | ||
| Middleठ| 172 (34.8) | 864 (34.9) | ||
| Middle low§ | 129 (26.1) | 391 (15.8) | ||
| Low | 68 (13.8) | 112 (4.5) | ||
| A significant differences in academic achievement between groups by post hoc analysis (Bonferroni method) was as follow; †vs. middle, ‡vs. middle low, §vs. low | ||||
| Internet and smartphone usage patterns (yes)** | ||||
| Social media use | 346 (68.5) | 1217 (48.8) | <0.001 | 65.164 |
| Academic education | 117 (35) | 983 (39.4) | 0.071 | 3.422 |
| Online gaming | 321 (63.6) | 1539 (61.8) | 0.451 | 0.582 |
| Mobile messenger | 399 (79) | 1816 (72.9) | 0.004 | 8.200 |
| Media content | 419 (83) | 1899 (76.2) | 0.001 | 10.971 |
| Searching | 366 (72.5) | 1755 (70.4) | 0.362 | 0.853 |
| Community | 90 (17.8) | 257 (10.3) | <0.001 | 23.125 |
| Internet shopping | 154 (30.5) | 436 (17.5) | <0.001 | 44.877 |
| Finance | 49 (9.7) | 114 (4.6) | <0.001 | 21.473 |
| Social media use time (minutes)* | 254.6±342.4 | 149.4±249.9 | <0.00 | 6.557 |
Table 2.
The stress factors associated with social media use in the problematic Internet/smartphone use group (N=505) and the control group (N=2,492) by binary logistic regression analyses
| B | S.E. | p | Exp. (B) | CI | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Problematic internet/smartphone use* | ||||||
| Relationship with parents | 0.468 | 0.305 | 0.125 | 1.597 | 0.879 | 2.902 |
| Sibling rivalry | 0.680 | 0.297 | 0.022 | 1.974 | 1.104 | 3.529 |
| Appearance | 0.190 | 0.322 | 0.557 | 1.209 | 0.643 | 2.274 |
| Physical health | 0.989 | 0.358 | 0.006 | 2.688 | 1.333 | 5.420 |
| Psychological health | 0.004 | 0.367 | 0.992 | 1.004 | 0.489 | 2.060 |
| Economic problems | -0.182 | 0.431 | 0.672 | 0.833 | 0.358 | 1.939 |
| Peer relationships | -0.147 | 0.361 | 0.684 | 0.863 | 0.425 | 1.753 |
| Heterosexual relationships | 0.055 | 0.402 | 0.891 | 1.057 | 0.481 | 2.324 |
| Hierarchical relationships | -0.662 | 0.580 | 0.254 | 0.516 | 0.165 | 1.609 |
| Relationship with teachers | -0.640 | 0.437 | 0.144 | 0.527 | 0.224 | 1.243 |
| Career problems | -0.632 | 0.337 | 0.060 | 0.532 | 0.275 | 1.028 |
| Academic problems | -0.267 | 0.346 | 0.441 | 0.766 | 0.388 | 1.509 |
| Control** | ||||||
| Relationship with parents | -0.111 | 0.133 | 0.406 | 0.895 | 0.690 | 1.162 |
| Sibling rivalry | 0.163 | 0.121 | 0.177 | 1.177 | 0.929 | 1.491 |
| Appearance | -0.338 | 0.126 | 0.007 | 0.713 | 0.558 | 0.912 |
| Physical health | 0.017 | 0.155 | 0.911 | 1.018 | 0.751 | 1.379 |
| Psychological health | 0.193 | 0.172 | 0.263 | 1.213 | 0.865 | 1.700 |
| Economic problems | 0.231 | 0.214 | 0.280 | 1.260 | 0.828 | 1.917 |
| Peer relationships | 0.063 | 0.170 | 0.712 | 1.065 | 0.762 | 1.487 |
| Heterosexual relationships | -0.516 | 0.227 | 0.023 | 0.597 | 0.383 | 0.931 |
| Hierarchical relationships | -0.344 | 0.274 | 0.209 | 0.709 | 0.414 | 1.213 |
| Relationship with teachers | -0.128 | 0.206 | 0.533 | 0.880 | 0.588 | 1.316 |
| Career problems | 0.210 | 0.146 | 0.151 | 1.233 | 0.926 | 1.643 |
| Academic problems | -0.231 | 0.128 | 0.070 | 0.794 | 0.618 | 1.019 |
REFERENCES
1. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5®). Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association Publishing; 2013.
2. World Health Organization. International Statistical Classification of Diseases (11th Ed). Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2017.
3. Christakis D. The challenges of defining and studying “digital addiction” in children. JAMA 2019;321:2277-2278.


4. Ministry of Science Information and Communications Technology. Survey for currnet status of internet usage in 2018. Available at: https://www.msit.go.kr/web/msipContents/contentsView.do?cateId=mssw11241&artId=1643636. 2019. Accessed February 6, 2020.
5. Haug S, Castro RP, Kwon M, Filler A, Kowatsch T, Schaub MP. Smartphone use and smartphone addiction among young people in Switzerland. J Behav Addict 2015;4:299-307.



6. Ha JH, Chin B, Park DH, Ryu SH, Yu J. Characteristics of excessive cellular phone use in Korean adolescents. Cyberpsychol Behav 2008;11:783-784.


7. Ko CH, Yen JY, Yen CF, Lin HC, Yang MJ. Factors predictive for incidence and remission of internet addiction in young adolescents: a prospective study. Cyberpsychol Behav 2007;10:545-551.


8. Jeong SH, Kim H, Yum JY, Hwang Y. What type of content are smartphone users addicted to? SNS vs. games. Comput Human Behav 2016;54:10-17.

9. Duggan M, Brenner J. The Demographics of Social Media Users, 2012. Washington, DC: Pew Research Center’s Internet & American Life Project; 2013.
10. Rideout VJ, Foehr UG, Roberts DF. Generation M2: Media in the Lives of 8-to 18-year-olds. San Francisco, CA: Kaiser Family Foundation; 2010.
12. Kraut R, Patterson M, Lundmark V, Kiesler S, Mukophadhyay T, Scherlis W. Internet paradox: a social technology that reduces social involvement and psychological well-being? Am Psychol 1998;53:1017-1031.


13. Hwang JM, Cheong PH, Feeley TH. Being young and feeling blue in Taiwan: examining adolescent depressive mood and online and offline activities. New Media Soc 2009;11:1101-1121.

14. Selfhout MHW, Branje SJT, Delsing M, Ter Bogt TFM, Meeus WHJ. Different types of internet use, depression, and social anxiety: the role of perceived friendship quality. J Adolesc 2009;32:819-833.


15. Best P, Manktelow R, Taylor B. Online communication, social media and adolescent wellbeing: a systematic narrative review. Child Youth Serv Rev 2014;41:27-36.

16. Assunção R, Matos PM. Adolescents’ profiles of problematic facebook use and associations with developmental variables. Comput Human Behav 2017;75:396-403.

17. Chen Y, Li R, Zhang P, Liu X. The moderating role of state attachment anxiety and avoidance between social anxiety and social networking sites addiction. Psychol Rep 2019;123:633-647.


18. Bullingham L, Vasconcelos AC. ‘The presentation of self in the online world’: Goffman and the study of online identities. J Inform Sci 2013;39:101-112.

19. Goffman E. The Presentation of Self in Everyday Life. Harmondsworth, London: Penguin Books; 1978.
20. Wheeler S. Connected Minds, Emerging Cultures: Cybercultures in Online Learning. In: Miller H, Arnold J, editor. Identity in Cyberspace. North Carolina: IAP-Information Age Publishing, Inc, 2009, p. 53-64.
21. Jacobsen M. The Contemporary Goffman. In: Jacobsen M, editor. Goffman through the Looking Glass: From ‘Classical’ to Contemporary Goffman. New York: Routledge, 2010, p. 1-50.
22. Laughey D. Key Themes in Media Theory. New York: McGraw-Hill Education (UK); 2007.
23. Jo SJ, Yim HW, Lee HK, Lee HC, Choi JS, Baek KY. The internet game use-elicited symptom screen proved to be a valid tool for adolescents aged 10-19 years. Acta Paediatr 2018;107:511-516.


24. Shin KW, Kim DI, Jeong YJ. Report: Development of Korean Smartphone Addiction Proneness Scale for Youth and Adults. Seoul, South Korea: National Information Society Agency; 2011.
25. Salehan M, Negahban A. Social networking on smartphones: when mobile phones become addictive. Comput Human Behav 2013;29:2632-2639.

26. De-Sola Gutiérrez J, Rodríguez de Fonseca F, Rubio G. Cell-Phone addiction: a review. Front Psychiatry 2016;7:175



27. Huisman A, Garretsen HFL, van den Eijnden RJJM. Problematisch Internetgebruik: een pilot study in Rotterdam. Rotterdam, Netherlands: IVO, Instituut voor Onderzoek naar Leefwijzen & Verslaving; 2000.
28. McHale SM, Updegraff KA, Whiteman SD. Sibling relationships and influences in childhood and adolescence. J Marriage Fam 2012;74:913-930.



29. McHale SM, Whiteman SD, Kim JY, Crouter AC. Characteristics and correlates of sibling relationships in two-parent African American families. J Fam Psychol 2007;21:227-235.


30. Bank L, Burraston B, Snyder J. Sibling conflict and ineffective parenting as predictors of adolescent boys’ antisocial behavior and peer difficulties: additive and interactional effects. J Res Adolesc 2004;14:99-125.

31. Stocker CM, Burwell RA, Briggs ML. Sibling conflict in middle childhood predicts children’s adjustment in early adolescence. J Fam Psychol 2002;16:50-57.


32. Hanprathet N, Manwong M, Khumsri J, Yingyeun R, Phanasathit M. Facebook addiction and its relationship with mental health among Thai high school students. J Med Assoc Thai 2015;98:S81-S90.
33. Fergus TA, Dolan SL. Problematic internet use and internet searches for medical information: the role of health anxiety. Cyberpsychol Behav Soc Netw 2014;17:761-765.


34. Hart J, Björgvinsson T. Health anxiety and hypochondriasis: description and treatment issues highlighted through a case illustration. Bull Menninger Clin 2010;74:122-140.


35. Choi SW, Kim DJ, Choi JS, Ahn H, Choi EJ, Song WY, et al. Comparison of risk and protective factors associated with smartphone addiction and internet addiction. J Behav Addict 2015;4:308-314.



36. Xie YB, Zhou P, Xu LP, Peng ZW. Prevalence of internet addiction and the related factors in middle school students in Guangzhou. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 2010;30:1801-1804.








