 |
 |
- Search
| Psychiatry Investig > Volume 13(2); 2016 > Article |
Abstract
Psychophysiological and functional neuroimaging studies have frequently and consistently shown that emotional information can be processed outside of the conscious awareness. Non-conscious processing comprises automatic, uncontrolled, and fast processing that occurs without subjective awareness. However, how such non-conscious emotional processing occurs in patients with various psychiatric disorders requires further examination. In this article, we reviewed and discussed previous studies on the non-conscious emotional processing in patients diagnosed with anxiety disorder, schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and depression, to further understand how non-conscious emotional processing varies across these psychiatric disorders. Although the symptom profile of each disorder does not often overlap with one another, these patients commonly show abnormal emotional processing based on the pathology of their mood and cognitive function. This indicates that the observed abnormalities of emotional processing in certain social interactions may derive from a biased mood or cognition process that precedes consciously controlled and voluntary processes. Since preconscious forms of emotional processing appear to have a major effect on behaviour and cognition in patients with these disorders, further investigation is required to understand these processes and their impact on patient pathology.
We reviewed studies of emotional processing outside of awareness in patients with psychiatric disorders, particularly those suffering from anxiety disorder, schizophrenia, bipolar disorder and depression. In addition to their disorder-specific symptoms, these patients commonly show abnormal cognition and abnormal behaviour when processing emotional stimuli. The search for the basis of abnormal emotion processing has been studied widely, both by measuring behavioural (through reported identification, discrimination or detection of emotional stimuli) and neurophysiological responses (through electrophysiological measurements and brain activity). However, the process by which psychiatric patients process emotion outside of conscious awareness has not been specifically investigated. It is important to identify the extent and limit of emotion perception without cognitive awareness, since the process of non-conscious perception of emotion may be qualitatively different from the process of conscious perception.1 Non-conscious perception of emotion shows several characteristics that contrast with the characteristics of conscious emotion perception. For example, non-conscious perception of emotion often carries coarse information of emotional stimuli automatically without the need for focused attention.1 Several studies have observed that non-conscious and conscious perception of emotion activates different regions of the brain, further indicating that their pathways may be qualitatively different. Moreover, the non-conscious processing of emotion may influence behaviour and decision-making, and often more strongly than when the stimuli are processed consciously.2 Despite the significant influence that non-consciously processed emotion may have on our lives, the investigation of emotion processing in this respect has been relatively neglected in studies of patients with psychiatric disorders. Studying this non-conscious perception of emotion will provide a more balanced understanding of the emotion processing occurring within patients with psychiatric disorders. To answer whether the processes of non-conscious perception of emotion are intact, and if not, then to understand to what extent they are damaged, to properly understand the pathology of these patients
In this article, we will discuss general findings of emotion processing outside of conscious awareness in healthy subjects. Then, we will examine studies of emotion processing outside of awareness in patients with anxiety, schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and depression (Table 1).
Many studies have reported, through a variety of methods, that emotion can be non-consciously perceived.3 This means that even as an observer remains unaware of the presence or the contents of the emotional stimuli, psychological or psychophysiological responses will indicate changes within their mental state.4 The backward masking paradigm is one of the most commonly used methods to observe the effects of non-conscious perception of emotions. In this paradigm, an emotional stimulus is presented (usually for less than 30 ms), and is immediately followed by the presentation of an emotionally neutral stimulus. This neutral stimulus interrupts, or masks, the conscious awareness of the emotional stimulus. Behavioural performances such as accuracy of detection, discrimination or identification of the emotional stimuli, are typically recorded at chance levels, which indicates the participant's unawareness of the emotional stimulus. Despite the unawareness of the emotional stimulus, Liddell et al.5 found changes in the neurophysiological responses by studying the event-related potentials (ERPs). They found that compared to masked neutral faces, masked fearful faces induced a greater negative amplitude of the N2 component (a negative peak that occurs between 200-350 ms after stimulus onset; it is primarily observed at the anterior scalp sties). The N2 is considered to be a reflection of the automatic response to task-relevant emotional stimuli. Similarly, when fearful faces were presented for a longer duration, such that they are processed consciously, an increased positive amplitude of the P3 component was observed (which is the positive deflection of the waveform, observed at frontal sites between 300-450 ms after stimulus onset). The P3 indicates the cognizant integration of emotional information. The increased amplitude of the N2 component for perceptually invisible emotional stimuli and the increased amplitude of the P3 component for consciously perceived emotional stimuli have been frequently observed in ERP studies.5678 Moreover, another study found that significant negativity of the N170 component, which is the representative component of consciously processed emotional faces, was also observed for fearful faces perceived non-consciously.9
In addition to cortical ERP responses, the amygdala and superior colliculi are the most frequently discussed brain regions involved in the non-conscious perception of emotion. The right hemisphere of these areas, in particular, is considered more related to the non-conscious processing of emotional stimuli than the left hemispheres.101112 These regions show a greater response to emotional stimuli compared to neutral stimuli even when there is no conscious awareness of said stimuli.13 Suslow et al.14 demonstrated that the responses of the amygdala and insular cortex were positively correlated with non-conscious priming of sad faces in healthy participants. That is, greater responses in the amygdala and insular cortex indicated a greater negative judgmental bias through non-conscious processing of sad faces, compared to that of happy or neutral faces. Other studies have also observed a modulation of attentional orientation towards negative emotion in the amygdala.1516 Another study by Dannlowski et al.17 also showed that responses in the right amygdala significantly correlated with the negative judgment bias of both non-conscious sad and angry faces in patients with clinical depression. Furthermore, patients with an increased severity of illness showed an increased negative judgment bias. Conversely, Suslow et al.18 showed correlated responses between positive judgment bias and responses in the amygdala in healthy participants. Those with greater positive judgment biases through non-conscious processing of happy faces showed greater activation in the amygdala compared to those with smaller positive judgment biases. However, there are other research groups that did not observe amygdalar activation in response to non-conscious emotional stimuli. For example, Pessoa et al.19 used a simple backward masked paradigm and did not find an amygdalar responses to non-conscious fearful, happy, or neutral face stimuli. However, in contrast to the previous studies, the behavioural responses used to indicate participants' unawareness of the stimuli were hits, misses, correct rejections, and false alarms, which were analysed according to signal detection theory.20
Using the backward masking paradigm, previous studies demonstrated a way in which automatic and non-consciously processed emotion could be manipulated, even during high-level cognitive processing. Winkielman et al.21 showed that thirsty participants were inclined to drink more water after they subliminally perceived happy faces, compared to subliminal angry faces. Their interpretation of these results was that the motivation to drink water was manipulated by non-consciously perceived emotional faces. The Flexas et al.22 study also revealed that non-conscious perception of happy expressions compared to expressions of disgust expressions increased participants' preferences for certain types of artwork. This evidence suggests that perceptually invisible emotional stimuli changes are capable of altering our emotional states, which appear to effect decision-making processes by manipulating high-level cognitive processes. The impact of non-conscious perception of emotion on decision-making may be more critical for patients with psychiatric disorders who suffer from unstable emotional modulation.
Additionally, non-conscious perception of emotion may manipulate lower perception levels. Carlson et al.15 conducted an interesting study where participants viewed subliminally presented fearful or neutral faces that were followed by a dot that appeared at either a congruent or incongruent location in relationship to the subliminally presented emotional face. The reaction time to identify the location of the dot was significantly faster when it appeared at a position congruent to the fearful face location. One function of subliminal processing is to attract attention to the relevant stimuli such that the it leads to a conscious awareness of the stimuli for further detailed information gathering.23 This result indicates that subliminal emotions can effect early perception processing by manipulating spatial attention.
Before moving on to discuss the behavioural and neurophysiological responses of non-conscious emotion processing in patients with psychiatric disorders, it is worth noting that responses to non-conscious emotions can also be correlated with characteristic traits of healthy persons. For example, non-pathological participants who experienced childhood trauma showed a significant correlation between their responses to non-conscious sad faces and amygdalar activation.24 This positive correlation between the processing of non-conscious sad faces and amygdalar activation is also observed in major depression, as will be discussed later. In addition, personality characteristics of healthy participants, such as high/low novelty seeking and harm-avoidance traits, influenced non-conscious processing of masked emotional pictures.25 Those with high novelty seeking or harm-avoidance traits responded to masked positive or negative emotional stimuli with high skin conductance responses. Genetic factors, such as a functional polymorphism in the serotonin transporter gene (5-HTTLPR), which is known to modulate amygdalar responses, are also involved in the non-conscious processing of emotion. In the Dannlowski et al.26 study, healthy participants with the 5-HTTLPR genotype showed greater responses to sad faces in the right amygdala, whereas their responses to happy faces were comparable to those of participants without that genotype. These results imply that the 5-HTTLPR genotype may bias amygdalar responses toward negative emotions.27 It is important to understand the process of non-conscious perception of emotion in psychiatric patients who have dysfunctional emotion regulation and dysfunctional social interactions because non-consciously processed emotion manipulates perception in both early and late processing levels.
The influence of anxiety on non-conscious perception of emotion has been studied frequently in non-clinical individuals with high- and low-trait anxiety levels. However, there are fewer studies regarding patients diagnosed with anxiety disorders.
Studies of the non-conscious perception of emotion in anxious individuals have largely focused on the manipulation of attention. This manipulation of attention affected by anxiety is observed both in conscious282930 and non-conscious perception of emotional stimuli.3132 When emotion is not consciously perceived, anxiety seems to drive the focus of attention toward negatively valenced emotions, such as anger, fear, and feeling threatened. Although more studies of patients with anxiety disorder are clearly required, the results from both clinically and non-clinically anxious individuals seem to show similarities regarding an attentional bias towards negatively valenced emotions. A meta-analysis of threat-related bias showed no significant difference in the of magnitude of biases between clinical and non-clinical anxious individuals, both for conscious and non-conscious perceptions of emotion.33 For example, patients with anxiety disorder consistently show automatic attentional bias towards anxiety-related words during a modified Stroop task.34353637 Naming the colour of the background was slower when masked anxiety-related words were presented than when masked neutral words were presented. Although these findings suggest that anxious subjects are more biased toward negatively polarised stimuli, contradicting results have been reported using the same method. Van Emmichoven et al.38 did not find an interference effect from masked threat-related words using the same modified Stroop task. Also, non-clinically anxious individuals were more biased towards smiling faces than angry faces during a subliminal affective priming paradigm, showing an absence of automatic bias towards negatively valenced emotions.29
Functional neuroimaging studies frequently show that amygdalar activation is associated with abnormal emotion processing outside of conscious awareness in both clinically and non-clinically anxious subjects.3940 These studies found that amygdalar activation was sensitive to the severity of the anxiety level of the person.41 In non-clinical anxious individuals, the basolateral amygdala was found to be more sensitive to anxiety levels only when emotional stimuli were processed without conscious awareness.39 ERP studies also showed that psychophysiological responses to non-conscious emotional stimuli were influenced by anxiety. However, whether early or late processing of emotion is associated with anxiety is still unclear. Some have found evidence of early automatic processing by reporting early components, such as the P1 component, being modulated by anxiety levels,173042 while others have not.43 However, many have observed that anxiety levels modified late components relevant to emotion encoding. One particular ERP study using patients with clinical anxiety observed a modulation of both amplitude and latency in early ERPs (80-180 ms) by anxiety levels, but only for non-consciously perceived emotional stimuli.44
In conclusion, these results suggest that even when emotional stimuli are processed outside of conscious awareness, anxious states automatically and involuntarily manipulate perception and behaviour, particularly towards negatively polarised emotional stimuli. However, most studies have used non-clinically anxious subjects, and further investigations are necessary to see whether the same results are observed consistently in clinically anxious patients.
Studies have shown that the difficulty to express appropriate emotional behaviours by patients with schizophrenia may be derived from the a deficit in the classification of emotion.4546 Impaired emotional processing is one reason why healthy social functions are difficult for patients with schizophrenia.4748 Incorrect interpretation of social cues and events combined with lack of social skills are considered to be the consequences of their impaired emotion processing.49 Furthermore, these deficits may also be early trait markers or even early signs shown before the onset of schizophrenia.5051
Studies regarding the conscious processing of emotion in patients with schizophrenia have revealed that their explicit recognition and identification of emotional stimuli is impaired.52535455 Impairments in their behavioural performance were accompanied by abnormal psychophysiological responses, such as slower latency and smaller amplitude of the N170 component for neutral or emotional face stimuli.56575859 Lee et al.60 found that patients with schizophrenia used facial features differently than healthy subjects. Not only did they require more facial features to discriminate emotion, but they also tended to direct attention to the mouth region regardless of the emotional valence of the face. This may have led to their poor performance in the identification and discrimination of the emotion of the faces, which was supported by a negative correlation between performance level and the severity of their symptoms.6162
Non-conscious perception of emotion in schizophrenia has been understudied. However, several studies have revealed that the automatic and early stages of non-conscious perception may be intact, since the decline in performance only appeared when the stimuli were processed consciously.6364 They have found that the subliminal priming effect of non-emotional stimuli, such as numbers, was as strong in patients with schizophrenia as in healthy subjects. This indicates that early bottom-up processing is not significantly impaired in patients with schizophrenia, and that higher cognitive processes may be the possible cause of the cognitive impairment in these patients. Similar findings were also observed with non-conscious emotion perception. These studies demonstrated that a deficit in emotion processing is found only during the conscious process of emotion perception, but not when emotional stimuli are processed non-consciously or processed outside the focus of attention.65 When patients with schizophrenia were not explicitly required to recognise and identify emotional faces, their performances in the gender discrimination task,66 in the simultaneous matching working memory task,67 and during the judgment of non-emotional stimuli,68 were not different from healthy controls.
However, fMRI studies investigating emotion processing outside conscious awareness using the backward masking paradigm have found that non-conscious processing of emotion could also be impaired in schizophrenia.6970 They have suggested that hyper-activation of the amygdalar response to masked positive and negative valences of emotional faces was greater in patients with schizophrenia than in healthy controls. They furthermore demonstrated that the severity of symptoms positively correlated with the strength of the amygdalar responses during unawareness tasks. These results are consistent with enhanced right amygdalar responses to conscious emotion processing in patients with schizophrenia.717273 The most recent study by Suslow et al.74 examined changes of amygdalar responses over time in non-conscious emotion processing using a similar backward masking paradigm to investigate the stage at which emotion perception is impaired. They found that during the first part of the experiment, right amygdalar activation to masked angry and happy facial expressions was greater in patients with schizophrenia compared to healthy subjects. However, responses then showed the opposite pattern over time. At the second part of the experiment, healthy subjects showed greater activity of the amygdala to masked emotional faces than patients with schizophrenia.
These contradicting results in the study of non-conscious emotion processing in schizophrenia may be due to the use of different paradigms to induce non-conscious perception of emotional information. Many of the behavioural studies observed an automatic attentional focus to the emotional stimuli. Conversely, psychophysiological studies have attempted to induce unawareness using a backward masking paradigm that isolates non-conscious processing within the amygdala. Regardless, the direct comparison between conscious and non-conscious emotional processing should be investigated further to confirm whether non-conscious perception of emotion is impaired in patients with schizophrenia.
In general, patients with bipolar disorder are less impaired in processing emotion than patients with schizophrenia, but more impaired than patients who are depressive or anxious.75 The cognitive bias towards the negative valence of emotional stimuli is not observed consistently in patients with bipolar disorder as it is in patients with anxiety disorder. This may be due to the different clinical courses of mood stages of bipolar disorder.76 Several studies on bipolar disorder have shown that patients are impaired in the conscious processing of fearful expressions, but not in the conscious processing of happy expressions. During conscious emotion processing, patients with bipolar disorder tended to view extreme emotions as mild, and required more intensive expressions and additional time in order to correctly process and identify the emotion.777879 However, the stronger priming effect by sad faces, which was evident during the conscious condition when compared to healthy subjects, was absent in the non-conscious condition.80 In the non-conscious condition, both euthymic bipolar patients and healthy controls demonstrated similar priming effects from sad facial expressions.
The association between the prefrontal cortex and the amygdala may be a relevant factor in the impairment of conscious emotion processing in patients with bipolar disorder.81 Hyper-activation of the amygdala and a reduced dorsal prefrontal response to emotional stimuli, in particular, have been considered to be psychophysiological indications of impaired emotion processing in bipolar disorder.
Abnormal amygdalar responses to emotional faces during non-conscious processing showed different responses by patients with manic and depressed bipolar disorder.82 While patients with depressed bipolar disorder showed a hyper-activation in the fronto-striato-thalamic regions in response to happy faces, patients with manic bipolar disorder exhibited hyper-activation in of the cortico-limbic regions, including the amygdala in response to sad faces. Using a non-conscious affective paradigm, Grotegert et al. reported that patients with depressed bipolar disorder showed hyper-activation of the amygdala to happy faces, compared to neutral faces.8384 However, in conscious processing, Almeida et al.85 reported that sad facial induced stronger left amygdalar responses in patients with depressed bipolar patients disorder compared to patients with major depressive disorder. However, the results from both studies indicated that the amygdalar response to sad faces serves as a marker that can dissociate depressed bipolar disorder from major depressive disorder.
Further studies on emotion processing outside of conscious awareness in bipolar disorder are required. Not only should differential responses in different stages of bipolar disorder be considered, but also whether prefrontal interactions with the amygdala are relevant to the observed impairment in emotion processing.
Studies on the non-conscious perception of emotion by patients with depressive disorder are relatively pervasive and consistent. Both conscious and non-conscious perception of emotion in depressive disorder show cognitive and emotional bias towards mood-congruent negative emotions, particularly those of sadness.858687
Several studies have found that clinically depressed subjects were more susceptible to by anxiety-relevant stimuli than anxious subjects were.3437 Depressive patients have an attentional bias towards sad faces, showing faster reaction time and better accuracy for sad faces.3788899091 Concurrently, patients with depression require a greater intensity of emotional expression to identify happy faces. The automatic response to sad faces has been more elaborately demonstrated by Sterzer et al.92 using a continuous flash suppression paradigm (CFS).93 In this paradigm, a stimulus is presented to one eye while Mondrian patterns changing at 10 Hz are presented to the other eye. Theoretically, the continuously changing Mondrian patterns suppress awareness of the target stimulus even when it is clearly perceived by one eye. It is an effective paradigm to induce unawareness of a stimulus for a long duration without changing the features of the stimulus. Sterzers et al.92 reported participants' automatic bias by measuring when non-consciously processed emotional faces broke suppression and reached conscious awareness. In depressive patients, non-consciously presented sad faces broke suppression (or became conscious) more easily, and patients reported detection of sad faces more quickly. However, presentation of happy faces was suppressed for a specific duration, which suggests that it was more difficult for the patients to detect the happy faces. This demonstrated patients' automatic and emotional biases toward sad faces, and that the non-conscious processing of happy faces was slower and weaker.
Moreover, a greater response in the amygdala to non-conscious sad faces9495 and a weaker response to non-conscious happy faces,96 has been continuously associated with impaired non-conscious perception in patients with depression, as compared to healthy subjects. These findings show that activation of the amygdala in response sad faces positively correlated with the severity of the patient symptoms, further supports the notion that emotional bias in patients with depression is automatic and involuntary. As mentioned above, the enhanced conscious response in the amygdala to sad faces is a biomarker of patients with depressive bipolar disorder, which distinguishes them from patients with depression.
In summation, patients with depressive disorder show attentional and emotional biases towards negative emotions, such as sadness. Such biases have been demonstrated by a faster reaction time to sad faces, and more accurate performance even without conscious awareness. Furthermore, over-responsiveness of the amygdala to sad faces has been a trait-marker for this particular disorder, and the severity of symptoms is positively correlated with the abnormal response in the amygdala.
We have thus far discussed and compared behavioural and psychophysiological studies regarding the non-conscious perception of emotion in anxiety disorder, schizophrenia, bipolar disorder and depression. The results from studies with patients with psychiatric disorders are not as clear as the results from healthy controls. One possible explanation for these contradictory results may be the difference between different stages, and symptom severity levels, of the patients with psychiatric disorders. Also, there are a relatively small number of studies on non-conscious perception of emotion by patients with psychiatric disorders, and these studies have used different paradigms to induce unawareness. According to Tamietto and de Gelder1, different types of experimental paradigms involve different types of consciousness, such as attentional awareness and or sensory awareness. Attentional unawareness is the pre-attentive stage of awareness, while sensory unawareness is involved in the changes of psychophysiological responses (such as ERP responses) during non-conscious subjective responses of awareness. Further investigations of non-conscious perception of emotion should use paradigms such as the binocular rivalry or CFS that manipulates awareness and not attention.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) and funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (No. 2012R1A1A2043992). This research was also supported by the NRF, funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (No. 2013K2A1A2053850). We thank JC who supported all procedures in this study.
References
1. Tamietto M, de Gelder B. Neural bases of the non-conscious perception of emotional signals. Nat Rev Neurosci 2010;11:697-709. PMID: 20811475.


2. Jacoby LL, Whitehouse K. An illusion of memory: false recognition influenced by unconscious perception. J Exp Psychol Gen 1989;118:126-135.

3. Faivre N, Berthet V, Kouider S. Nonconscious influences from emotional faces: a comparison of visual crowding, masking, and continuous flash suppression. Front Psychol 2012;3:129PMID: 22563325.



4. Kihlstrom JF. The Psychological Unconscious. In: Pervin LA, John OP, editor. Handbook of Personality: Theory and Research. New York, London: The Guilford Press, 1999, p. 424-442.
5. Liddell BJ, Williams LM, Rathjen J, Shevrin H, Gordon E. A temporal dissociation of subliminal versus supraliminal fear perception: an event-related potential study. J Cogn Neurosci 2004;16:479-486. PMID: 15072682.


6. Eimer M, Kiss M, Holmes A. Links between rapid ERP responses to fearful faces and conscious awareness. J Neuropsychol 2008;2:165-181. PMID: 19330049.



7. Halgren E, Marinkovic K. Neurophysiological Networks Integrating Human Emotions. In: Gazzaniga MS, editor. The Cognitive Neurosciences. Cambridge, MA: The MIT Press, 1995, p. 1137-1151.
8. Kiss M, Eimer M. ERPs reveal subliminal processing of fearful faces. Psychophysiology 2008;45:318-326. PMID: 17995905.


9. Pegna AJ, Landis T, Khateb A. Electrophysiological evidence for early non-conscious processing of fearful facial expressions. Int J Psychophysiol 2008;70:127-136. PMID: 18804496.


10. Brooks SJ, Savov V, Allzén E, Benedict C, Fredriksson R, Schiöth HB. Exposure to subliminal arousing stimuli induces robust activation in the amygdala, hippocampus, anterior cingulate, insular cortex and primary visual cortex: a systematic meta-analysis of fMRI studies. Neuroimage 2012;59:2962-2973. PMID: 22001789.


11. Meneguzzo P, Tsakiris M, Schloth HB, Stein DJ, Brooks SJ. Subliminal versus supraliminal stimuli activate neural responses in anterior cingulate cortex, fusiform gyrus and insula: a meta-analysis of fMRI studies. BMC Psychol 2014;2:52PMID: 25593703.



12. Pantazatos SP, Talati A, Pavlidis P, Hirsch J. Cortical functional connectivity decodes subconscious, task-irrelevant threat-related emotion processing. Neuroimage 2012;61:1355-1363. PMID: 22484206.



13. Whalen PJ, Rauch SL, Etcoff NL, McInerney SC, Lee MB, Jenike MA. Masked presentations of emotional facial expressions modulate amygdala activity without explicit knowledge. J Neurosci 1998;18:411-418. PMID: 9412517.



14. Suslow T, Kugel H, Ohrmann P, Stuhrmann A, Grotegerd D, Redlich R, et al. Neural correlates of affective priming effects based on masked facial emotion: an fMRI study. Psychiatry Res 2013;211:239-245. PMID: 23131525.


15. Carlson JM, Reinke KS, Habib R. A left amygdala mediated network for rapid orienting to masked fearful faces. Neuropsychologia 2009;47:1386-1389. PMID: 19428403.


16. Rosa PJ, Esteves F, Arriaga P. Effects of fear-relevant stimuli on attention: integrating gaze data with subliminal exposure In: Medical Measurements and Applications (MeMeA), 2014 IEEE International Symposium; June 11-12 2014.
17. Li W, Zinbarg RE, Paller KA. Trait anxiety modulates supraliminal and subliminal threat: brain potential evidence for early and late processing influences. Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci 2007;7:25-36. PMID: 17598732.


18. Lichev V, Sacher J, Ihme K, Rosenberg N, Quirin M, Lepsien J, et al. Automatic emotion processing as a function of trait emotional awareness: an fMRI study. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci 2015;10:680-689. PMID: 25140051.


19. Pessoa L, Japee S, Sturman D, Ungerleider LG. Target visibility and visual awareness modulate amygdala responses to fearful faces. Cerebral Cortex 2006;16:366-375. PMID: 15930371.


20. Green DM, Swets JA. Signal Detection Theory and Psychophysics. New York: Wiley & Sons Inc.; 1966.
21. Winkielman P, Berridge KC, Wilbarger JL. Unconscious affective reactions to masked happy versus angry faces influence consumption behavior and judgments of value. Pers Soc Psychol Bull 2005;31:121-135. PMID: 15574667.


22. Flexas A, Rosselló J, Christensen JF, Nadal M, Olivera La Rosa A, Munar E. Affective priming using facial expressions modulates liking for abstract art. PLoS One 2013;8:e80154PMID: 24260350.



23. Eastwood JD, Smilek D. Functional consequences of perceiving facial expressions of emotion without awareness. Conscious Cogn 2005;14:565-584. PMID: 16091271.


24. Dannlowski U, Kugel H, Huber F, Stuhrmann A, Redlich R, Grotegerd D, et al. Childhood maltreatment is associated with an automatic negative emotion processing bias in the amygdala. Hum Brain Mapp 2013;34:2899-2909. PMID: 22696400.


25. Yoshino A, Kimura Y, Yoshida T, Takahashi Y, Nomura S. Relationships between temperament dimensions in personality and unconscious emotional responses. Biol Psychiatry 2005;57:1-6. PMID: 15607293.


26. Dannlowski U, Konrad C, Kugel H, Zwitserlood P, Domschke K, Schöning S, et al. Emotion specific modulation of automatic amygdala responses by 5-HTTLPR genotype. Neuroimage 2010;53:893-898. PMID: 19962442.


27. Pezawas L, Meyer-Lindenberg A, Drabant EM, Verchinski BA, Munoz KE, Kolachana BS, et al. 5-HTTLPR polymorphism impacts human cingulate-amygdala interactions: a genetic susceptibility mechanism for depression. Nat Neurosci 2005;8:828-834. PMID: 15880108.


28. Li W, Paller KA, Zinbarg RE. Conscious intrusion of threat information via unconscious priming in anxiety. Cogn Emot 2008;22:44-62.

29. Paul ES, Pope SA, Fennell JG, Mendl MT. Social anxiety modulates subliminal affective priming. PLoS One 2012;7:e37011PMID: 22615873.



30. Walentowska W, Wronka E. Trait anxiety and involuntary processing of facial emotions. Int J Psychophysiol 2012;85:27-36. PMID: 22210124.


31. Bradley BP, Mogg K, Falla SJ, Hamilton LR. Attentional bias for threatening facial expressions in anxiety: manipulation of stimulus duration. Cogn Emot 1998;12:737-753.

32. Mogg K, Garner M, Bradley BP. Anxiety and orienting of gaze to angry and fearful faces. Biol Psychol 2007;76:163-169. PMID: 17764810.



33. Bar-Haim Y, Lamy D, Pergamin L, Bakermans-Kranenburg MJ, van Ijzendoorn MH. Threat-related attentional bias in anxious and nonancious individuals: a meta-analytic study. Psychol Bull 2007;133:1-24. PMID: 17201568.


34. Mogg K, Bradley BP, Williams R. Attentional bias in anxiety and depression: the role of awareness. Br J Clin Psychol 1995;34:17-36. PMID: 7757037.


35. Mogg K, Bradley BP, Williams R, Mathews A. Subliminal processing of emotional information in anxiety and depression. J Abnorm Psychol 1993;102:304-311. PMID: 8315143.


36. Mogg K, Millar N, Bradley BP. Biases in eye movements to threatening facial expressions in generalized anxiety disorder and depressive disorder. J Abnorm Psychol 2000;109:695-704. PMID: 11195993.


37. Bradley B, Mogg K, Williams R. Implicit and explicit memory for emotion-congruent information in clinical depression and anxiety. Behav Res Ther 1995;33:755-770. PMID: 7677713.


38. Zeijlmans van Emmichoven IA, Van Ijzendoorn MH, de Ruiter C, Brosschot JF. Selective processing of threatening information: effects of attachment representation and anxiety disorder on attention and memory. Dev Psychopathol 2003;15:219-237. PMID: 12848443.


39. Etkin A, Klemenhagen K, Dudman J, Rogan M, Hen R, Kandel E, et al. Individual differences in trait anxiety predict the response of the basolateral amygdala to unconsciously processed fearful faces. Neuron 2004;44:1043-1055. PMID: 15603746.


40. Monk CS, Telzer EH, Mogg K, Bradley BP, Mai X, Louro HM, et al. Amygdala and ventrolateral prefrontal cortex activation to masked angry faces in children and adolescents with generalized anxiety disorder. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2008;65:568-576. PMID: 18458208.



41. Davis M, Whalen PJ. The amygdala: vigilance and emotion. Mol Psychiatry 2001;6:13-34. PMID: 11244481.


42. Li W, Zinbarg RE, Boehm SG, Paller KA. Neural and behavioral evidence for affective priming from unconsciously perceived emotional facial expressions and the influence of trait anxiety. J Cogn Neurosci 2008;20:95-107. PMID: 17919076.


43. Rossignol M, Philippot P, Douilliez C, Crommelinck M, Campanella S. The perception of fearful and happy facial expression is modulated by anxiety: an event-related potential study. Neurosci Lett 2005;377:115-120. PMID: 15740848.


44. Williams LM, Kemp AH, Felmingham K, Liddell BJ, Palmer DM, Bryant RA. Neural biases to covert and overt signals of fear: dissociation by trait anxiety and depression. J Cogn Neurosci 2007;19:1595-1608. PMID: 17854280.


45. Bleuler E. Dementia Praecox or the Group of Schizophrenias. Oxford: International Universities Press; 1950.
46. Hamm J, Pinkham A, Gur RC, Verma R, Kohler CG. Dimensional information-theoretic measurement of facial emotion expressions in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res Treatment 2014;2014:243907PMID: 24724025.



47. Irani F, Seligman S, Kamath V, Kohler C, Gur RC. A meta-analysis of emotion perception and functional outcomes in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 2012;137:203-211. PMID: 22341200.



48. Poole JH, Tobias FC, Vinogradov S. The functional relevance of affect recognition errors in schizophrenia. J Int Neuropsychol Soc 2000;6:649-658. PMID: 11011511.


49. Young HF, Bentall RP. Hypothesis testing in patients with persecutory delusions: comparison with depressed and normal subjects. Br J Clin Psychol 1995;34:353-369. PMID: 8845775.


50. Walker EF, Grimes KE, Davis DM, Smith AJ. Childhood precursors of schizophrenia: facial expressions of emotion. Am J Psychiatry 1993;150:1654-1660. PMID: 8214173.


51. Lee SY, Kim KR, Park JY, Song YY, Kang JI, Lee E, et al. 1342-Deficits and biases of facial emotion recognition in ultra-high risk for psychosis and first-episode schizophrenia. Euro Psychiatry 2013;28:1

52. Feinberg TE, Rifkin A, Schaffer C, Walker E. Facial discrimination and emotional recognition in schizophrenia and affective disorders. Arch Gen Psychiatry 1986;43:276-279. PMID: 3954548.


53. Whittaker JF, Deakin JFW, Tomenson B. Face processing in schizophrenia: defining the deficit. Psychol Med 2001;31:499-507. PMID: 11305858.


54. Jung HT, Kim DW, Kim S, Im CH, Lee SH. Reduced source activity of event-related potentials for affective facial pictures in schizophrenia patients. Schizophr Res 2012;136:150-159. PMID: 22118731.


55. Kim DW, Lee SH, Im CH. Source activation during facial emotion perception correlates with positive and negative symptoms scores of schizophrenia In: Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), 2013 35th Annual International Conference of the IEEE; Osaka, IEEE. 2013;pp 6325-6328.
56. Caharel S, Bernard C, Thibaut F, Haouzir S, Di Maggio-Clozel C, Allio G, et al. The effects of familiarity and emotional expression on face processing examined by ERPs in patients with schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 2007;95:186-196. PMID: 17644314.


57. Turetsky BI, Kohler CG, Indersmitten T, Bhati MT, Charbonnier D, Gur RC. Facial emotion recognition in schizophrenia: when and why does it go awry? Schizophr Res 2007;94:253-263. PMID: 17583481.



58. Lee SH, Kim EY, Kim S, Bae SM. Event-related potential patterns and gender effects underlying facial affect processing in schizophrenia patients. Neurosci Res 2010;67:172-180. PMID: 20214929.


59. Kim DW, Kim HS, Lee SH, Im CH. Positive and negative symptom scores are correlated with activation in different brain regions during facial emotion perception in schizophrenia patients: a voxel-based sLORETA source activity study. Schizophr Res 2013;151:165-174. PMID: 24268468.


60. Lee J, Gosselin F, Wynn JK, Green MF. How do schizophrenia patients use visual information to decode facial emotion? Schizophr Bull 2011;37:1001-1008. PMID: 20156852.


61. Edwards J, Pattison PE, Jackson HJ, Wales RJ. Facial affect and affective prosody recognition in first-episode schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 2001;48:235-253. PMID: 11295377.


62. Mueser KT, Penn DL, Blanchard JJ, Bellack AS. Affect recognition in schizophrenia: a synthesis of findings across three studies. Psychiatry 1997;60:301-308. PMID: 9460099.


63. Del Cul A, Dehaene S, Leboyer M. Preserved subliminal processing and impaired conscious access in schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2006;63:1313-1323. PMID: 17146006.



64. Huddy VC, Aron AR, Harrison M, Barnes TR, Robbins TW, Joyce EM. Impaired conscious and preserved unconscious inhibitory processing in recent onset schizophrenia. Psychol Med 2009;39:907-916. PMID: 18796175.


65. Gur RE, McGrath C, Chan RM, Schroeder L, Turner T, Turetsky BI, et al. An fMRI study of facial emotion processing in patients with schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 2002;159:1992-1999. PMID: 12450947.


66. van't Wout M, Aleman A, Kessels RP, Cahn W, de Haan EH, Kahn RS. Exploring the nature of facial affect processing deficits in schizophrenia. Psychiatry Res 2007;150:227-235. PMID: 17313979.


67. Linden SC, Jackson MC, Subramanian L, Wolf C, Green P, Healy D, et al. Emotion-cognition interactions in schizophrenia: implicit and explicit effects of facial expression. Neuropsychologia 2010;48:997-1002. PMID: 19945472.


68. Roux P, Christophe A, Passerieux C. The emotional paradox: dissociation between explicit and implicit processing of emotional prosody in schizophrenia. Neuropsychologia 2010;48:3642-3649. PMID: 20801135.


69. Rauch AV, Reker M, Ohrmann P, Pedersen A, Bauer J, Dannlowski U, et al. Increased amygdala activation during automatic processing of facial emotion in schizophrenia. Psychiatry Res 2010;182:200-206. PMID: 20488680.


70. Rauch AV, Reker M, Ohrmann P, Pedersen A, Bauer J, Dannlowski U, et al. Amygdala response during automatic processing of facial emotion in schizophrenia and its association with psychopathology: a 3-T fMRI study. Klin Neurophysiol 2008;39:A203

71. Kosaka H, Omori M, Murata T, Iidaka T, Yamada H, Okada T, et al. Differential amygdala response during facial recognition in patients with schizophrenia: an fMRI study. Schizophr Res 2002;57:87-95. PMID: 12165379.


72. Namiki C, Hirao K, Yamada M, Hanakawa T, Fukuyama H, Hayashi T, et al. Impaired facial emotion recognition and reduced amygdalar volume in schizophrenia. Psychiatry Res 2007;156:23-32. PMID: 17728113.


73. Pankow A, Friedel E, Sterzer P, Seiferth N, Walter H, Heinz A, et al. Altered amygdala activation in schizophrenia patients during emotion processing. Schizophr Res 2013;150:101-106. PMID: 23911256.


74. Suslow T, Lindner C, Dannlowski U, Walhöfer K, Rödiger M, Maisch B, et al. Automatic amygdala response to facial expression in schizophrenia: initial hyperresponsivity followed by hyporesponsivity. BMC Neurosci 2013;14:140PMID: 24219776.



75. Addington J, Addington D. Facial affect recognition and information processing in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Schizophr Res 1998;32:171-181. PMID: 9720122.


76. Rubinsztein JS, Michael A, Underwood BR, Tempest M, Sahakian BJ. Impaired cognition and decision-making in bipolar depression but no 'affective bias' evident. Psychol Med 2006;36:629-639. PMID: 16420729.


77. Degabriele R, Lagopoulos J, Malhi G. Neural correlates of emotional face processing in bipolar disorder: an event-related potential study. J Affect Disord 2011;133:212-220. PMID: 21497913.


78. Rocca CC, Heuvel Ev, Caetano SC, Lafer B. Facial emotion recognition in bipolar disorder: a critical review. Rev Bras Psiquiatr 2009;31:171-180. PMID: 19578691.


79. Schaefer KL, Baumann J, Rich BA, Luckenbaugh DA, Zarate CA Jr. Perception of facial emotion in adults with bipolar or unipolar depression and controls. J Psychiatr Res 2010;44:1229-1235. PMID: 20510425.



80. Kim TS, Lee SY, Ha RY, Kim E, Kyoon S, Ha K, et al. Emotional priming with facial exposures in euthymic patients with bipolar disorder. J Nerv Ment Dis 2011;199:971-977. PMID: 22134456.


81. Yurgelun-Todd DA, Gruber SA, Kanayama G, Killgore WD, Baird AA, Young AD. fMRI during affect discrimination in bipolar affective disorder. Bipolar Disord 2000;2:237-248. PMID: 11249801.


82. Chen CH, Lennox B, Jacob R, Calder A, Lupson V, Bisbrown-Chippendale R, et al. Explicit and implicit facial affect recognition in manic and depressed states of bipolar disorder: a functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Biol Psychiatry 2006;59:31-39. PMID: 16112653.


83. Grotegerd D, Stuhrmann A, Kugel H, Schmidt S, Redlich R, Zwanzger P, et al. Prediction of unipolar and bipolar depression on the basis of pattern classification techniques using amygdala excitability to subliminally presented emotional faces. Pharmacopsychiatry 2013;46:A11

84. Grotegerd D, Stuhrmann A, Kugel H, Schmidt S, Redlich R, Zwanzger P, et al. Amygdala excitability to subliminally presented emotional faces distinguishes unipolar and bipolar depression: an fMRI and pattern classification study. Hum Brain Mapp 2013;35:2995-3007. PMID: 24038516.



85. Gotlib IH, Krasnoperova E, Yue DN, Joormann J. Attentional biases for negative interpersonal stimuli in clinical depression. J Abnorm Psychol 2004;113:121-135. PMID: 14992665.


86. Gur RC, Erwin RJ, Gur RE, Zwil AS, Heimberg C, Kraemer HC. Facial emotion discrimination: II. Behavioral findings in depression. Psychiatry Res 1992;42:241-251. PMID: 1496056.


87. Almeida JR, Versace A, Hassel S, Kupfer DJ, Phillips ML. Elevated amygdala activity to sad facial expressions: a state marker of bipolar but not unipolar depression. Biol Psychiatry 2010;67:414-421. PMID: 19931855.


88. Dannlowski U, Kersting A, Lalee-Mentzel J, Donges US, Arolt V, Suslow T. Subliminal affective priming in clinical depression and comorbid anxiety: a longitudinal investigation. Psychiatry Res 2006;143:63-75. PMID: 16725208.


89. Dannlowski U, Kersting A, Donges US, Lalee-Mentzel J, Arolt V, Suslow T. Masked facial affect priming is associated with therapy response in clinical depression. Euro Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 2006;256:215-221.

90. Gilboa-Schechtman E, Presburger G, Marom S, Hermesh H. The effects of social anxiety and depression on the evaluation of facial crowds. Behav Res Ther 2005;43:467-474. PMID: 15701357.


91. Joormann J. Attentional bias in dysphoria: the role of inhibitory processes. Cogn Emot 2004;18:125-147.

92. Sterzer P, Hilgenfeldt T, Freudenberg P, Bermpohl F, Adli M. Access of emotional information to visual awareness in patients with major depressive disorder. Psychol Med 2011;41:1615-1624. PMID: 21208495.


94. Stuhrmann A, Dohm K, Kugel H, Zwanzger P, Redlich R, Grotegerd D, et al. Mood-congruent amygdala responses to subliminally presented facial expressions in major depression: associations with anhedonia. J Psychiatry Neurosci 2013;38:249-258. PMID: 23171695.



95. Suslow T, Konrad C, Kugel H, Rumstadt D, Zwitserlood P, Schöning S, et al. Automatic mood-congruent amygdala responses to masked facial expressions in major depression. Biol Psychiatry 2010;67:155-160. PMID: 19748075.


96. Victor TA, Furey ML, Fromm SJ, Öhman A, Drevets WC. Relationship between amygdala responses to masked faces and mood state and treatment in major depressive disorder. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2010;67:1128-1138. PMID: 21041614.



97. Liu TY, Hsieh JC, Chen YS, Tu PC, Su TP, Chen LF. Different patterns of abnormal gamma oscillatory activity in unipolar and bipolar disorder patients during an implicit emotion task. Neuropsychologia 2012;50:1514-1520. PMID: 22406691.


98. Thomas LA, Brotman MA, Bones BL, Chen G, Rosen BH, Pine DS, et al. Neural circuitry of masked emotional face processing in youth with bipolar disorder, severe mood dysregulation, and healthy volunteers. Dev Cogn Neurosci 2014;8:110-120. PMID: 24239048.


99. Victor TA, Furey ML, Fromm SJ, Bellgowan PS, Öhman A, Drevets WC. The extended functional neuroanatomy of emotional processing biases for masked faces in major depressive disorder. PLoS One 2012;7:e46439PMID: 23056309.



Table 1
Summary of studies about non-conscious emotion processing in patients with psychiatric disorders since 2010
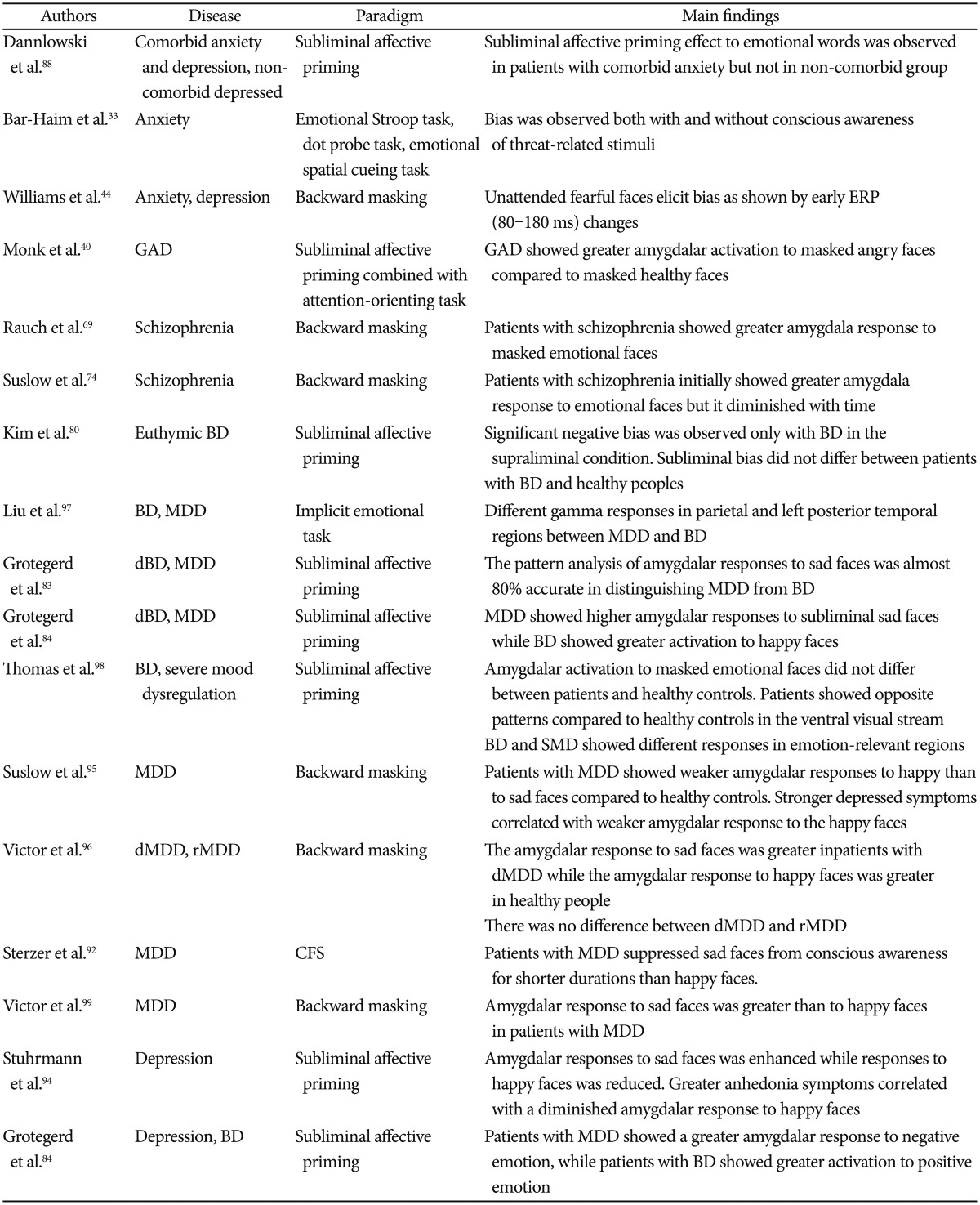
Earlier studies on anxiety are listed here because recent studies on non-conscious emotion processing in anxiety could not be found. GAD: generalized anxiety disorder, BD: bipolar disorder, MDD: major depressive disorder, dBD: depressed bipolar disorder, dMDD: depressed major depressive disorder, rMDD: remitted major depressive disorder, ERP: event related potential, fMRI: functional magnetic resonance imaging, MEG: magnetoencephalography, CFS: continuous flash suppression






