|
 |
- Search
| Psychiatry Investig > Volume 13(3); 2016 > Article |
Abstract
Objective
It has been known that mind-body training (MBT) can affect personality and behavior system as well as emotional well-being, but different effects of MBT on them has not been reported according to BDNF genetic polymorphism.
Methods
Healthy subjects consisted of 64 subjects and the MBT group who practiced meditation regularly consisted of 72 practitioners. Participants completed neuroticism-extraversion-openness (NEO) Five-Factor Inventory and Behavioral Activation System/Behavioral Inhibition System (BAS/BIS) scales. All subjects were genotyped for the BDNF Val66Met polymorphism.
Results
In the same genotypes of the BDNF Val/Val+Val/Met group, MBT group showed the increased Extraversion (p=0.033) and the increased Openness to Experience (p=0.004) compared to the control group. Also, in the same Met/Met carriers, MBT group exhibited the increase of Extraversion (p=0.008), the reduction of Neuroticism (p=0.002), and the increase of Openness to Experience (p=0.008) compared to the control group. In the same genotypes of the BDNF Val/Val+Val/Met group, MBT group showed the decreased BAS-Reward Responsiveness (p=0.016) and the decrease of BIS (p=0.004) compared to the control group. In the BDNF Met/Met group, MBT group increased BAS-Fun Seeking (p=0.045) and decreased BIS (p=0.013) compared to the control group.
The effects of mind-body training (MBT) on attentional and emotional processes may have a long-term impact on the brain and behavior.1 Also, in the medial prefrontal cortex of meditators the increased activation may be associated with emotional processing.2 Considering that emotional experience was significantly correlated with theta activity,3 the increased activation of alpha and theta activation during meditation4 may contribute to a long-term improvement of the personality including emotion. Increasing emotional competence led to long-term significant increases in Extraversion and Agree-ableness as well as a decrease in Neuroticism.5 As meditation practice affected the decrease of Neuroticism,6 the enhancement of emotional well-being and the decrease of Neuroticism through MBT are thought to play an important role on personality. Given that personality traits were associated with the neural substrates of Extraversion, Neuroticism, Openness, and Conscientiousness in the amplitude of spontaneous low-frequency oscillations,7 effects of MBT on personality seem to be based on the structural and functional brain plasticity. In addition, individuals lower in Extraversion had higher levels of IL-6,8 and mental stress increased pro-inflammatory cytokine, IL-6.9 As meditation training can improve perceived stress and negative mood10 and increased meditation practice was associated the decrease of IL-6,11 MBT would be able to change and improve personality traits as well as the immune system.
Gray12 suggested two motivational systems of a behavioral inhibition system (BIS) and a behavioral activation system (BAS). BIS functions to stop ongoing behaviour and BAS is believed to govern the engagement of action.13 BAS and Extraversion tended to mutually increase the impact of each other, while BIS diminished the effect of BAS.14 Higher self-reported BAS predicted better working-memory performance, suggesting personality differences in cognitive control.15 Also, as brief mindfulness training significantly improved working memory, better working-memory through MBT seems to be able to affect enhancement of BAS. Considering that the BIS may be more strongly associated with fitness-related exercise behavior, whereas the BAS may play a relatively greater role in terms of subjective exercise enjoyment,16 MBT may differently contribute to BAS and BIS according to individual differences of personality. This study focuses on different effects of MBT on personality and BAS/BIS, based on individual differences according to genetic polymorphism.
Behavior genetic studies reveal that personality traits are substantially influenced by the genes17 and individual differences in coping styles and life events can be explained by moderate genetic and substantial environmental influences.18 BDNF Met carriers were more introverted, and 5-HTTLPR LL carriers scored lower on Neuroticism in the presence of the BDNF Val variant, but scored higher on Neuroticism in the presence of the BDNF Met variant.19 It was reported that the interaction of COMT and DRD2 polymorphisms predicts the behavioural approach system20 and that significant associations between the A1 allele of the DRD2 TaqI A polymorphism and a high BAS-Reward Responsiveness were observed.21 However, a relationship of BAS and BIS with BDNF genetic polymorphism has not been known. In addition, little is known about the various long-term effects of MBT on NEO personality traits and BAS/BIS according to BDNF genetic polymorphism. Thus, the first aim of this study was to examine whether BDNF genetic polymorphism is associated with the NEO personality and BAS and BIS. Finally, hypothesis of this study is that MBT would differently contribute to NEO personality and BAS/BIS according to BDNF Val66Met polymorphism.
All participants in the control and MBT groups engaged voluntarily in this research. The MBT group consisted of 64 subjects who practiced meditation regularly, and the control group consisted of 72 healthy subjects. The Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-IV Non-patient Version was used to assess psychiatric disorders in the participants. Exclusion criteria included a life-time history of psychosis, bipolar disorder, major depressive disorder, substance abuse or dependence, significant head injury, seizure disorder, or mental retardation. This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board at Seoul National University Hospital, and informed consent was obtained from all the participants. Subjects in the MBT group had been practicing meditation for a mean of 43 months (range 3-144 months). This study included subjects who were homogeneous in age and who practiced the same type of meditation. All subjects in the MBT group engaged in "Brain Wave Vibration" MBT, which is known to facilitate the process by which the negative thoughts that generate negative brain waves change into positive thoughts that generate positive brain waves. This process has also been described as brain respiration because it focuses primarily on the brain and its development, although the actual practice of this discipline resembles yoga, martial arts, and meditation. Brain Wave Vibration is a MBT technique designed to relax both mind and body through natural rhythmic movements. It is intended to be a simple meditation technique, a kind of moving meditation that can be used to manage stress and optimize brain health. This technique is designed to help quiet the thinking mind and release emotions, particularly negative emotions, through physical movements and focus on body sensations. The first step is to consciously move the body, starting by gently shaking the head to the left and to the right. The second step involves following one's own natural rhythm and focusing on physical sensations and vibrations, which may spread to all parts of the body. Once the vibration becomes natural and familiar, practitioners reflexively engage in the third step, characterized by an increased awareness of the movement of energy within the body.22
The subjects' DNA was genotyped at the BDNF Val66Met locus. Whole blood was withdrawn from each participant and collected into EDTA-containing tubes. The volume was measured, recorded, and a 1-mL aliquot was stored at -20℃ until genomic DNA extraction. Genomic DNA was isolated from 200 µL of whole blood using the QIAamp DNA Blood Mini kit according to the manufacturer's instructions (QIAGEN, Hilden, Germany). All polymorphisms were detected by TaqMan allelic discrimination assays on an ABI Prism 7500 Sequence Detection System (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA). BDNF Val66Met (rs6265, C-11592758-10) was used for genotyping (Applied Biosystems). The PCR reaction consisted of 95℃ for 10 min and 50 cycles of 92℃ for 30 s and 60℃ for 1 min. A total of 10 µL of PCR reaction mixture was prepared with 5 µL of 2×TaqMan Genotyping Master mix, 0.5 µL of 20×Drug Metabolism Genotyping Assay mix, 3.5 µL of DNase-free water, and 1 µL of genomic DNA. The ABI Prism 7500 Sequence Detection System software ver. 2.0.1 (Applied Biosystems) was used for the analysis. The genotyping procedure screened for BDNF.
Personality was assessed using the reliable and validated questionnaire based on the NEO Five-Factor Inventory (NEO-FFI) theory of personality.23 This well established questionnaire consists of 60 items with a 5-Likert scale response format (1-5 points) including "not at all" (1), "somewhat" (2), "moderately" (3), "very much" (4), or "absolutely" (5). Scores for each domain are calculated by summing the 12 item responses. The NEO-FFI measures the personality dimensions: Agreeableness, Conscientiousness, Extraversion, Neuroticism, and Openness to Experience.
The BAS/BIS Scale24 was also used to assess BAS and BIS sensitivity. The BAS/BIS Scale contains 20-items and a four-point Likert scale with BIS items (7) and BAS items (13) intermixed. There is one BIS scale and three BAS subscales: BAS-Reward Responsiveness, BAS-Drive and BAS-Fun Seeking.
The demographic characteristics of the two groups are shown in Table 1. No significant differences were observed for age or gender between the MBT and control groups. No statistically significant differences in genetic polymorphism were found between control and MBT subjects (Table 1).
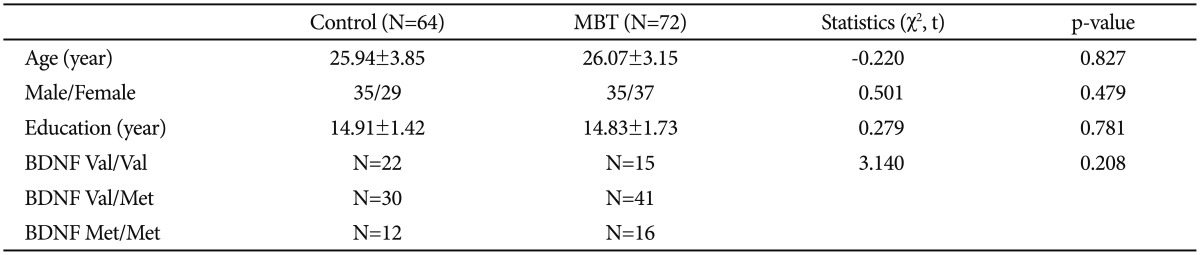
First of all, how BDNF genetic polymorphism is associated with the NEO personality and BAS/BIS was investigated in the control group. BDNF Val/Val subjects scored higher Extraversion than Met/Met in the control group (p=0.016) (Figure 1A). BDNF Met/Met subjects scored higher Neuroticism than Val/Val in the control group (p=0.046) (Figure 1A). BDNF Val/Val+Val/Met in the control group showed higher BAS-Fun Seeking than BDNF Met/Met homozygous in the control group (p=0.004) (Figure 1B).
Next, we examined that effects of MBT on NEO personality and BAS/BIS would be affected by BDNF genetic polymorphism in the MBT group. BDNF Met/Met showed the lower Neuroticism compared to BDNF Val/Val+Val/Met within the MBT group (p=0.049) (Figure 2). However, associations of BDNF genetic polymorphism with BAS/BAS scale did not show any significant results in the MBT group.
Finally, differences of NEO personality and BAS/BIS between the control and MBT groups were investigated. In the same genotypes of the BDNF Val/Val+Val/Met group, MBT group showed the increased Extraversion (p=0.033) and the increased Openness to Experience (p=0.004) compared to the control group (Figure 3A). Also, in the same Met/Met carriers, MBT group exhibited the increase of Extraversion (p=0.008), the reduction of Neuroticism (p=0.002), and the increase of Openness to Experience (p=0.008) compared to the control group (Figure 3B). In the same genotypes of the BDNF Val/Val+Val/Met group, MBT group showed the decreased BAS-Reward Responsiveness (p=0.016) and the decrease of BIS (p=0.004) compared to the control group (Figure 4A). In the BDNF Met/Met group, MBT group increased BAS-Fun Seeking (p= 0.045) and decreased BIS (p=0.013) compared to the control group (Figure 4B).
The studies on associations between BDNF genetic polymorphism and personality have been known but the various long-term effects of MBT on NEO personality traits and BAS/BIS according to BDNF genetic polymorphism has little been known. We have found that MBT would differently contribute to NEO personality and BAS/BIS according to BDNF Val66Met polymorphism. First, MBT group in the BDNF Val/Val+al/Met subjects showed the increased Extraversion and the increased Openness to Experience compared to the control group, and MBT group in the same Met/Met carriers exhibited the increase of Extraversion, the reduction of Neuroticism and the increase of Openness to Experience compared to the control group (Figure 3). Second, MBT group in the BDNF Val/Val+Val/Met group showed the decreased BAS-Reward Responsiveness and the decrease of BIS compared to the control group (Figure 4A). MBT group in the BDNF Met/Met group increased BAS-Fun Seeking and decreased BIS compared to the control group (Figure 4B).
First of all, whether BDNF genetic polymorphism is associated with the NEO personality and BAS/BIS was investigated. A study that BDNF Met carriers were more introverted19 supports our result that BDNF Val/Val showed higher Extraversion than that of Met/Met in the control group (Figure 1A). Extraversion was positively correlated with meditation practice and Neuroticism was negatively correlated with meditation practice.6 In particular, the increase of Extraversion in MBT group compared to the control group is thought to be associated with the decrease of Neuroticism through MBT (Figure 3). In this study, BDNF Met/Met subjects scored higher Neuroticism than Val/Val in the control group (Figure 1A). In BDNF Met carriers, elevations in Neuroticism and trait depression and stress were associated with lower hippocampal volume, but there were no such associations in Val homozygotes.25 On the other hand, Met/Met and Val/Met individuals, as compared to Val/Val, showed a significant lower Neuroticism score.26 Also, among individuals with at least one copy of the DAT 9-repeat allele, carriers of the BDNF Met allele exhibited significantly lower Neuroticism scores than noncarriers.27 Although the reported studies on associations of BDNF Val66Met genetic polymorphism with Neuroticism are controversial, higher neuroticism of Met/Met subjects than Val/Val in the control group seems to be able to be explained by other results such as lower extraversion of Met/Met subjects than Val/Val (Figure 1A). Within the MBT group, BDNF Met/Met carriers showed lower Neuroticism than that of BDNF Val/Val+Val/Met (Figure 2), which seems to be consistent with the decrease of Neuroticism of Met/Met carriers in MBT group compared to the control group (Figure 3). The decreased Neuroticism in BDNF Met/Met through MBT may be mediated by complement of vulnerability for higher Neuroticism of the Met/Met carriers (Figure 1A). The decrease of Neuroticism through MBT was shown in the BDNF Met/Met, but not Val/Val+Val/Met group (Figure 3B). Higher Neuroticism in Met/Met compared to Val/Val (Figure 1A) may induce the significant decrease of Neuroticism in Met/Met, indicating more decrease effect of MBT on Neuroticism in Met/Met subjects. The BDNF Met-early life stress interaction also predicted elevated Neuroticism and higher depression and anxiety by elevations in body arousal.28 Thus, the reduction of stress through MBT22 may contribute to the decrease of Neuroticism in Met/Met carriers of the MBT group compared to the control group (Figure 3B).
In addition to the reduction of stress, enhancement of emotional well-being through MBT seems to induce the decrease of Neuroticism and the increase of Extraversion. The increase of emotional competence was related to long-term significant increases in Extraversion and Agreeableness as well as a decrease in Neuroticism.5 Gene-stress susceptibility factors contribute to a brain-arousal profile indicative of risk for depression.29 Considering that introverts are more aroused than are extraverts30 and BDNF Met carriers were more introverted,19 the stress-related high arousal of Met carriers is thought to be decreased to optimal level of arousal through the reduction of stress and Neuroticism by practicing MBT. Discussion on association of MBT with maintaining an optimal level of arousal31 seems to be able to explain the increase of Extraversion in both BDNF Val/Val+Val/Met and Met/Met groups. In addition to the increase of Extraversion, MBT group in BDNF Val/Val+Val/Met subjects increased the Openness to Experience compared to the control group (Figure 3). The increase of Openness to Experience through MBT seems to be associated with the enhancement of creativity.32 Thus, MBT may enhance the potential of brain capacity such as creativity in addition to complement of different vulnerability according to genetic polymorphism.
It was revealed that MBT differently affected the BAS and BIS as well as NEO personality traits according to genetic polymorphism in this study. We found that the Val/Val+Val/Met subjects showed higher BAS-Fun Seeking than that of the Met/Met carriers in the control group (Figure 1B). On the other hand, in the Met/Met subjects, MBT group showed increased BAS-Fun Seeking (Figure 4B), which seems to restore vulnerability of low BAS-Fun Seeking in the control Met/Met group. In both Val/Val+Val/Met and Met/Met groups, MBT group showed decreased BIS (Figure 4). As higher BIS subjects generated a more right hemisphere activation for some negative emotions such as fear, anger, and surprise,33 the decreased BIS in MBT group compared to the control group (Figure 4) may be related to the reduction of negative emotions in the right hemisphere activation. Given that Neuroticism positively correlated with the BIS in this study, though the result was not presented, the reduction of Neuroticism through MBT may in part contribute to the decrease of BIS. High Extraversion and Openness and low Neuroticism and Agreeableness predicted fearless dominance which was related to low BIS activity and high BAS activity.34 Thus, the decrease of BIS in MBT group compared to the control group (Figure 4) seems to be related to the reduction of Neuroticism, or the increase of Extraversion and Openness (Figure 3). Also, the decrease of Neuroticism and increase of Extraversion in Met/Met subjects through MBT (Figure 3B) is thought to be associated with the increase of BAS-Fun Seeking in Met/Met subjects (Figure 4B). Considering that BAS correlated with positive affect,35 the increase of positive affect through MBT22 may be related to the increase of BAS-Fun Seeking in Met/Met subjects. Also, as Extraversion increases BAS and vice versa,14 higher Extraversion and lower Neuroticism in Val/Val homozygotes compared to the Met/Met within the control group (Figure 1A) may be related to the higher BAS-Fun Seeking in Val/Val+Val/Met compared to the Met/Met (Figure 1B). As a result, the increase of Extraversion through MBT seems to contribute to the increase of the BAS-Fun Seeking in Met/Met subjects.
Significant associations between the A1 allele of the DRD2 TaqI A polymorphism and a high BAS-Reward Responsiveness were reported21 but a relationship of BDNF with BAS-Reward Responsiveness has not been studied. High scores on BAS-Drive and BAS-Reward Responsiveness was associated with a strategy that first seeks to maximize the likelihood of reward, and then to maximize the amount of reward.36 Considering that in Val/Val+Val/Met subjects, MBT group had lower BAS-Reward Responsiveness than that of the control group (Figure 4A), the reduction of BAS-Reward Responsiveness through MBT may be more associated with the increase of intrinsic motivation which exists within the individual rather than relying on any external reward.
BIS activity was associated with increased amygdala and hippocampal gray matter volume37 and a reduced volume in the striatum might be associated with enhanced reward sensitivity and deficits in inhibitory control,38 suggesting that BAS and BIS was associated with a structure of brain. Thus, MBT is postulated to affect the structure and function of brain related to BAS/BIS and personality.
Neuroticism increased the risk of later schizophrenia, whereas Extraversion reduced the risk.39 Low Extraversion scores were significantly correlated with gray matter volume reductions in the right posterior fusiform gyrus in chronic schizophrenia.40 Also, Neuroticism predicted positive symptoms of schizophrenia and depression.41 Thus, the decrease of Neuroticism and increase of Extraversion through MBT can represent the effects of complementary and alternative medicine for schizophrenia and depression. Considering that social anxiety disorder showed decreased BAS-Fun Seeking and increased BIS,42 the decrease of anxiety through MBT is thought to contribute to the increase of BAS-Fun Seeking and the decrease of BIS. Because BIS was negatively correlated with cardiovascular fitness16 and higher BIS sensitivity correlated positively with anxiety scores43 and correlated with longer duration of illness,44 the decrease of BIS through MBT is thought to be associated with the improvement of physical and emotional fitness. We can suggest plausible reasons for the different effects of MBT depending on BDNF genotype as follows. First, NEO personality and BIS/BAS show different traits according to BDNF genetic polymorphism, which can induce the different effects of MBT on them. Second, MBT can complement and restore the specific vulnerability in each genetic polymorphism such as compensating for NEO-Extraversion/Neuroticism and BAS-Fun Seeking in BDNF Met/Met subjects. Third, MBT can more strengthen some strong points like NEO-Extraversion in BDNF Val/Val+Val/Met subjects. Fourth, MBT seems to enhance the potential personality such as NEO-Openness to Experience in all subjects. Thus, MBT can restore the specific vulnerability and strengthen some advantages in each genetic polymorphism, enhancing the potential of brain capacity and personality, which may induce different effects of MBT on personality and behavioral systems depending on BDNF genotype. Biological mechanisms accounting for different effects of MBT on them depending on BDNF genotype need to be explored in future studies.
Since this study was limited by its cross-sectional design, a longitudinal study which can investigate before and after MBT following the same people over a longer period of time is required to confirm our results. The sample size was very small for the proving the association between NEO (or BAS/BIS) and BDNF polymorphism. Nevertheless, as subjects in the MBT group had been practicing MBT for a mean of 43 months with the same type of MBT, the results of this study deserve to be approved. To elucidate the effects and hidden mechanisms of MBT an integrative study is needed from molecule to behavior based on genetic differences in the future.
In conclusion, MBT showed different effects on NEO personality and BAS/BIS according to BDNF genetic differences, suggesting that MBT can complement and restore the specific vulnerability in each genetic polymorphism. Also, MBT would induce the beneficial changes of specific personality and behavioral system and enhance the potential of brain capacity according to genetic differences. These findings suggest the potential of brain to complement and restore vulnerability of individual behavioral system and personality based on the different effects of MBT according to genetic polymorphisms. Considering that MBT showed complemental effects on the relative balance of plasma catecholamines according to BDNF and COMT genetic polymorphisms,45 the different effects of MBT on personality and behavioral systems according to BDNF polymorphism support that MBT can be helpful for personalized medicine.
Acknowledgments
The authors give special thanks to Korean Institute of Brain Science for the assistance in the current study. This work was supported by Cognitive Neuroscience Program of the Korean Ministry of Science and Technology (M10644020003-08N4402-00310).
References
1. Lutz A, Slagter HA, Dunne JD, Davidson RJ. Attention regulation and monitoring in meditation. Trends Cogn Sci 2008;12:163-169. PMID: 18329323.



2. Hölzel BK, Ott U, Hempel H, Hackl A, Wolf K, Stark R, et al. Differential engagement of anterior cingulate and adjacent medial frontal cortex in adept meditators and non-meditators. Neurosci Lett 2007;421:16-21. PMID: 17548160.


3. Aftanas LI, Golocheikine SA. Human anterior and frontal midline theta and lower alpha reflect emotionally positive state and internalized attention: high-resolution EEG investigation of meditation. Neurosci Lett 2001;310:57-60. PMID: 11524157.


4. Corby JC, Roth WT, Zarcone VP Jr, Kopell BS. Psychophysiological correlates of the practice of Tantric Yoga meditation. Arch Gen Psychiatry 1978;35:571-577. PMID: 365124.


5. Nelis D, Kotsou I, Quoidbach J, Hansenne M, Weytens F, Dupuis P, et al. Increasing emotional competence improves psychological and physical well-being, social relationships, and employability. Emotion 2011;11:354-366. PMID: 21500904.


6. Delmonte MM. Personality correlates of meditation practice frequency and dropout in an outpatient population. J Behav Med 1988;11:593-597. PMID: 3075240.


7. Kunisato Y, Okamoto Y, Okada G, Aoyama S, Nishiyama Y, Onoda K, et al. Personality traits and the amplitude of spontaneous low-frequency oscillations during resting state. Neurosci Lett 2011;492:109-113. PMID: 21291958.


8. Chapman BP, Khan A, Harper M, Stockman D, Fiscella K, Walton J, et al. Gender, race/ethnicity, personality, and interleukin-6 in urban primary care patients. Brain Behav Immun 2009;23:636-642. PMID: 19162168.


9. Steptoe A, Willemsen G, Owen N, Flower L, Mohamed-Ali V. Acute mental stress elicits delayed increases in circulating inflammatory cytokine levels. Clin Sci (Lond) 2001;101:185-192. PMID: 11473494.


10. Lane JD, Seskevich JE, Pieper CF. Brief meditation training can improve perceived stress and negative mood. Altern Ther Health Med 2007;13:38-44. PMID: 17283740.
11. Pace TW, Negi LT, Adame DD, Cole SP, Sivilli TI, Brown TD, et al. Effect of compassion meditation on neuroendocrine, innate immune and behavioral responses to psychosocial stress. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2009;34:87-98. PMID: 18835662.


12. Gray JA. Critique of Eysenck's Theory of Personality. In: Eysenck HJ, editor. A Model for Personality. Berlin: Springer, 1981, p. 246-276.
14. Knyazev GG. Behavioural activation as predictor of substance use: mediating and moderating role of attitudes and social relationships. Drug Alcohol Depend 2004;75:309-321. PMID: 15283952.


15. Gray JR, Braver TS. Personality predicts working-memory-related activation in the caudal anterior cingulate cortex. Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci 2002;2:64-75. PMID: 12452585.


16. Schneider ML, Graham DJ. Personality, physical fitness, and affective response to exercise among adolescents. Med Sci Sports Exerc 2009;41:947-955. PMID: 19276837.



17. Bouchard TJ Jr, Loehlin JC. Genes, evolution, and personality. Behav Genet 2001;31:243-273. PMID: 11699599.


18. Wang X, Trivedi R, Treiber F, Snieder H. Genetic and environmental influences on anger expression, John Henryism, and stressful life events: the Georgia Cardiovascular Twin Study. Psychosom Med 2005;67:16-23. PMID: 15673619.


19. Terracciano A, Tanaka T, Sutin AR, Deiana B, Balaci L, Sanna S, et al. BDNF Val66Met is associated with introversion and interacts with 5-HTTLPR to influence neuroticism. Neuropsychopharmacology 2010;35:1083-1089. PMID: 20042999.


20. Reuter M, Schmitz A, Corr P, Hennig J. Molecular genetics support Gray's personality theory: the interaction of COMT and DRD2 polymorphisms predicts the behavioural approach system. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 2006;9:155-166. PMID: 15896265.


21. Lee SH, Ham BJ, Cho YH, Lee SM, Shim SH. Association study of dopamine receptor D2 TaqI A polymorphism and reward-related personality traits in healthy Korean young females. Neuropsychobiology 2007;56:146-151. PMID: 18259088.


22. Jung YH, Kang DH, Jang JH, Park HY, Byun MS, Kwon SJ, et al. The effects of mind-body training on stress reduction, positive affect, and plasma catecholamines. Neurosci Lett 2010;479:138-142. PMID: 20546836.


23. Costa PT, McCrae RR. Revised NEO Personality Inventory (NEO PI-R) and NEO Five-Factor Inventory (FFI): Professional Manual. Odessa, FL: Psychological Assessment Resources; 1992.
24. Carver CS, White TL. Behavioral inhibition, behavioral activation, and affective responses to impending reward and punishment: the BIS/BAS scales. J Pers Soc Psychol 1994;67:319-333.

25. Joffe RT, Gatt JM, Kemp AH, Grieve S, Dobson-Stone C, Kuan SA, et al. Brain derived neurotrophic factor Val66Met polymorphism, the five factor model of personality and hippocampal volume: implications for depressive illness. Hum Brain Mapp 2009;30:1246-1256. PMID: 18548532.


26. Frustaci A, Pozzi G, Gianfagna F, Manzoli L, Boccia S. Meta-analysis of the brain-derived neurotrophic factor gene (BDNF) Val66Met polymorphism in anxiety disorders and anxiety-related personality traits. Neuropsychobiology 2008;58:163-170. PMID: 19088493.


27. Hünnerkopf R, Strobel A, Gutknecht L, Brocke B, Lesch KP. Interaction between BDNF Val66Met and dopamine transporter gene variation influences anxiety-related traits. Neuropsychopharmacology 2007;32:2552-2560. PMID: 17392738.


28. Gatt JM, Nemeroff CB, Dobson-Stone C, Paul RH, Bryant RA, Schofield PR, et al. Interactions between BDNF Val66Met polymorphism and early life stress predict brain and arousal pathways to syndromal depression and anxiety. Mol Psychiatry 2009;14:681-695. PMID: 19153574.


29. Gatt JM, Nemeroff CB, Schofield PR, Paul RH, Clark CR, Gordon E, et al. Early life stress combined with serotonin 3A receptor and brain-derived neurotrophic factor valine 66 to methionine genotypes impacts emotional brain and arousal correlates of risk for depression. Biol Psychiatry 2010;68:818-824. PMID: 20728877.


30. Smith BD, Kline R, Lindgren K, Ferro M, Smith DA, Nespor A. The lateralized processing of affect in emotionally labile extraverts and introverts: central and autonomic effects. Biol Psychol 1995;39:143-157. PMID: 7734627.


31. Slagter HA, Davidson RJ, Lutz A. Mental training as a tool in the neuroscientific study of brain and cognitive plasticity. Front Hum Neurosci 2011;5:17PMID: 21347275.



32. McCrae RR. Creativity, divergent thinking, and openness to experience. J Pers Soc Psychol 1987;52:1258-1265.

33. Balconi M, Mazza G. Brain oscillations and BIS/BAS (behavioral inhibition/activation system) effects on processing masked emotional cue.s ERS/ERD and coherence measures of alpha band. Int J Psychophysiol 2009;74:158-165. PMID: 19709636.


34. Ross SR, Benning SD, Patrick CJ, Thompson A, Thurston A. Factors of the psychopathic personality inventory: criterion-related validity and relationship to the BIS/BAS and five-factor models of personality. Assessment 2009;16:71-87. PMID: 18703823.


35. Campbell-Sills L, Liverant GI, Brown TA. Psychometric evaluation of the behavioral inhibition/behavioral activation scales in a large sample of outpatients with anxiety and mood disorders. Psychol Assess 2004;16:244-254. PMID: 15456380.


36. Scheres A, Sanfey AG. Individual differences in decision making: drive and reward responsiveness affect strategic bargaining in economic games. Behav Brain Funct 2006;2:35PMID: 17049091.



37. Barrós-Loscertales A, Meseguer V, Sanjuán A, Belloch V, Parcet MA, Torrubia R, et al. Behavioral Inhibition System activity is associated with increased amygdala and hippocampal gray matter volume: a voxel-based morphometry study. Neuroimage 2006;33:1011-1015. PMID: 16979909.


38. Barrós-Loscertales A, Meseguer V, Sanjuán A, Belloch V, Parcet MA, Torrubia R, et al. Striatum gray matter reduction in males with an overactive behavioral activation system. Eur J Neurosci 2006;24:2071-2074. PMID: 17040475.


39. Van Os J, Jones PB. Neuroticism as a risk factor for schizophrenia. Psychol Med 2001;31:1129-1134. PMID: 11513380.


40. Onitsuka T, Nestor PG, Gurrera RJ, Shenton ME, Kasai K, Frumin M, et al. Association between reduced extraversion and right posterior fusiform gyrus gray matter reduction in chronic schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 2005;162:599-601. PMID: 15741479.



41. Barrantes-Vidal N, Ros-Morente A, Kwapil TR. An examination of neuroticism as a moderating factor in the association of positive and negative schizotypy with psychopathology in a nonclinical sample. Schizophr Res 2009;115:303-309. PMID: 19822406.


42. Morgan BE, van Honk J, Hermans EJ, Scholten MR, Stein DJ, Kahn RS. Gray's BIS/BAS dimensions in non-comorbid, non-medicated social anxiety disorder. World J Biol Psychiatry 2009;10:925-928. PMID: 19191073.


43. Biuckians A, Miklowitz DJ, Kim EY. Behavioral activation, inhibition and mood symptoms in early-onset bipolar disorder. J Affect Disord 2007;97:71-76. PMID: 16890995.


44. Scholten MR, van Honk J, Aleman A, Kahn RS. Behavioral inhibition system (BIS), behavioral activation system (BAS) and schizophrenia: relationship with psychopathology and physiology. J Psychiatr Res 2006;40:638-645. PMID: 16643947.


45. Jung YH, Kang DH, Byun MS, Shim G, Kwon SJ, Jang GE, et al. Influence of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and catechol O-methyl transferase polymorphisms on effects of meditation on plasma catecholamines and stress. Stress 2012;15:97-104. PMID: 21790467.


Figure 1
Differences of NEO personality and BAS/BIS according to BDNF genetic polymorphism in the control group. A: V/V; Val/Val (N=22), M/M; Met/Met (N=12). B: V/V+V/M; Val/Val+Val/Met (N=52), M/M; Met/Met (N=12). *p<0.05, **p<0.01. BAS-RR: BAS-Reward Responsiveness, BAS-D: BAS-Drive, BAS-FS: BAS-Fun Seeking, BIS: Behavioral inhibition system, NEO: neuroticism-extraversion-openness.
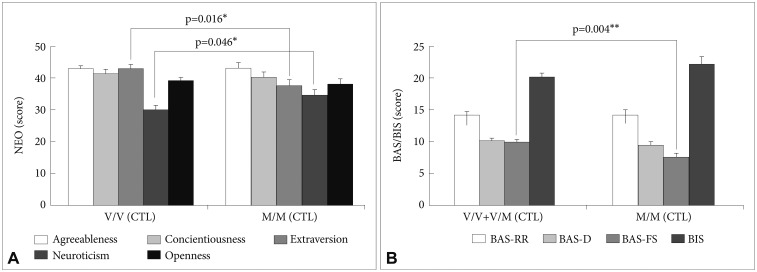
Figure 2
Differences of NEO personality according to BDNF genetic polymorphism on NEO in the MBT group. V/V+V/M: Val/Val+Val/Met (N=56), M/M: Met/Met (N=16). *p<0.05. NEO: neuroticism-extraversion-openness.
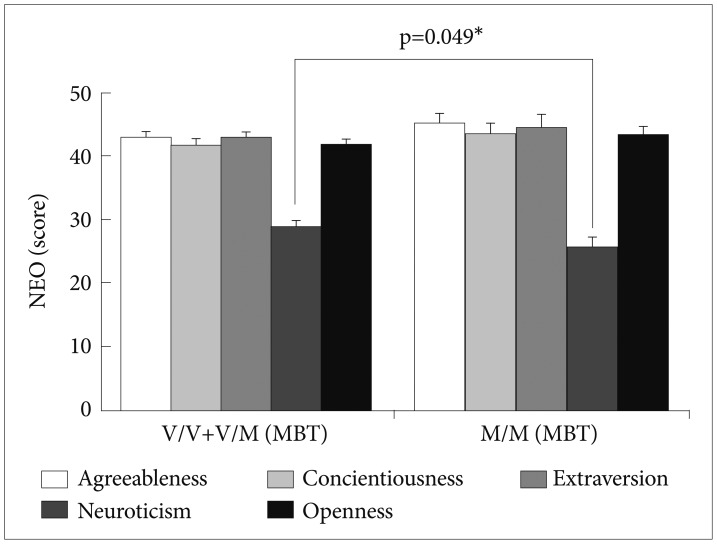
Figure 3
The different effects of MBT on NEO according to BDNF genetic differences. A: CTL group [V/V+V/M: Val/Val+Val/Met (N=52)], MBT group [V/V+V/M: Val/Val+Val/Met (N=56)]. B: CTL group [M/M: Met/Met (N=12)], MBT group [M/M: Met/Met (N=16)]. *p<0.05, **p<0.01. NEO: neuroticism-extraversion-openness, MBT: mind-body traning.
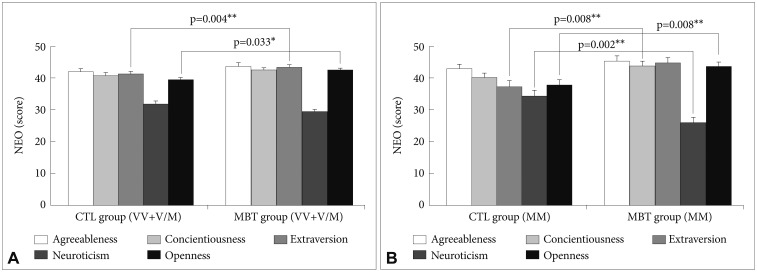
Figure 4
The different effects of MBT on BAS/BIS according to BDNF genetic differences. A: CTL group [V/V+V/M: Val/Val+Val/Met (N=52)], MBT group [V/V+V/M: Val/Val+Val/Met (N=56)]. B: CTL group [M/M: Met/Met (N=12)], MBT group [M/M: Met/Met (N=16)]. *p<0.05, **p<0.01. BAS-RR: BAS-Reward Responsiveness, BAS-D: BAS-Drive, BAS-FS: BAS-Fun Seeking, BIS: behavioral inhibition system, BAS: behavioral activation system, MBT: mind-body traning, CTL: control.