 |
 |
- Search
| Psychiatry Investig > Volume 14(3); 2017 > Article |
Abstract
Objective
The aims of this prospective study were to investigate temporal changes in mood status and distress level, as well as the development of depression, during pegylated interferon (PEG-IFN)-based treatment of patients with chronic hepatitis C (CHC). We also explored whether baseline demographic, psychiatric, and personality traits predicted the evolution of depression.
Methods
CHC patients without depression were screened with laboratory tests; psychiatric interviews; and evaluations of mood symptoms, level of distress, and personality traits. A total of 67 treatment-naïve patients with CHC were consecutively treated with PEG-IFN-α-2a plus ribavirin for 48 (genotype 1, n=29) or 24 (genotype 2, n=38) weeks. Patients were followed prospectively every 4 weeks during the treatment period.
Results
Seven patients (10.4%) were diagnosed with major depressive disorder (MDD), and eight (11.9%) developed subsyndromal depression. Times to onset of MDD and subsyndromal depression were 6.67±5.01 and 11.11±5.58 weeks, respectively, after initiation of treatment. Patients who developed MDD had significantly increased fatigue and anxiety and poor psychological well-being during the course of treatment. Pretreatment subthreshold mood symptoms were a significant predictor of depression.
Globally, hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection is the most frequent cause of chronic liver disease; approximately 2.2% of adults worldwide are chronically infected with HCV.1 Despite recent advances in direct-acting antivirals (DAAs), combined treatment with pegylated interferon-α (PEG-IFN-α) and ribavirin (RBV) is still regarded as the standard backbone treatment for chronic hepatitis C (CHC), due to the considerably high cost of DAAs, especially in developing countries.2
Psychiatric adverse events, including depression, fatigue, cognitive impairment, and insomnia, are frequently encountered to varying degrees during PEG-IFN-based treatment.3 In general, PEG-IFN-α-based treatment for CHC usually induces depression in 20-40% of patients with CHC.456 The clinical symptoms associated with IFN-induced depression are analogous to those seen in major depressive disorder (MDD). Since IFN-induced depressive symptoms usually limit the IFN dosage, they may compromise antiviral efficacy and bring substantial distress to some patients with CHC.4 Furthermore, moderate-to-severe depressive symptoms often lead to treatment delays or premature withdrawal from antiviral therapy,7 with a strong negative impact on quality of life (QOL).89
Although depressed mood is one of the core symptoms of MDD, this symptom may not be as prominent in patients with CHC.10 Other symptoms, such as somatic complaints, loss of appetite, and fatigue, may be more prevalent and problematic during IFN-based treatment.11 However, to date, there has been limited evidence regarding which symptoms of depressive disorder are likely to develop or when these symptoms occur during IFN-based treatment against HCV infection.
Previous studies reported that depressive symptoms are common in early stages of IFN-based treatment121314 and return to normal after the end of IFN-based treatment.1516 Most studies evaluated the extent of depressive symptoms only at selected time points; for example, at weeks 4, 12, 24, 36, and 48 of IFN-based treatment.16 In a recent study, Loftis et al.11 evaluated depressive symptoms in patients with CHC biweekly during the first 16 weeks of IFN-based treatment. However, IFN-induced depression can occur even after 24 weeks of treatment.17 Because of serious adverse effects caused by depression, it is important to prevent the onset of depressive symptoms, as well as to detect depressive symptoms early in patients with CHC receiving IFN-based treatment.
At present, there are no established clinical and psychological risk factors to predict the development of depression during IFN-based treatment in patients with CHC. It is generally believed that the frequency of serious psychiatric adverse events increases when IFN is given for longer durations or at higher doses. There is also a greater likelihood of developing depression when patients with clinically significant premorbid depression or worsened depressive symptoms undergo IFN-based treatment.56 However, additional research is required to confirm the predictive performance of these potential risk factors for IFN-induced psychiatric adverse effects.
The primary aim of this study was to investigate prospectively and comprehensively the time course of mood symptoms and level of distress, as well as the development of depressive disorder, in patients with CHC every 4 weeks during IFN-based treatment. We also attempted to determine whether baseline clinical, psychiatric, and personality characteristics predicted subsequent changes in mood symptoms and the development of depressive disorder. In addition, we examined associations between the development of depressive disorder and level of distress and IFN responsiveness in patients with CHC.
Patients aged 20 to 75 years with CHC at Seoul Metropolitan Government Seoul National University (SMG-SNU) Boramae Medical Center were consecutively enrolled in the prospective cohort between August 2011 and November 2013. The diagnosis of CHC was made on the basis of seropositivity for anti-HCV antibodies and detectability of HCV RNA in sera before starting antiviral therapy, irrespective of aminotransferase levels. CHC patients treated with PEG-IFN-α-2a (Pegasys; Hoffmann-La Roche Inc., Basel, Switzerland) combined with ribavirin (RBV) were eligible for this prospective cohort study. Those with the following conditions were excluded: previous treatment with IFN-α or PEG-IFN; chronic liver disease other than CHC such as seropositivity for hepatitis B surface antigen, autoimmune hepatitis, primary biliary cirrhosis, sclerosing cholangitis, and Wilson disease; decompensated liver cirrhosis (Child-Pugh class B or C); heavy alcohol consumption (≥20 g/day); previous liver transplantation; presence of hepatocellular carcinoma; psychiatric disease including depression; overt hypo- or hyperthyroidism at baseline; platelets <90,000/mm3; hemoglobin <12 (men) or <11 (women) g/dL; neutrophils <1,500/mm3; and serum creatinine ≥1.5 mg/dL. Pregnant and nursing women were also excluded. The study was approved by the SMG-SNU Boramae Medical Center Institutional Review Board (IRB No. 06-2011-130), and it complied with the ethical guidelines of the 1975 Declaration of Helsinki. Written informed consent was obtained from all study participants who were enrolled in this prospective cohort study. This investigation is registered as “NCT01465919” (http://clinicaltrials.gov).
Patients with CHC and without depressive disorder who were started on antiviral therapy with PEG-IFN-α-2a plus RBV were examined at baseline and then followed prospectively every 4 weeks for the entire treatment period. After collecting baseline psychiatric measurements, PEG-IFN-α-2a (fixed dose, 135 or 180 µg) was injected subcutaneously weekly and oral RBV was administered twice daily based on patient body weight (1.0 g, ≤75 kg; 1.2 g, >75 kg) for patients with genotype 1. A fixed dose (0.8 g) of RBV was given to those with genotype 2. Treatment duration differed according to HCV genotypes: antiviral treatment was maintained for 48 weeks in patients infected with HCV genotype 1 and for 24 weeks in those with genotype 2. Study participants were followed every 4 weeks during PEG-IFN/RBV treatment, with a physical examination, laboratory testing, and assessments of subjective adverse events conducted at each visit. PEG-IFN-α-2a was discontinued when the absolute neutrophil count was <500/mL or the platelet count was <25,000/mm3. If anemia (hemoglobin <8 g/dL) was persistent during combination therapy, RBV was withdrawn gradually according to the manufacturer's recommendations.
After providing informed consent, study participants routinely underwent: 1) a diagnostic psychiatric interview to assess lifetime and current histories of psychiatric illness, including current and past medications, and family history of mood disorder; 2) self-report questionnaires about psychiatric features, including mood status, degree of stress, and personality; and 3) laboratory tests such as anti-HCV antibody (ADVIA Centaur XP, Siemens Healthcare Diagnostics S.L., Tarrytown, NY, USA), HCV RNA (Abbott Laboratories, Abbott Park, IL, USA), and HCV genotyping (HCV Genotyping Chip kit, Biocore, Seoul, Korea). HCV RNA was evaluated at baseline, at 4 and 12 weeks of treatment, at the end of treatment, and 24 weeks after the end of treatment. Clinical and psychiatric assessments were made at baseline and monthly over the course of PEG-IFN-α-2a/RBV treatment. If patients showed a Beck Depression Inventory (BDI) score of ≥10 at any time point during the study period, they were reevaluated by the psychiatrist using the 17-item Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (HAMD-17) and the Structured Clinical Interview for the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (SCID) to identify the diagnostic criteria for MDD.1819
Prior to antiviral treatment, the mood status of all participants was assessed with the BDI, Beck Anxiety Inventory (BAI), and Profile of Mood States (POMS).2021 The BDI is a 21-item self-report inventory measuring characteristic atti-tudes and symptoms of depression; nondepression is defined as a BDI <10.22 The BAI consists of 21 symptoms that are rated on a four-point scale measuring the severity of anxiety symptoms experienced during the past week. Scores for the 21 items are summed to yield a single anxiety score. The POMS represents various affective mood states. It consists of 65 predicate adjectives that are rated by subjects on a five-point scale. Six factors have been derived from this scale: tension-anxiety, depression-dejection, anger-hostility, fatigue-inertia, vigor-activity, and confusion-bewilderment. In the current study, we used the Korean version of the POMS (K-POMS).21
Degree of stress was measured with a Psychosocial Well-Being Index (PWI) questionnaire containing 45 items.23 This tool was developed on the basis of the General Health Questionnaire generated by Goldberg, which was designed to evaluate psychological stability among community populations and was subsequently modified to meet the characteristics of Korean populations.24 It contains questions about physical and psychological status over the last few weeks, covering social role performance, self-confidence, depression, sleep disturbance, anxiety, and the general well-being of respondents.
To assess personality, the short form of the Korean version of Neuroticism-Extraversion-Openness Personality Inventory revised (NEO-PI-R) was used.2526 The NEO-PI-R assesses personality characteristics according to the Big Five model of personality and is widely used in personality research.27 The Big Five model evaluates five dimensions of personality: neuroticism (includes traits such as being tense, moody, and anxious), extraversion (includes traits such as being talkative, assertive, and energetic), agreeableness (includes traits such as being sympathetic, affectionate, and kind), openness to experience (includes traits such as having wide-ranging interests and being imaginative and insightful), and conscientiousness (includes traits such as being organized, thorough, and competent).28 A brief explanation of these five personality constructs is covered elsewhere.29
To measure impulsivity as one of the personality dimensions, we used the Korean version of the Barratt Impulsiveness Scale, version 11 (BIS-11).3031 The BIS-11 consists of three factors: cognitive impulsiveness (making quick decisions), motor impulsiveness (acting without thinking), and nonplanning impulsiveness (a lack of “futuring” or foresight).3233
We used the behavioral inhibition system (BIS) and behavioral activation system (BAS) scales to assess sensitivity to rewards and punishment.34 The BIS and BAS scales consist of 20 items rated on a four-point Likert scale from ‘‘totally agree” to ‘‘totally disagree.” The BIS and BAS scales consist of 7 and 13 items, respectively. The BAS scale can be subdivided into three subscales: fun seeking (BAS-fun; four items), reward responsiveness (BAS-reward; five items), and drive (BAS-drive; four items).
Study participants underwent liver biopsy within the 4 weeks prior to the start of antiviral treatment. The META-analysis VIRus hepatitis histological scoring system (METAVIR) was used to assess the histological fibrosis stage for hepatitis C.35 Simultaneously, liver stiffness as a mechanical fibrosis indicator was measured by means of acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI) elastography (Acuson S2000; Siemens AG, Erlangen, Germany) as described elsewhere.36
After initiating antiviral therapy, we conducted a self-report questionnaire survey that included BDI, BAI, K-POMS, and PWI regularly every 4 weeks during PEG-IFN-α-2a-based treatment. IFN-induced depressive disorder was categorized as either MDD or subsyndromal depression. A trained psychiatrist meticulously evaluated all study participants and diagnosed them with MDD or subsyndromal depression, according to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM)-IV, using the SCID. A diagnosis of subsyndromal depression was made if there were two or more simultaneous symptoms listed in the DSM-IV depressive episode criteria. These symptoms must have been present at all times for at least 2 weeks and have been associated with evidence of functional dysfunction. Additionally, the individual must not have met the criteria for a diagnosis of major depression. The incidence of MDD was diagnosed with a HAMD-17 score of ≥14 as well as the DSM-IV major depressive episode criteria. The severity of depressive disorder was also assessed by means of HAMD-17. To determine antiviral treatment response, sustained virological response (SVR) was defined as undetectable serum HCV RNA by quantitative PCR at 24 weeks after the completion of treatment. Relapse was defined as an increase in serum HCV RNA titers after achieving end of treatment response (ETR).
Demographic and clinical variables are expressed as mean±standard deviation (SD) or frequencies and proportions (%). The two-sample t-test for continuous variables and the χ2 test or Fisher's exact test for categorical variables were used for group comparisons. More information about several psychiatric mood symptoms was obtained repeatedly throughout IFN-based treatment. To evaluate the sequential change in mood symptoms over time, a linear mixed-effects model for repeated measures from same subjects37 was used, which uses all available data and provides the valid results in the presence of missing data under the assumption that missing data are missing at random.3839 Differences between nondepressed patients and those with major depression, and between patients with genotype 1 and those with genotype 2 over time were also compared using the linear mixed-effects model. The model considered sex, age, status of major depression, time, and status-by-time interaction as fixed effects and incorporated a random intercept effect. For multiple comparisons, the Bonferroni correction was universally applied. In addition, logistic regression analysis was conducted to assess whether psychiatric, personality, or HCV-related factors contributed to the development of depressive disorder. P values of <0.05 were considered statistically significant. All statistical analyses were performed with IBM SPSS Statistics version 20 (IBM Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) and R version 3.1.0 (http://www.r-project.org).
A total of 69 treatment-naïve patients with HCV were included in the prospective cohort study. Of these, two patients declined to participate in the study. The most predominant genotypes of HCV are 1b or 2a/c in Korean patients with hepatitis C. In the current study, all study participants were treated with PEG-IFN-α-2a plus RBV for 48 (HCV genotype 1b, n=29) or 24 (HCV genotype 2a/c, n=38) weeks. Table 1 shows the demographic and clinical characteristics of all study subjects. There were no significant differences in age, sex ratio, body mass index (BMI), baseline PWI, measures of personality, HCV genotype, liver stiffness, METAVIR fibrosis stage, or initial IFN dose between patients with IFN-induced depression and those without depression. Although mood status scores for all subjects were within the normal range for BDI and BAI, there were significant differences in BDI and BAI scores between the groups. In addition, there were also significant differences in K-POMS total and subscale scores (except tension-anxiety, anger-hostility, and vigor-activity) between the groups.
Of all subjects (n=67), 15 (22.4%) met the criteria for depressive disorder following initiation of IFN-based treatment. Seven subjects (10.4%) met the criteria for MDD, and eight (11.9%) fulfilled the criteria for subsyndromal depression. Times of onset of MDD and subsyndromal depression were 6.67±5.01 and 11.11±5.58 weeks, respectively, after initiation of IFN-based treatment. All susceptible patients developed depressive disorder within 20 weeks after initiation of IFN-based treatment. Mean scores of HAMD-17 at diagnosis of MDD and subsyndromal depression were 18.43±3.64 and 9.17±2.56, respectively. Of four patients with depressive disorder and HCV genotype 1, three dropped out prematurely and only one completed antiviral treatment for 48 weeks.
Among all participants, BDI and PWI scores did not change significantly during the course of PEG-IFN-α-2a-based treatment (Figure 1). However, the BAI score (Figure 1) and fatigue-inertia subscale of the K-POMS (Figure 2) showed significant changes in all participants during the course of antiviral treatment. Significant increases in the BAI score after initiation of PEG-IFN-α-2a-based treatment were found at 8 (PBonferroni=0.013), 16 (PBonferroni=0.016), and 20 (PBonferroni=0.017) weeks compared to the baseline BAI score. A significant increase in the fatigue-inertia subscale score of the K-POMS was found at 8 weeks (PBonferroni=0.018) compared to the baseline score.
Figures 3 and 4 show the temporal kinetics of mood symptoms and level of distress in patients with MDD and those with no depression. There were significant differences in the BDI score from baseline through 28 weeks between patients with MDD and those without depression. The peak time for an increase in the BDI score after initiation of PEG-IFN-α-2a-based treatment was 16 weeks (least squares mean of BDI score=24.09). There were significant differences in the BAI score from baseline through 28 weeks between patients with MDD and nondepressed patients. Degree of distress, as measured by PWI, showed two peak times, with an increase in the score at 8 and 24 weeks, indicating higher levels of distress in patients with IFN-induced MDD (Figure 3). There were significant differences in K-POMS subscale scores for tension-anxiety, depression-dejection, anger-hostility, fatigue-inertia, and confusion-bewilderment from 4 weeks through 28 weeks between patients with IFN-induced MDD and those without depression (Figure 4). However, there were no significant differences in BDI, BAI, PWI, and K-POMS subscale scores during the first 24 weeks of treatment between patients with genotype 1 and those with genotype 2.
To find factors predictive of the development of depressive disorder following PEG-IFN-α-2a-based treatment, logistic regression analysis was conducted between variables, including demographic, psychiatric, personality, and HCV-related characteristics, and depressive disorder. Logistic regression analysis showed that BDI, BAI, and K-POMS total scores at pretreatment were significant predictors of the onset of depressive disorder [BDI: odds ratio (OR) 1.14, 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.02-1.27, p=0.025, BAI: OR 1.15, 95% CI 1.03-1.29, p=0.017, and K-POMS total: OR 1.04, 95% CI 1.01-1.07, p=0.010]. In addition, K-POMS subscales (except vigor-hostility) also predicted the development of depressive disorder (data not shown). Level of distress at baseline tended to predict the onset of depressive disorder, although it did not reach statistical significance (PWI: OR 1.03, 95% CI 1.00-1.07, p=0.067). Other psychiatric and personality traits, as well as HCV-related factors, including HCV genotype, liver stiffness, METAVIR stage, and initial IFN dose, did not predict the onset of depressive disorder significantly.
There was no significant association between IFN-induced depressive disorder and SVR or relapse rate (Table 1). With respect to dropout rate, of patients with depressive disorder (n=15), six (40.0%) dropped out prematurely after initiation of IFN-based treatment, whereas 28.8% of nondepressed patients with HCV dropped out of IFN-based treatment. The main reason for dropout in patients with depressive disorder (four out of six) was the depressive disorder itself.
The present study tracked the prospective course of mood symptoms and level of distress in patients with HCV infection every 4 weeks during PEG-IFN-α-2a-based treatment and investigated comprehensively the relationship between the development of depressive disorder and clinical, psychiatric, and personality traits.
We found that 22.4% (n=15) of patients treated with PEG-IFN-α-2a/RBV met the criteria for depressive disorder following initiation of IFN-based treatment. Of patients with depressive disorder, 10.4% (n=7) met the diagnostic criteria for MDD and 11.9% (n=8) fulfilled criteria for subsyndromal depression. In line with previous reports.4011 IFN-based treatment was accompanied by a significant increase in depressive symptoms in our study. Previous studies reported that depressive symptoms are common in the early stage of antiviral treatment and reach peak levels at 4-16 weeks.121314 Hauser et al.5 also found that depression developed rapidly in patients with CHC during IFN-based treatment. In 62% (8/13) of patients who developed IFN-induced MDD, BDI scores increased from ≤10 to ≥18 within 2 weeks.5 In the present study, we found that onset of depressive disorder after initiation of IFN-based treatment was approximately 9.33±5.64 weeks. Furthermore, MDD developed relatively earlier than did subsyndromal depression, although this was not statistically significant (6.67±5.01 and 11.11±5.58 weeks, respectively). In accordance with the aforementioned findings, onset of depressive disorder was seen in the early stage of antiviral treatment. A possible explanation for the development of depressive disorder resulting from IFN-based treatment is that IFN induces a surge in the activity of indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygense (IDO), which is a tryptophan (TRP)-catabolizing enzyme, leading to greater breakdown of TRP to kynurenine (KYN). Thus, a markedly reduced concentration of TRP is available for serotonin synthesis in the brain.941 Baranyi et al.15 reported that a decrease in TRP availability in the brain, as well as an increase in neurotoxic challenge, develops in patients with depression during IFN-based treatment. A notable neurotoxic challenge due to the accumulation of KYN metabolites was found in patients with depression during the first several months after initiation of IFN-based treatment.15 The aforementioned biological alterations could support the development of depressive disorder in the earlier stages of IFN-based treatment. Accordingly, clinicians should be vigilant for the presence of depressive symptoms during the early stage of IFN-based treatment.
In the current study, all patients with chronic HCV infection showed significant changes in fatigue, among the various depressive symptoms, during the course of IFN-based treatment. Furthermore, fatigue at pretreatment predicted the onset of subsequent IFN-induced depressive disorder. According to Shakoor et al.,42 fatigue or loss of energy was the second most common symptom, following loss of interest, in patients with depressive disorder induced by IFN-based treatment. Furthermore, fatigue might be a more common symptom than depressed mood itself.42 Loftis et al.11 reported that an increase in depressive symptoms during IFN-based treatment is the result of significant increases in somatic symptoms.11 Moreover, when present, somatic symptoms can interfere with both successful completion of IFN-based treatment and steady maintenance of QOL.4344 Therefore, it is of critical importance to pay attention to somatic symptoms, especially fatigue, and to manage them actively during IFN-based treatment.
Stress is the body's reaction to changes that require a physical, mental, or emotional adjustment or response. Controlling stress is important to health, and stress that continues without relief can lead to a condition called distress, a negative stress reaction. Distress can disturb the body's internal balance or equilibrium, leading to physical symptoms such as headache, upset stomach, elevated blood pressure, chest pain, sexual dysfunction, and problems sleeping. Emotional problems such as anxiety and worry can also result from distress. Higher levels of distress are also associated with lower QOL.4546 In the present study, patients who developed MDD showed higher levels of distress during IFN-based treatment. The pretreatment level of distress, as measured by PWI, was associated with the subsequent depressive disorder at a trend level. Therefore, stress management may be helpful in preventing IFN-induced depressive disorder, as well as in improving psychological well-being in patients with hepatitis C receiving PEG-IFN-α-2a/RBV.
In the present study, we examined risk factors associated with the development of depressive disorder during IFN-based treatment. The identification of risk factors for depressive disorder may assist in detecting high-risk patients who may benefit from psychological support and in improving the QOL of patients receiving IFN-based treatment.47 We comprehensively evaluated various kinds of risk factors, including personality, pretreatment mood states, degree of stress, and HCV-related characteristics. Pretreatment BDI, BAI, and K-POMS scores were significant predictors of IFN-induced depressive disorder. Udina et al.17 reported that clinical factors, such as baseline subthreshold depressive symptoms, are associated with a higher incidence of major depressive episode during antiviral treatment, along with the presence of a past depressive or psychiatric disorder.17 Although subjects included in the present study had no previous or current psychiatric disorders, pretreatment subthreshold depression, anxiety, or somatic symptoms could increase the likelihood of developing depressive disorder during the course of PEG-IFN-α-2a-based treatment. We did not find significant associations between specific personality traits and the development of depressive disorder. However, previous studies reported that individuals with higher neuroticism, lower agreeableness, or lower self-directedness may be more likely to suffer depression.4849
According to our findings and those of previous studies, it is important to screen and monitor mood symptoms before and during IFN-based treatment to enhance psychological well-being as well as adherence to IFN-based treatment. The association between the development of depressive disorder and adherence to IFN-based treatment was also supported by the present study. Patients with depressive disorder showed higher rates of dropout due to the depressive disorder itself compared to other reasons for dropout. With respect to the influence of depression on the response to IFN-based treatment (i.e., SVR or relapse rate), we could not find any significant association between the development of depressive disorder and IFN responsiveness. However, once depressive disorder develops, it may adversely affect adherence to IFN-based treatment.
The strengths of our study are its prospective design, with monthly time points during IFN-based treatment, and our exploration of the relationship between psychiatric factors, including personality and degree of distress, and the development of depressive disorder during PEG-IFN-α-2a-based treatment. Nevertheless, this study was limited by a relatively small sample size, which may have affected our ability to detect depressive symptoms.
Despite the limitation, our results demonstrated that depressive disorder occurred in 22.4% of patients receiving PEG-IFN-α-2a during the early stage of antiviral treatment. All patients with HCV infection showed significant changes in fatigue, among other various depressive symptoms, during the course of IFN-based treatment. Those who developed MDD suffered higher levels of distress, indicating poor psychological well-being. Pretreatment BDI, BAI, and K-POMS scores were found to be useful predictors of IFN-induced depressive disorder. In light of our findings, we recommend that clinicians conduct a thoughtful psychological evaluation, addressing depression, anxiety, and somatic symptoms, as well as level of distress, before starting IFN-based treatment in patients with HCV infection. This may aid in improving psychological well-being and QOL, as well as compliance with IFN-based treatment.
Acknowledgments
We thank all the participants who gave us their time and support. This work was supported by a clinical research grant-in-aid from the Seoul Metropolitan Government Seoul National University (SMG-SNU) Boramae Medical Center (03-2011-3).
References
1. Global Burden Of Hepatitis C Working Group. Global burden of disease (GBD) for hepatitis C. J Clin Pharmacol 2004;44:20-29. PMID: 14681338.


2. Nelson DR. The role of triple therapy with protease inhibitors in hepatitis C virus genotype 1 naive patients. Liver Int 2011;31(Suppl 1):53-57. PMID: 21205138.


3. Schaefer M, Engelbrecht MA, Gut O, Fiebich BL, Bauer J, Schmidt F, et al. Interferon alpha (IFNalpha) and psychiatric syndromes: a review. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 2002;26:731-746. PMID: 12188106.


4. Dieperink E, Willenbring M, Ho SB. Neuropsychiatric symptoms associated with hepatitis C and interferon alpha: a review. Am J Psychiatry 2000;157:867-876. PMID: 10831463.


5. Hauser P, Khosla J, Aurora H, Laurin J, Kling MA, Hill J, et al. A prospective study of the incidence and open-label treatment of interferon-induced major depressive disorder in patients with hepatitis C. Mol Psychiatry 2002;7:942-947. PMID: 12399946.



6. Lotrich FE, Rabinovitz M, Gironda P, Pollock BG. Depression following pegylated interferon-alpha: characteristics and vulnerability. J Psychosom Res 2007;63:131-135. PMID: 17662748.



7. Rowan PJ, Tabasi S, Abdul-Latif M, Kunik ME, El-Serag HB. Psychosocial factors are the most common contraindications for antiviral therapy at initial evaluation in veterans with chronic hepatitis C. J Clin Gastroenterol 2004;38:530-534. PMID: 15220690.


8. Leutscher PD, Lagging M, Buhl MR, Pedersen C, Norkrans G, Langeland N, et al. Evaluation of depression as a risk factor for treatment failure in chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology 2010;52:430-435. PMID: 20683942.


9. Raison CL, Borisov AS, Broadwell SD, Capuron L, Woolwine BJ, Jacobson IM, et al. Depression during pegylated interferon-alpha plus ribavirin therapy: prevalence and prediction. J Clin Psychiatry 2005;66:41-48. PMID: 15669887.



10. Patterson AL, Morasco BJ, Fuller BE, Indest DW, Loftis JM, Hauser P. Screening for depression in patients with hepatitis C using the Beck Depression Inventory-II: do somatic symptoms compromise validity? Gen Hosp Psychiatry 2011;33:354-362. PMID: 21762832.



11. Loftis JM, Patterson AL, Wilhelm CJ, McNett H, Morasco BJ, Huckans M, et al. Vulnerability to somatic symptoms of depression during interferon-alpha therapy for hepatitis C: a 16-week prospective study. J Psychosom Res 2013;74:57-63. PMID: 23272989.


12. Horikawa N, Yamazaki T, Izumi N, Uchihara M. Incidence and clinical course of major depression in patients with chronic hepatitis type C undergoing interferon-alpha therapy: a prospective study. Gen Hosp Psychiatry 2003;25:34-38. PMID: 12583926.


13. Malaguarnera M, Laurino A, Di Fazio I, Pistone G, Castorina M, Guccione N, et al. Neuropsychiatric effects and type of IFN-alpha in chronic hepatitis C. J Interferon Cytokine Res 2001;21:273-278. PMID: 11429157.


14. Wichers MC, Koek GH, Robaeys G, Praamstra AJ, Maes M. Early increase in vegetative symptoms predicts IFN-alpha-induced cognitive-depressive changes. Psychol Med 2005;35:433-441. PMID: 15841878.


15. Baranyi A, Meinitzer A, Stepan A, Putz-Bankuti C, Breitenecker RJ, Stauber R, et al. A biopsychosocial model of interferon-alpha-induced depression in patients with chronic hepatitis C infection. Psychother Psychosom 2013;82:332-340. PMID: 23942342.


16. Schaefer M, Sarkar R, Knop V, Effenberger S, Friebe A, Heinze L, et al. Escitalopram for the prevention of peginterferon-alpha2a-associated depression in hepatitis C virus-infected patients without previous psychiatric disease: a randomized trial. Ann Intern Med 2012;157:94-103. PMID: 22801672.


17. Udina M, Castellví P, Moreno-España J, Navinés R, Valdés M, Forns X, et al. Interferon-induced depression in chronic hepatitis C: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Psychiatry 2012;73:1128-1138. PMID: 22967776.


18. Beck AT, Ward CH, Mendelson M, Mock J, Erbaugh J. An inventory for measuring depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry 1961;4:561-571. PMID: 13688369.


19. Hamilton M. A rating scale for depression. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 1960;23:56-62. PMID: 14399272.



20. Beck AT, Epstein N, Brown G, Steer RA. An inventory for measuring clinical anxiety: psychometric properties. J Consult Clin Psychol 1988;56:893-897. PMID: 3204199.



21. Kim EJ. Reliabilities and Validities of the POMS (Profile of Mood States, Korean Edition) for the Normal High School and College Students. M. Sc. Thesis. Chungbuk: The Chungbuk National University, Department of Medicine; 2001.
22. Steer RA, Beck AT, Brown G, Berchick RJ. Self-reported depressive symptoms that differentiate recurrent-episode major depression from dysthymic disorders. J Clin Psychol 1987;43:246-250. PMID: 3571504.


23. Kim JH. The reliability and validity test of psychosocial well-being index (PWI). J Korean Acad Nurs 1999;29:304-313.

24. Derose S. Demographic and Psychosocial Factors. In: Kane R, editor. Understanding Health Care Outcomes Research. Gaithersberg, MD: Aspen, 1997, p. 175-209.
25. Min BM, Lee KI, Jeong JC. NEO-PI-R. Seoul: PSI Consulting; 1997.
26. Kim DY, Yoo TY. The relationship between the Big Five personality factors and contextual performance in work organizations. Korean J Ind Organ Psychol 2002;15:1-14.
27. Costa PT, McCrae RR. Normal personality assessment in clinical practice: the NEO Personality Inventory. Psychol Assess 1992;4:5-13.

28. Papastylianou A. Relating on the internet, personality traits and depression: research and implications. Eur J Couns Psychol 2013;2:65-78.

29. Hwang JY, Shin YC, Lim SW, Park HY, Shin NY, Jang JH, et al. Multidimensional comparison of personality characteristics of the Big Five model, impulsiveness, and affect in pathological gambling and obsessive-compulsive disorder. J Gambl Stud 2012;28:351-362. PMID: 21938524.


30. Chung YO, Lee CW. A study of factor structures of the Barratt impulsiveness scale in Korean university students. Korean J Clin Psychol 1997;16:111-114.
31. Lee HS. Impulsivity Test. Seoul: Korea Guidance; 1992.
32. Barratt ES. Anxiety and impulsiveness related to psychomotor efficiency. Percept Mot Skills 1959;9:191-198.

33. Patton JH, Stanford MS, Barratt ES. Factor structure of the Barratt impulsiveness scale. J Clin Psychol 1995;51:768-774. PMID: 8778124.


34. Carver CS, White TL. Behavioral-inhibition, behavioral activation, and affective responses to impending reward and punishment - the bis bas scales. J Per Soc Psychol 1994;67:319-333.

35. Bedossa P, Poynard T. The METAVIR Cooperative Study Group. An algorithm for the grading of activity in chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology 1996;24:289-293. PMID: 8690394.


36. Joo SK, Kim JH, Oh S, Kim BG, Lee KL, Kim HY, et al. Prospective comparison of noninvasive fibrosis assessment to predict advanced fibrosis or cirrhosis in Asian patients with hepatitis C. J Clin Gastroenterol 2015;49:697-704. PMID: 25203365.


37. Laird NM, Ware JH. Random-effects models for longitudinal data. Biometrics 1982;38:963-974. PMID: 7168798.


38. Cnaan A, Laird NM, Slasor P. Using the general linear mixed model to analyse unbalanced repeated measures and longitudinal data. Stat Med 1997;16:2349-2380. PMID: 9351170.


39. Verbeke G, Molenberghs G. Linear Mixed Models for Longitudinal Data. New York: Springer Verlag; 2009.
40. Chapman J, Oser M, Hockemeyer J, Weitlauf J, Jones S, Cheung R. Changes in depressive symptoms and impact on treatment course among hepatitis C patients undergoing interferon-alpha and ribavirin therapy: a prospective evaluation. Am J Gastroenterol 2011;106:2123-2132. PMID: 21826113.


41. Bonaccorso S, Marino V, Biondi M, Grimaldi F, Ippoliti F, Maes M. Depression induced by treatment with interferon-alpha in patients affected by hepatitis C virus. J Affect Disord 2002;72:237-241. PMID: 12450640.


42. Shakoor A, Shafqat F, Mehmud T, Akram M, Riaz S, Iqbal Z, et al. Frequency of depression and somatic symptoms in patients on interferon alpha/ribavirin for chronic hepatitis C. J Ayub Med Coll Abbottabad 2010;22:6-9. PMID: 22455250.

43. Bernstein D, Kleinman L, Barker CM, Revicki DA, Green J. Relationship of health-related quality of life to treatment adherence and sustained response in chronic hepatitis C patients. Hepatology 2002;35:704-708. PMID: 11870387.


44. Karaivazoglou K, Iconomou G, Triantos C, Hyphantis T, Thomopoulos K, Lagadinou M, et al. Fatigue and depressive symptoms associated with chronic viral hepatitis patients. health-related quality of life (HRQOL). Ann Hepatol 2010;9:419-427. PMID: 21057161.


45. Faul LA, Jim HS, Williams C, Loftus L, Jacobsen PB. Relationship of stress management skill to psychological distress and quality of life in adults with cancer. Psychooncology 2010;19:102-109. PMID: 19253915.


46. Hartl K, Engel J, Herschbach P, Reinecker H, Sommer H, Friese K. Personality traits and psychosocial stress: quality of life over 2 years following breast cancer diagnosis and psychological impact factors. Psychooncology 2010;19:160-169. PMID: 19189279.


47. Neri S, Bertino G, Petralia A, Giancarlo C, Rizzotto A, Calvagno GS, et al. A multidisciplinary therapeutic approach for reducing the risk of psychiatric side effects in patients with chronic hepatitis C treated with pegylated interferon α and ribavirin. J Clin Gastroenterol 2010;44:e210-e217. PMID: 20838237.


48. Castellvi P, Navinés R, Gutierrez F, Jiménez D, Márquez C, Subirà S, et al. Pegylated interferon and ribavirin-induced depression in chronic hepatitis C: role of personality. J Clin Psychiatry 2009;70:817-828. PMID: 19573480.


49. Lotrich FE, Ferrell RE, Rabinovitz M, Pollock BG. Risk for depression during interferon-alpha treatment is affected by the serotonin transporter polymorphism. Biol Psychiatry 2009;65:344-348. PMID: 18801474.


Figure 1
Time course of depressive mood (A), anxiety (B), and level of distress (C) in all patients during interferon-based treatment. *p<0.05; horizontal bar represents standard error. BDI: Beck Depression Inventory, BAI: Beck Anxiety Inventory, PWI: Psychosocial Well-being Index.
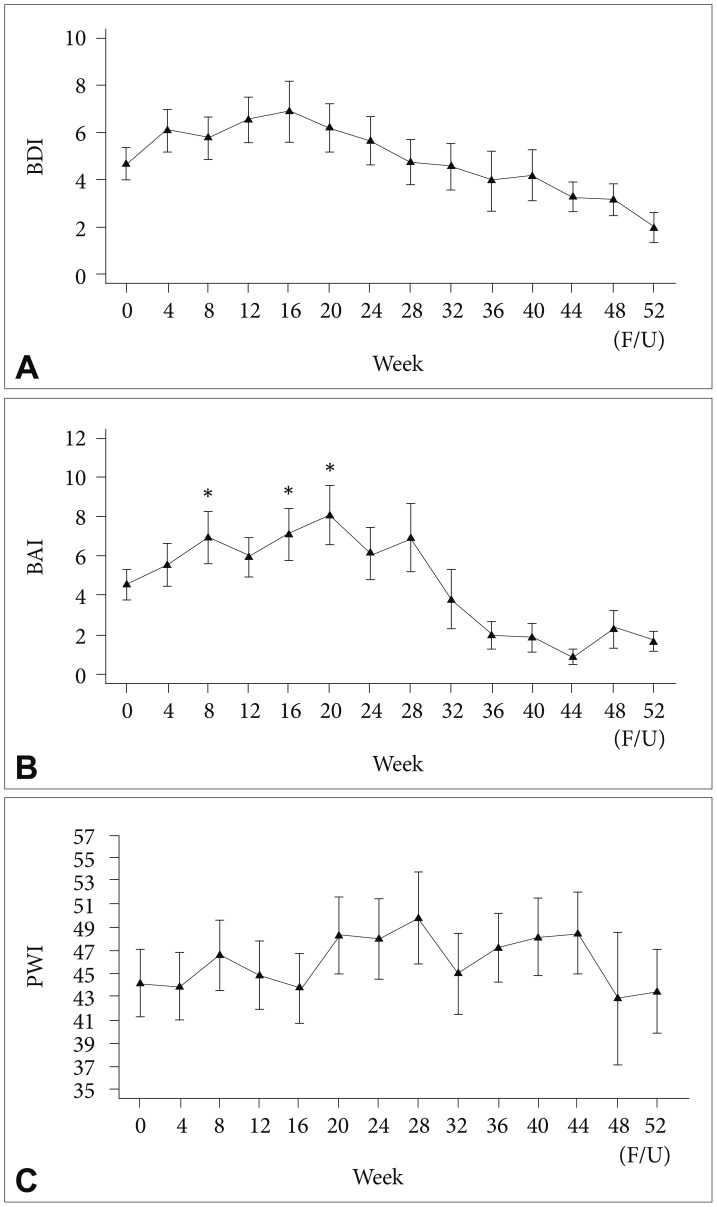
Figure 2
Time course of scores in Korean version of Profile of Mood States (K-POMS; A: tension-anxiety, B: depression-dejection, C: anger-hostility, D: vigor-activity, E: fatigue-inertia, F: confusion-bewilderment) in all patients during interferon-based treatment. *p<0.05; horizontal bar represents standard error.
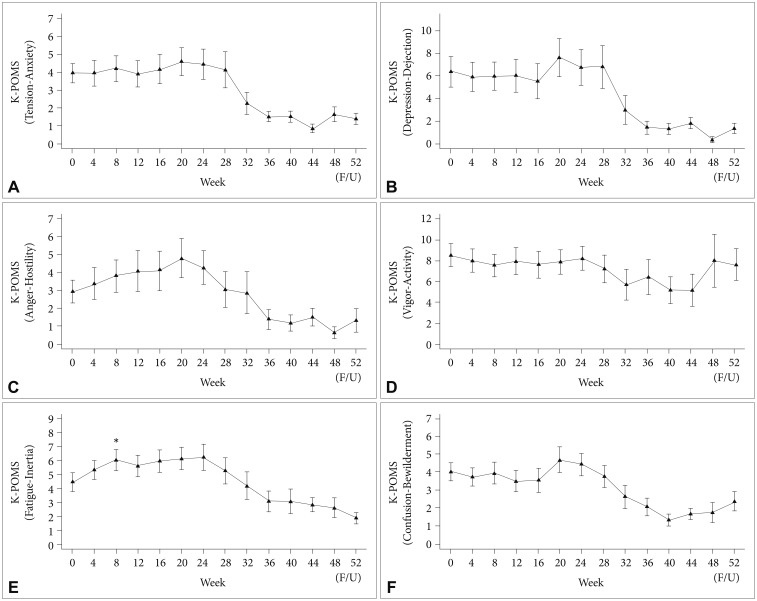
Figure 3
Time course of depressive mood (A), anxiety (B), and level of distress (C) in patients with major depressive disorder and those without depression during interferon-based treatment. As there was only one patient with depressive disorder and HCV genotype 1 who completed antiviral treatment for 48 weeks, this figure expressed data from baseline through 28 weeks. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001; horizontal bar represents standard error. BDI: Beck Depression Inventory, BAI: Beck Anxiety Inventory, PWI: Psychosocial Well-being Index, HCV: hepatitis C virus.

Figure 4
Time course of scores in Korean version of Profile of Mood States (K-POMS; A: tension-anxiety, B: depression-dejection, C: anger-hostility, D: vigor-activity, E: fatigue-inertia, F: confusion-bewilderment) in patients with major depressive disorder and those without depression during interferon-based treatment. As there was only one patient with depressive disorder and HCV genotype 1 who completed antiviral treatment for 48 weeks, this figure expressed data from baseline through 28 weeks. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001; horizontal bar represents standard error. HCV: hepatitis C virus.
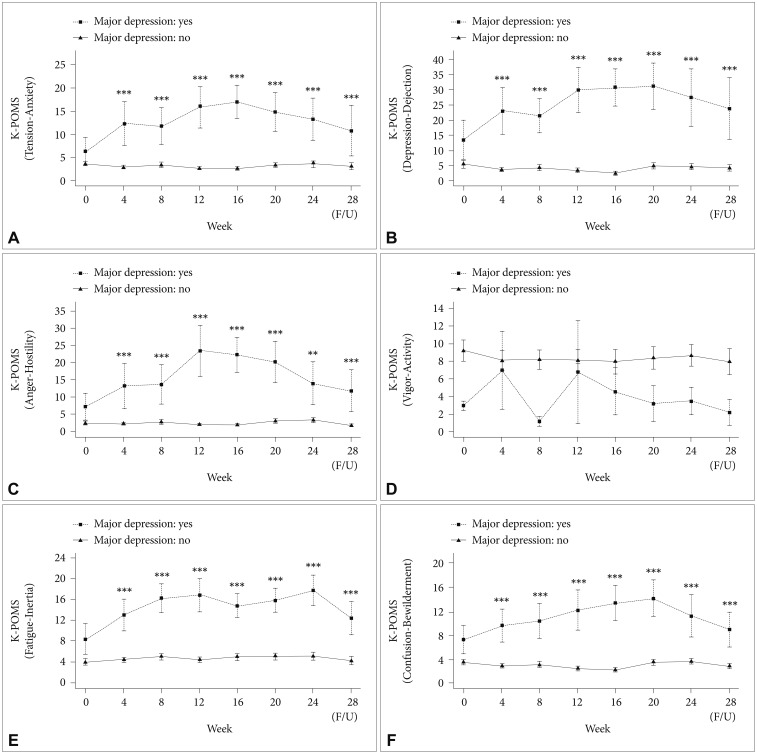
Table 1
Demographic and clinical characteristics of study subjects

*p<0.05, †histologic data of liver biopsy were available in 57 patients (85.1%). BMI: Body Mass Index, BDI: Beck Depression Inventory, BAI: Beck Anxiety Inventory, PWI: Psychosocial Well-being Index, K-POMS: Korean version of Profile Of Mood States, NEO-PI-R: Neuroticism-Extraversion-Openness Personality Inventory Revised, BIS: Behavioral Inhibition System, BAS: Behavioral Activation System, BIS-11: Barratt Impulsiveness Scale-version 11, METAVIR: META-analysis VIRus hepatitis histologic scoring system, IFN: Interferon, SVR: Sustained Virological Response






