|
 |
- Search
| Psychiatry Investig > Volume 10(4); 2013 > Article |
Abstract
Objective
Lexical fluency tests are frequently used to assess language and executive function in clinical practice. We investigated the influences of age, gender, and education on lexical verbal fluency in an educationally-diverse, elderly Korean population and provided its' normative information.
Methods
We administered the lexical verbal fluency test (LVFT) to 1676 community-dwelling, cognitively normal subjects aged 60 years or over.
Results
In a stepwise linear regression analysis, education (B=0.40, SE=0.02, standardized B=0.506) and age (B=-0.10, SE=0.01, standardized B=-0.15) had significant effects on LVFT scores (p<0.001), but gender did not (B=0.40, SE=0.02, standardized B=0.506, p>0.05). Education explained 28.5% of the total variance in LVFT scores, which was much larger than the variance explained by age (5.42%). Accordingly, we presented normative data of the LVFT stratified by age (60-69, 70-74, 75-79, and ≥80 years) and education (0-3, 4-6, 7-9, 10-12, and ≥13 years).
The term verbal fluency refers to a person's capacity for generating suitable words for a given category or subcategory in a limited amount of time. Verbal fluency tests (VFTs) are widely used as measures of language and executive functions in neuropsychological testing. VFTs are the most widely employed measures for assessing cognitive functioning following neurological damage and involve associative exploration and word retrieval. Researchers have observed that VFT performance declines in patients with frontotemporal lobar degeneration,1 Parkinson's disease,2 subcortical vascular dementia,3 and Alzheimer's disease.4 Reportedly, VFT was also useful for identifying individuals with early Alzheimer's disease5 or who were at risk of dementia, including age-associated memory impairment6 and mild cognitive impairment.4
There are two forms of VFT: the categorical verbal fluency test (CVFT), which requires the examinee to generate a list of words within a specific category (e.g., animals, fruits and vegetables, or shopping items), and the lexical verbal fluency test(LVFT), which requires the examinee to generate a list of words beginning with a specific alphabet letter. Despite some commonalities, CVFT and LVFT differ in the mental search strategies they examine; a CVFT assesses strategies that are guided by a category's semantic attributes, whereas an LVFT assesses strategies that are guided by grapheme cues.
Not only are they short, easy to administer, and sensitive to the early stages of dementia, but test performances also have potential in differentiating among various types of dementias. While cognitively intact people typically generate more words on category than letter based fluency tasks, the opposite or a much more equal production is often found in patients with Alzheimer's disease,7,8 reflecting the early loss in semantic memory in AD. In contrast, patients with vascular dementia typically show an equal reduction on the two types of fluency tests9 and patients with atypical Parkinson's diseases show a pattern where lexical fluency is more impaired than semantic fluency.7 Because of these differences in impairment patterns seen in different neurodegenerative disorders it has been suggested that the discrepancy between semantic and lexical production is a useful neuropsychological measure. Functional imaging studies have generally upheld this distinction between CVFTs and LVFTs; CVFT heavily relies on left temporal regions10 whereas the LVFT relies more on left frontal regions.11
Verbal fluency is influenced by demographic characteristics, such as age, gender, education, language, ethnicity, and so forth. CVFT performance declines with advancing age; elderly individuals performed worse than young individuals on CVFTs in many previous studies.12,13 However, age-related performance changes in LVFT are still controversial. Some studies have shown significant differences in LVFT performance across age groups,14-16 whereas others have failed to detect any age-related differences.17 Additionally, the influences of gender and education on LVFT performances were inconsistent.18,19
In the present study, we investigated the influence of age, gender, and education on the LVFT performance in a large, non-demented, non-depressed sample of elderly Koreans having wide age- and educational level-ranges. We provided normative data of the LVFT for Korean elders aged 60 years or older.
All participants were community-dwelling persons, aged 60 or over, who participated in the Korean Longitudinal Study on Health and Aging (KLOSHA),20 the Ansan Geriatric study (AGE),21 and the Gwangju Dementia and Mild Cognitive Impairment Study (GDEMCIS).22 The KLoSHA was designed as a population-based prospective cohort study on health, aging and common geriatric diseases of Korean elders aged 65 years and over. The baseline study of the KLoSHA was conducted from September 2005 through September 2006 in Seongnam. The AGE study was designed as a populationbased prospective cohort study on health, aging, and common geriatric diseases of elderly Koreans aged 60 to 84 years in Ansan. The GDEMCIS was designed as a large, prospective, community-based study designed to assess the occurrence and risk factors of dementia in recruited elderly subjects of over 60 years old who resided within a well-defined geographic region in Gwangju, South Korea. The study protocol of the KLOSHA was approved by the institutional review board (IRB) of the Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, that of the AGE by the IRB of the Ansan Hosptial of the Korea University School of Medicine, and that of the GDEMCIS by the IRB of the Severance Mental Health Hospital.
A geropsychiatrist with advanced training in neuropsychiatry and dementia research evaluated each participant, using the Korean version of the Consortium to Establish a Registry for Alzheimer's Disease Assessment packet (CERAD-K)23 for the KLOSHA and the AGE and the Seoul Neuropsychological Screening Battery-Dementia Version (SNSB-D)24 for the GDEMCIS. For each participant with cognitive impairment, we also interviewed one or more reliable informants regarding the participant's cognitive and functional changes and medical history. We determined global dementia severity using the Clinical Dementia Rating (CDR)25 and evaluated depressive symptoms using the Korean version of the Geriatric Depression Scale (GDS).26 A trained neuropsychologist administered the LVFT along with comprehensive neuropsychological assessments: the Korean version of the CERAD neuropsychological assessment battery26 in the KLOSHA and AGE and the Seoul Neuropsychological Screening Battery24 in the GDEMCIS.
To establish normative data, we enrolled participants who, according to DSM-IV diagnostic criteria,27 had neither dementia nor major psychiatric disorders. All participants had adequate vision and hearing, although many wore glasses and some required hearing aids. We included individuals with minor physical abnormalities (e.g., diabetes with no serious complications, essential hypertension, or mild hearing loss). None of our subjects presented any of the following exclusion criteria: a history of significant hearing or visual impairment rendering participation in the interview difficult; neurological disorders (e.g., stroke, Parkinson's disease or active epilepsy); psychiatric disorders (e.g., schizophrenia, mental retardation, severe depression or mania); psychotropic medications, or a history of use of psychoactive substances. Subjects with physical illnesses or disorders that could interfere with the clinical study such as severe cardiac disorders, severe respiratory illnesses, uncontrolled diabetes, uncontrolled hypertension, malignancy, and hepatic or renal disorders were also excluded.
The participant was asked to generate as many words beginning with a specific letter as possible within one minute, without using proper nouns, repeating previously-generated words, or using the same word with a different suffix. We used the Korean letter "ㄱ"(phonetic substitute for English "k") in this study and scored the LVFT by counting the number of acceptable words produced. Unacceptable responses occur when a participant repeats a previous response (i.e., a perseveration), includes a word starting with the wrong letter, or commits another violation of the rules stated in the manual.28
To assess the relative contributions of age, education, and gender to LVFT scores, we performed a multiple linear regression analysis with stepwise variable selection.
We also performed a series of ANOVA to determine any main effects or interactions on LVFT performance by age group (60-69, 70-74, 75-79, and ≥80 years), educational level group (0-3, 4-6, 7-9, 10-12, and ≥13 years), and gender. When an ANOVA showed any main effect of age or education was significant at the p<0.05 level, we conducted post-hoc contrasts using Scheffé's method. We stratified the LVFT norms by those demographic factors having main effects on LVFT performance. To maximize the data's quantity and clinical usefulness, we used overlapping strata for developing the normative data, following the procedures described by Pauker.29
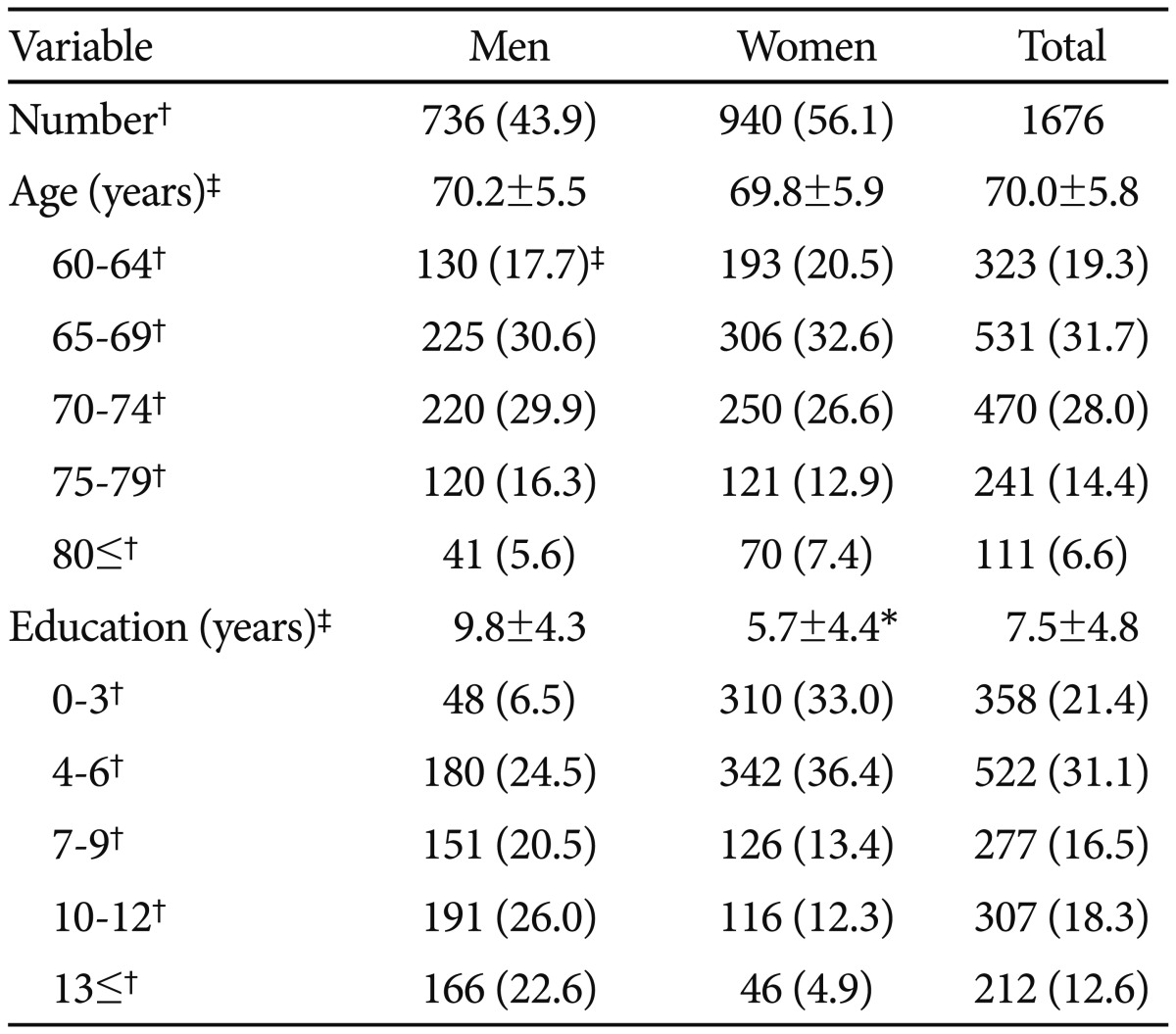
Table 1 summarizes the participants' characteristics. We enrolled 1676 normal elderly subjects (736 male and 940 female) who participated in the KLOSHA (n=638), the AGE (n=557) and the GDEMCIS (n=481). Mean age and education level were 70.0 (SD=5.8, range=60-90) years and 7.5 (SD=4.8, range=0-20) years, respectively. Men were more educated than women were (t=19.5, p<0.001). Age was comparable between men and women (t=1.33, p=0.184).
In the stepwise linear regression analysis, education (B=0.40, SE=0.02, standardized B=0.506) and age (B=-0.10, SE=0.01, standardized B=-0.15) had significant effects on LVFT score (p<0.001), but gender did not (B=0.40, SE=0.02, standardized B=0.506, p>0.05) (Table 2). Education explained 28.5% of the total variance in LVFT scores, which was much larger than the variance explained by age (5.42%).
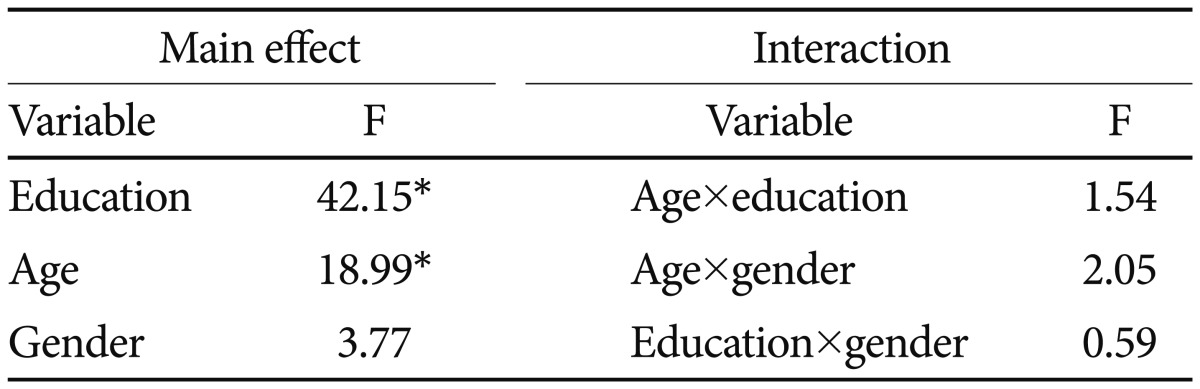
We carried out a three-way ANOVA to determine any main effects or interactions among age, gender, and education on LVFT performance (Table 3). We stratified the participants' ages into four groups (60-69, 70-74, 75-79, and 80 years or older), education into five groups (0-3, 4-6, 7-9, 10-12, and ≥13 years), and gender into two groups (men and women). The main effects of age [F (3, 196)=18.992, p<0.001] and educational level [F (4, 435)=42.150, p<0.001] were significant, but that of gender was not [F (1, 39)=3.771, p>0.05]. There were no interactions between these demographic variables. The mean LVFT scores were higher in the younger and more educated participants. Since the main effects of age and education were significant, we performed post hoc contrasts, using Scheffé's method, among same age and education groups. These post hoc contrasts revealed that younger groups showed significantly higher scores than older groups did and that more educated people performed better than the less educated did, demonstrating significant differences between each sequential pair of age groups and sequential pair of educational levels.
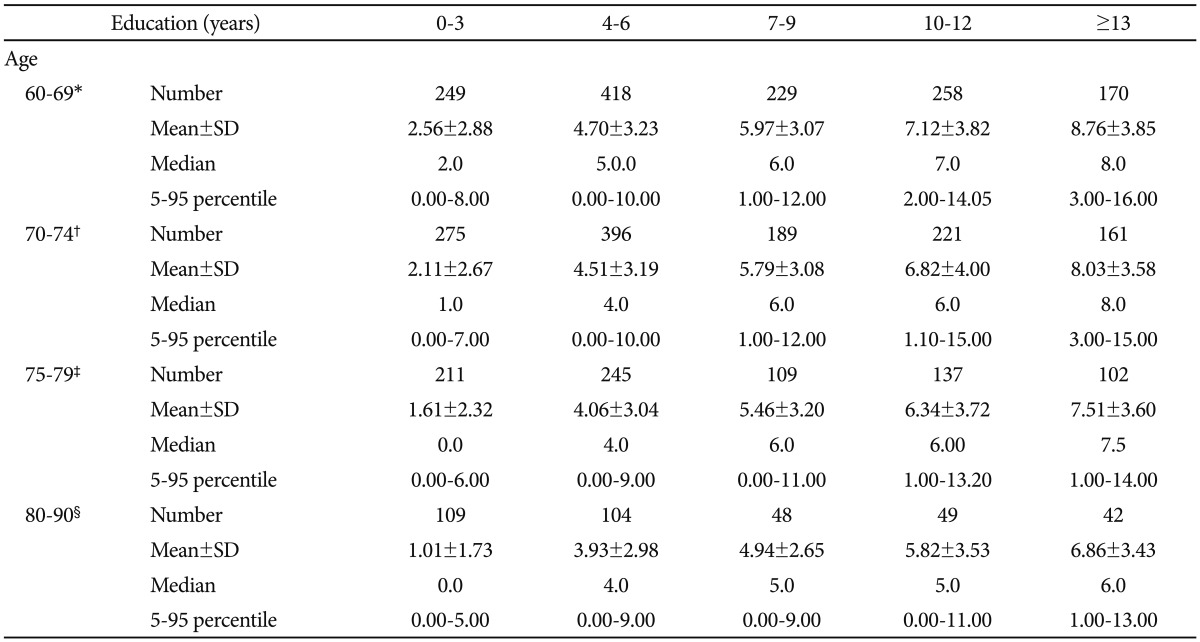
Based on our analysis of the demographic variables' effects, we decided to stratify the LVFT norm by age and education. We stratified the education into five groups (0-3, 4-6, 7-9, 10-12, and ≥13 years) according to the post hoc comparison results. We stratified age into four overlapping strata (60-74, 65-79, 70-84, and 75 years or older), to maximize the quantity of information and clinical usefulness of the data. The normative data from the age groups 60-74, 65-79, 70-84, and 75-90 years applied to persons whose ages ranged from 60-69, 70-74, 75-79, and 80 years or older. Table 4 presents the LVFT scores stratified by age and education in the form of mean, standard deviation, median, and the range from the 5th to the 95th percentile.
The present study examined the influence of age, gender, and education on LVFT performance and provided normative information from an educationally-diverse, elderly population, to allow clinicians and researchers to better interpret LVFT results.
In our population, we found age and education associated with LVFT performance but gender did not. These results are in line with previous reports that age and education have a much greater effect on fluency than does gender.16,30,31 LVFT performance decreased with advancing age in the present study, which is also consistent with previous observations.14,15,30 However, the influence of age on LVFT performance was much smaller than was that of education, indicating that education may have the most influence of any demographic factor on LVFT performance. In some previous studies, age was not associated with LVFT performance.17,32 Loonstra and Tarlow11 suggested that verbal intelligence might confound the association between age and LVFT performance if those studies included only participants with high verbal intelligence. Reportedly, level of educational attainment influences verbal intelligence.33
The gender effect on LVFT performance has been controversial. Two studies reported women have better lexical fluency. 13,19 However, a majority of other studies did not find this gender effect on lexical fluency.14-16,30,34,35 In the present study, the mean LVFT score was significantly higher in men than that in women. However, this gender difference disappeared when we adjusted for educational level, suggesting that this gender difference may be at least in part attributable to the differing educational levels between men and women. Researchers need to interpret gender-related LVFT performance differences in the previous studies13,36 with caution, since those studies did not adjust for education.
In establishing the LVFT normative data, we adopted the overlapping age stratification method to resolve the limited sample size of each cell.29 This procedure allowed us to present more stratified normative data tables, by providing adequate numbers of participants for most normative cells. Although we estimated the normative data in each age-overlapping table from a broader age range, overlapping with an adjacent one, we can apply these data to people within a narrow, non-overlapping age range. In addition, this procedure can provide a more stable means of stratification, resulting in less abrupt mean shifts between age strata than found in simple, non-overlapping age stratification. Our normative data included two strengths. First, because we strictly excluded cognitive disorders, including very mild dementia (CDR=0.5) and mood disorders, which are prevalent in elderly populations, through standardized diagnostic interviews by geropsychiatrists with expertise in dementia research, our data are likely not confounded by demented or depressive patients misclassified as normal elderly. Second, researchers in developing countries, where a substantial proportion of the elderly are still undereducated and thus the elderly population has a wide range of educational levels (from uneducated to post-graduate education), can reference our normative data.
Nevertheless, we must note some limitations. First, we employed only a single letter for evaluating lexical fluency. Although the neuropsychological test batteries for cognitive disorders have also widely adopted lexical fluency tests using a single letter,37-39 most previous studies on the association between demographic characteristics and lexical fluency have commonly used the Controlled Oral Word Association Test employing letter triads (FAS, CFL, PRW).40 Furthermore, LVFT performance reportedly varies according to the letter employed. 16,28,40 Second, the sample sizes for some normative data cells were relatively small, which may have increased standard errors and possibly reduced the stability of the estimated results. Third, in the low education cell (0-3 years), the scores for the median and fifth percentiles were zero, which might be due to the floor effect in those elderly with little education. The LVFT may not be applicable to this population, even when such persons are literate.
This study shows lexical fluency in the elderly was influenced by education and age but not by gender, and education was the most influential demographic factor. This study also provides age- and education-specific normative data of the LVFT for Korean elders.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a grant from the Korean Health Technology R&D Project, Ministry for Health, Welfare, & Family Affairs, Republic of Korea (Grant No. A092077).
References
1. Libon DJ, McMillan C, Gunawardena D, Powers C, Massimo L, Khan A, et al. Neurocognitive contributions to verbal fluency deficits in frontotemporal lobar degeneration. Neurology 2009;73:535-542. PMID: 19687454.



2. Bayles KA, Trosset MW, Tomoeda CK, Montgomery EB Jr, Wilson J. Generative naming in Parkinson disease patients. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol 1993;15:547-562. PMID: 8354708.


3. Cummings JL. Vascular subcortical dementias: clinical aspects. Dementia 1994;5:177-180. PMID: 8087175.


4. Lonie JA, Herrmann LL, Tierney KM, Donaghey C, O'Carroll R, Lee A, et al. Lexical and semantic fluency discrepancy scores in aMCI and early Alzheimer's disease. J Neuropsychol 2009;3:79-92. PMID: 19338718.


5. Eslinger PJ, Damasio AR, Benton AL, Van Allen M. Neuropsychologic detection of abnormal mental decline in older persons. JAMA 1985;253:670-674. PMID: 3968802.


6. Hänninen T, Hallikainen M, Koivisto K, Helkala EL, Reinikainen KJ, Soininen H, et al. A follow-up study of age-associated memory impairment: neuropsychological predictors of dementia. J Am Geriatr Soc 1995;43:1007-1015. PMID: 7657916.


7. Bak TH, Crawford LM, Hearn VC, Mathuranath PS, Hodges JR. Subcortical dementia revisited: similarities and differences in cognitive function between progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP), corticobasal degeneration (CBD) and multiple system atrophy (MSA). Neurocase 2005;11:268-273. PMID: 16093227.


8. Henry JD, Crawford JR, Phillips LH. Verbal fluency performance in dementia of the Alzheimer's type: a meta-analysis. Neuropsychologia 2004;42:1212-1222. PMID: 15178173.


9. Canning SJ, Leach L, Stuss D, Ngo L, Black SE. Diagnostic utility of abbreviated fluency measures in Alzheimer disease and vascular dementia. Neurology 2004;62:556-562. PMID: 14981170.


10. Pihlajamäki M, Tanila H, Hanninen T, Kononen M, Laakso M, Partanen K, et al. Verbal fluency activates the left medial temporal lobe: a functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Ann Neurol 2000;47:470-476. PMID: 10762158.


11. Audenaert K, Brans B, Van Laere K, Lahorte P, Versijpt J, van Heeringen K, et al. Verbal fluency as a prefrontal activation probe: a validation study using 99mTc-ECD brain SPET. Eur J Nucl Med 2000;27:1800-1808. PMID: 11189943.


12. Auriacombe S, Fabrigoule C, Lafont S, Jacqmin-Gadda H, Dartigues JF. Letter and category fluency in normal elderly participants: a populationbased study. Aging, Neuropsychol Cognition 2001;8:98-108.

13. Crossley M, D'Arcy C, Rawson NS. Letter and category fluency in community-dwelling Canadian seniors: a comparison of normal participants to those with dementia of the Alzheimer or vascular type. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol 1997;19:52-62. PMID: 9071641.


14. Mathuranath PS, George A, Cherian PJ, Alexander A, Sarma SG, Sarma PS. Effects of age, education and gender on verbal fluency. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol 2003;25:1057-1064. PMID: 14566579.


15. Gladsjo JA, Schuman CC, Evans JD, Peavy GM, Miller SW, Heaton RK. Norms for letter and category fluency: demographic corrections for age, education, and ethnicity. Assessment 1999;6:147-178. PMID: 10335019.


16. Tombaugh TN, Kozak J, Rees L. Normative data stratified by age and education for two measures of verbal fluency: FAS and animal naming. Arch Clin Neuropsychol 1999;14:167-177. PMID: 14590600.


17. Parkin AJ, Java RI. Deterioration of frontal lobe function in normal aging: influences of fluid intelligence versus perceptual speed. Neuropsychology 1999;13:539-545. PMID: 10527062.


18. Ardila A, Ostrosky-Solis F, Rosselli M, Gomez C. Age-related cognitive decline during normal aging: the complex effect of education. Arch Clin Neuropsychol 2000;15:495-513. PMID: 14590204.


19. Capitani E, Laiacona M, Basso A. Phonetically cued word-fluency, gender differences and aging: a reappraisal. Cortex 1998;34:779-783. PMID: 9872380.


20. Park JH, Lim S, Lim J, Kim K, Han M, Yoon IY, et al. An overview of the Korean longitudinal study on health and aging. Psychiatry Investig 2007;4:84-95.
21. Han C, Jo SA, Kim NH, Jo I, Park MH. Study design and methods of the Ansan Geriatric Study (AGE study). BMC Neurol 2009;9:10PMID: 19236723.



22. Lee KS, Cheong HK, Kim EA, Kim KR, Oh BH, Hong CH. Nutritional risk and cognitive impairment in the elderly. Arch Gerontol Geriatr 2009;48:95-99. PMID: 18160145.


23. Lee JH, Lee KU, Lee DY, Kim KW, Jhoo JH, Kim JH, et al. Development of the Korean version of the Consortium to Establish a Registry for Alzheimer's Disease Assessment Packet (CERAD-K): clinical and neuropsychological assessment batteries. J Gerontol B Psychol Sci Soc Sci 2002;57:P47-P53. PMID: 11773223.


24. Ahn HJ, Chin J, Park A, Lee BH, Suh MK, Seo SW, et al. Seoul Neuropsychological Screening Battery-dementia version (SNSB-D): a useful tool for assessing and monitoring cognitive impairments in dementia patients. J Korean Med Sci 2010;25:1071-1076. PMID: 20592901.



25. Hughes CP, Berg L, Danziger WL, Coben LA, Martin RL. A new clinical scale for the staging of dementia. Br J Psychiatry 1982;140:566-572. PMID: 7104545.


26. Kim JY, Park JH, Lee JJ, Huh Y, Lee SB, Han SK, et al. Standardization of the Korean version of the Geriatric Depression Scale: reliability, validity, and factor structure. Psychiatry Investig 2008;5:232-238.



27. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association Press; 1994.
28. Ruff RM, Light RH, Parker SB, Levin HS. Benton Controlled Oral Word Association Test: reliability and updated norms. Arch Clin Neuropsychol 1996;11:329-338. PMID: 14588937.


29. Pauker JD. Constructing overlapping cell tables to maximize the clinical usefulness of normative test data: rationale and an example from neuropsychology. J Clin Psychol 1988;44:930-933. PMID: 3216017.


30. Van der Elst W, Van Boxtel MP, Van Breukelen GJ, Jolles J. Normative data for the Animal, Profession and Letter M Naming verbal fluency tests for Dutch speaking participants and the effects of age, education, and sex. J Int Neuropsychol Soc 2006;12:80-89. PMID: 16433947.


31. Ivnik RJ, Malec JF, Smith GE, Tangalos EG, Petersen RC. Neuropsychological tests' norms above age 55: COWAT, BNT, MAE token, WRAT-R reading, AMNART, STROOP, TMT, and JLO. Clin Neuropsychologist 1996;10:262-278.

32. Kozora E, Cullum CM. Generative naming in normal aging: total output and qualitative changes using phonemic and semantic constraints. Clin Neuropsychologist 1995;9:313-320.

33. Dori GA, Chelune GJ. Education-stratified base-rate information on discrepancy scores within and between the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale--Third Edition and the Wechsler Memory Scale--Third Edition. Psychol Assess 2004;16:146-154. PMID: 15222811.


34. Kavé G. Phonemic fluency, semantic fluency, and difference scores: normative data for adult Hebrew speakers. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol 2005;27:690-699. PMID: 16019645.


35. Benito-Cuadrado MM, Esteba-Castillo S, Bohm P, Cejudo-Bolivar J, Pena-Casanova J. Semantic verbal fluency of animals: a normative and predictive study in a Spanish population. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol 2002;24:1117-1122. PMID: 12650236.


36. Kempler D, Teng EL, Dick M, Taussig IM, Davis DS. The effects of age, education, and ethnicity on verbal fluency. J Int Neuropsychol Soc 1998;4:531-538. PMID: 10050357.


37. Mathuranath PS, Nestor PJ, Berrios GE, Rakowicz W, Hodges JR. A brief cognitive test battery to differentiate Alzheimer's disease and frontotemporal dementia. Neurology 2000;55:1613-1620. PMID: 11113213.


38. Dubois B, Slachevsky A, Litvan I, Pillon B. The FAB: a Frontal Assessment Battery at bedside. Neurology 2000;55:1621-1626. PMID: 11113214.


Table 2
Stepwise multiple linear regression regarding age, education, and gender effects on lexical verbal fluency test scores

B: regression coefficient, SE (B): standard error of B, β: standardized regression coefficient, R2: spercent variance explained by each variable. Age and education were entered as continuous variables, and gender was coded as 0 and 1 for male and female, respectively.
*p<0.001, by stepwise multiple linear regression analyses