|
 |
- Search
| Psychiatry Investig > Volume 14(5); 2017 > Article |
Abstract
Objective
The autism susceptibility candidate 2 (AUTS2) gene has been implicated in multiple neurological disorders. Several recent studies have revealed that the polymorphism rs6943555 in the AUTS2 gene is broadly associated with human mental function and behavior. Therefore, in the present study we investigated whether the polymorphism rs6943555 is associated with human personality traits in Japanese university students. In addition, our previous study reported that the AUTS2 rs6943555-rs9886351 haplotype is associated with alcohol dependence. As a preliminary analysis, we also examined whether the AUTS2 haplotypes are related to personality traits.
Methods
After written informed consent had been obtained from the participants, two AUTS2 polymorphisms were analyzed, and personality was assessed using the Temperament and Character Inventory (TCI) in 190 university students. In addition, in order to exclude the influence of the results for students with mental health problems, we gave the Patient Health Questionnaire-9 (PHQ-9) to all subjects.
Results
In all the subjects, there was a main effect of the polymorphism rs6943555 genotype on reward dependence (p=0.038) and cooperativeness (p=0.031), although the significance was lost on Bonferroni correction. Similarly, on analysis that excluded the subjects with PHQ-9 scoresŌēź10, no significant association with any TCI dimension score among the rs6943555 genotypes was seen. There was no effect of the rs6943555-rs9886351 haplotypes on the TCI dimension scores.
Twin studies on heritability of personality traits demonstrated that personality traits measured by means of self-report questionnaires show moderate heritability.1 Genetic factors as well as environmental ones also contribute to the determination of human personality traits.2 According to Bouchard's report, approximately two-thirds of personality traits are estimated to be due to genetic influence.3 Some genes related to the characterization of personality traits are known to affect a wide range of human behavior including abnormal types, and polymorphisms of these same genes are associated with some disorders such as attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, alcohol and heroin dependence, autism, and schizophrenia.1 Therefore, these genes are thought to regulate aspects of impulsiveness and attention-process that are common to a normal personality as well as disturbances reflected in such diverse disorders.1
The autism susceptibility candidate 2 (AUTS2) gene has been implicated in multiple neurological disorders including autism,45 and others such as attention deficit hyperactivity disorder,6 schizophrenia,7 bipolar disorder.8 A very recent study revealed that AUTS2 is present not only in nuclei but also in the cytoplasm and neurites, especially at the growth cones, and that it is involved in the regulation of cortical neuronal migration and neuritogenesis in the developing brain.9 Therefore, these functional abnormalities caused by AUTS2 gene mutations in the brain development process, as a common base, might induce the pathogeneses of a variety of psychiatric disorders.9 Interestingly, several recent studies have shown that the polymorphism rs6943555 in the AUTS2 gene is associated with schizophrenia,10 heroin dependence,1112 suicide under the influenceof ethanol,13 and alcohol consumption.14 These findings suggest that AUTS2, especially the polymorphism rs6943555, might be involved in human mental function and behavior, and it is predicted to be one of the important factors affecting human personality traits.
The AUTS2 gene is located on chromosome 7q11.22 and consists of 19 exons, the first 6 exons being separated by very large introns and the last 13 exons being close.12 One of these common single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in the AUTS2 gene is rs6943555, which comprises a single nucleotide change of T to A in intron 4.12 Schumann et al.14 reported that the A allele of rs6943555 significantly increases AUTS2 gene expression in the prefrontal cortex of the human brain compared with the T allele. Meanwhile, Chen et al.11 found that subjects with the rs6943555 A/A genotype exhibit a significantly lower AUTS2 mRNA level in a lymphoblastoid cell lines (LCL) compared to subjects with the T/T and T/A genotypes.11 Although the expression of the AUTS2 gene might not be equal between brain tissue and LCL, the cause of this inconsistency is needed for further research.11 However, in any event, these studies suggest that the rs6943555 variants may influence transcriptional activity and expression of the AUTS2 gene.
Cloninger proposed that the three heritable dimensions of personality comprise novelty seeking, harm avoidance, and reward dependence.15 In subsequent research, the Temperament and Character Inventory (TCI), which is one of the self-report questionnaires, and has four temperament dimensions (novelty seeking, harm avoidance, reward dependence, and persistence) and three character dimensions (self-directedness, cooperativeness, and self-transcendence), was developed to assess the personality traits of individual.16 These dimensions are assumed to be as follows: the temperament traits are moderately heritable and stable throughout life, and the character traits are weakly heritable and moderately influenced by social learning.16
To our knowledge, a study on the relationship between AUTS2 gene polymorphisms and personality traits has not yet been reported. In the present study, we investigated whether the polymorphism rs6943555 in the AUTS2 gene is associated with human personality traits, as assessed by the TCI in Japanese university students. In addition, our recent study reported that the AUTS2 haplotype consisting of the polymorphisms rs6943555 and rs9886351 might affect the pathogenesis of alcohol dependence.17 Therefore, as a preliminary analysis, we also examined whether the AUTS2 haplotypes are related to personality traits.
The participants comprised 190 volunteers (male: 51; female: 139). In order to rule out confounding factors such as age and general intelligence level differences, all candidates for this research consisted of students in Azabu University, Japan. The mean age was 20.46┬▒1.15 (mean┬▒SD) years (male: 20.75┬▒1.45 years; female: 20.36┬▒1.00 years). The study was approved by the ethics committee of Azabu University, Japan (0648). After obtaining written informed consent, blood samples were obtained from all the subjects. In addition, we performed the Japanese versions of the TCI and Patient Health Questionnaire-9 (PHQ-9, 2013 NCNP version) for all subjects. The shortened version of the TCI is used to assess personality traits by means of a questionnaire comprising 125 items with four possible answers.18 The 4-point answer scale for each item comprises 1 (strongly disagree) to 4 (strongly agree). In addition, although the subjects in our study were ostensibly healthy students, it has been reported that depressive symptoms are accounted for the high frequency among the mental disorders found in university students.19 Therefore, in order to exclude the influence on the results of students with mental health problems, the PHQ-9 was also performed. The PHQ-9 is a self-report questionnaire based on the diagnosis of Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders-IV (DSM-IV) depressive disorders, and consists of nine questions related to the depression module of the Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ) that is used assess eight diagnoses (major depressive disorder, panic disorder, other anxiety disorder, bulimia nervosa, other depressive disorder, probable alcohol abuse/dependence, probable somatoform disorder, binge eating disorder).2021 Each of the nine questions of the PHQ-9 is scored from 0 (not at all) to 3 (nearly every day), therefore the PHQ-9 total score ranges from 0 to 27.22 The validity and reliability of the Japanese version of the TCI and PHQ-9 has already been confirmed in the Japanese population.1823
We performed extraction and purification of genomic DNA by the phenol/chloroform method. The polymorphisms AUTS2 rs6943555 and rs9886351 were genotyped by means of polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism (PCR-RFLP) according to the method of Zhang et al.10 In regard to the polymorphism rs9886351, the 188 subjects of genotyping has been completed. Genomic DNA was amplified with the following primers: rs6943555 (forward: 5'-TGG GTG TTG GAA GAG TTT TGA-3', reverse: 5'-ATA CAG TAT ACA TAA ACA TTG GAA AAG AGG GAA-3') and rs9886351 (forward: 5'-GGT GGA AAA TAA GCC AGT ATG C-3', reverse: 5'-TAG GAA AAT GGA TTA AAC GTA GGA G-3'). The PCR product (196 bp for rs6943555 and 221 bp for rs9886351) was digested with a restrictive enzyme, HinfI (New England Biolabs, Tokyo, Japan), and the digested products were subjected to electrophoresis on 5% polyacrylamide gels and visualized using the ethidium bromide staining method. Genotypes were determined according to fragment sizes: T/T=196 bp, T/A=196 bp+165 bp+34 bp, A/A=165 bp+34 bp, and rs9886351: A/A= 221 bp, A/G=221 bp+198 bp+26 bp, G/G= 198 bp+26 bp.
The Hardy-Weinberg disequilibrium was assessed using a chi-square test. First, in all the subjects, we compared the TCI dimension scores among the rs6943555 genotypes by performing statistical analysis using two-way analysis of variance with genotypes and gender as independent variable, and with the TCI dimension scores as dependent variable. Second, because a PHQ-9 score of 10 or higher is the threshold for major depression,212425 we excluded the subjects with this criterion from the analysis. Furthermore, as a preliminary analysis, we analyzedthe effect of the haplotypes consisting of the polymorphisms rs6943555 and rs9886351 on the TCI dimension scores in the subjects with PHQ-9 scores <10. Statistical analyses were performed using SPSS 12.0J for Windows. In addition, linkage disequilibrium (LD) coefficients (D' and r2) and haplotype effects were calculated with gPLINK 2.050 (http://zzz.bwh. harvard.edu/plink/index.shtml) and Haploview 4.2 (http:// www.broad.mit.edu/mpg/haploview/index.php).2627 In order to consider multiple issues, p-values were adjusted by means of Bonferroni correction. Statistical significance was defined as p<0.05.
The genotype frequencies of the polymorphisms AUTS2 rs6943555 and rs9886351 were as follows: rs6943555 (T/T type: 80, T/A type: 88, A/A type: 22) and rs9886351 (A/A type: 57, A/G type: 95, G/G type: 36). The rs6943555 and rs9886351 genotypes distribution was in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium (rs6943555: Žć2 (1)=0.0879, p=0.767; rs9886351: Žć2 (1)=0.103, p=0.748).
The TCI scores in all the subjects as to the rs6943555 genotype are shown in Table 1.
There was no main effect of the polymorphism rs6943555 genotype on the novelty seeking (NS), harm avoidance (HA), persistence (P), self-directedness (SD), and self-transcendence (ST) scores. On the other hand, there were significant association with reward dependence (RD) and cooperativeness (C) among the rs6943555 genotypes, although the significance was lost on Bonferroni correction (p>0.05). Interaction between the rs6943555 genotype and gender was not found for any TCI dimension score (NS: F=0.785, p=0.457; HA: F=1.495, p=0.227; RD: F=0.774, p=0.463; P: F=0.758, p=0.470; SD: F=0.159, p=0.853; C: F=1.001, p=0.369; ST: F=0.316, p=0.729).
The TCI scores in the subjects with PHQ-9 scores <10 as to the rs6943555 genotype are shown in Table 2.
In an analysis that excluded the subjects with PHQ-9 scores Ōēź10, no main effect of the polymorphism rs6943555 genotype on any TCI dimension score was seen. Similarly, interaction between the rs6943555 genotype and gender also was not found for any TCI dimension score (NS: F=0.369, p=0.692; HA: F=1.627, p=0.200; RD: F=0.532, p=0.588; P: F=1.006, p=0.368; SD: F=0.001, p=0.999; C: F=1.457, p=0.236; ST: F=1.173, p=0.312).
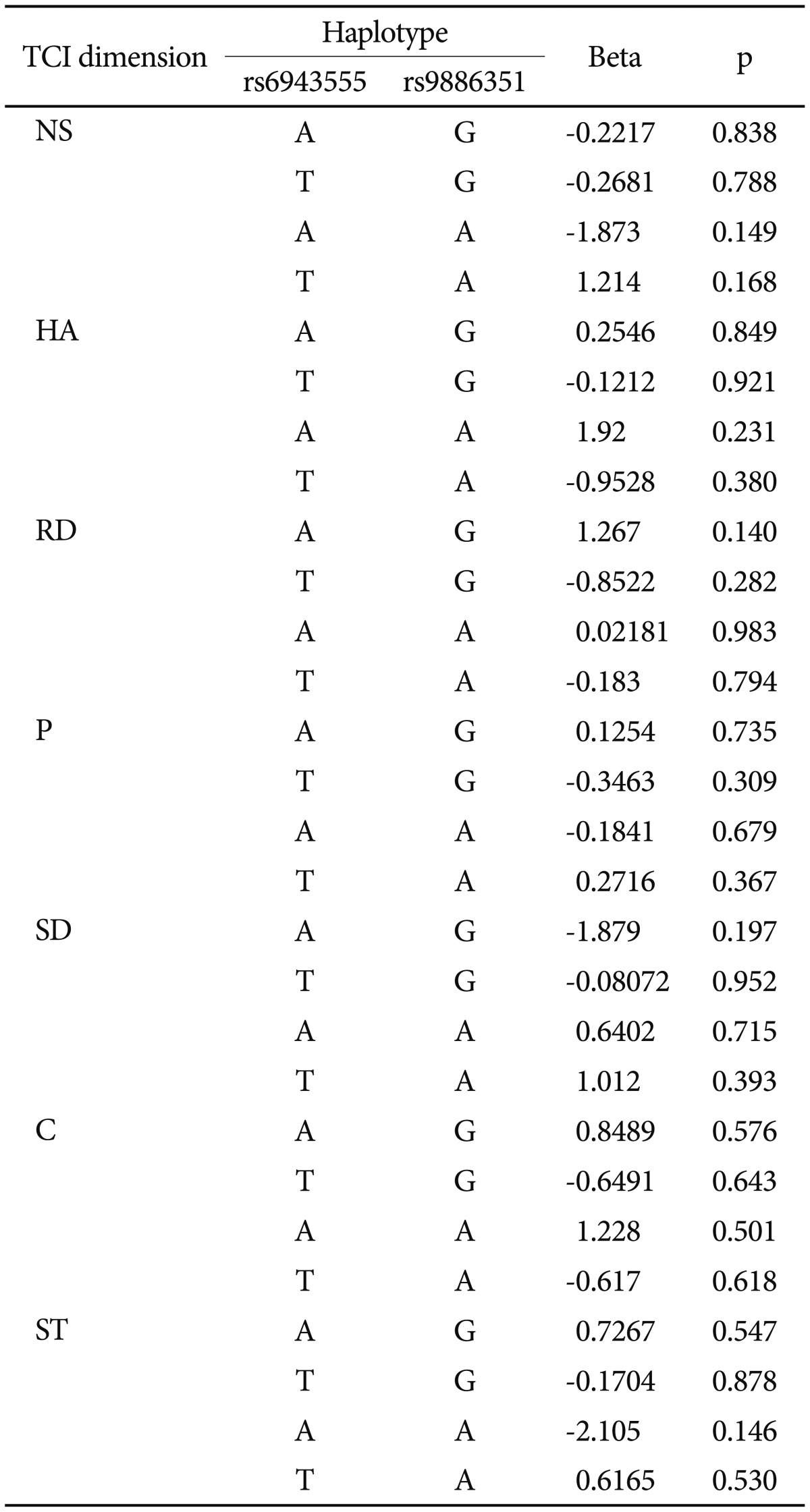
The effect of the AUTS2 haplotypes on the TCI scores in the subjects with PHQ-9 scores <10 are shown in Table 3.
There was no effect of the haplotypes consisting of the polymorphisms rs6943555 and rs9886351 on the TCI dimension scores.
In addition, the pairwise D' and r2 values for the polymorphisms AUTS2 rs6943555 and rs9886351 in our subjects were 0.250 and 0.042, respectively.
In this study, we investigated the association of the polymorphism rs6943555 in the AUTS2 gene and personality traits, as assessed by the TCI in Japanese university students.
Our results showed that there was no significant association between the polymorphism rs6943555 in the AUTS2 gene and personality traits measured by the TCI in all the subjects. Furthermore, even when subjects with more or less mental health problems (PHQ-9 scores Ōēź10) were excluded, no significant association was seen between them including the rs6943555-rs9886351 haplotypes. Incidentally, there was also no significant association between the polymorphism rs9886351 and personality traits (data not shown).
The AUTS2 gene has been implicated in multiple neurological disorders.28 Several recent studies have shown that the polymorphism rs6943555 in the AUTS2 gene is broadly associated with schizophrenia,10 heroin dependence,1112 suicide under the influence of ethanol,13 and alcohol consumption.14 Therefore, we expected that the single nucleotide exchange of T ŌåÆ A affect the individual differences of human personality traits, although no association was found between them in our study. Regarding other polymorphisms in the AUTS2 gene, a very recent genome-wide association study revealed that the intronic polymorphisms rs7785360 and rs12698828 are significantly associated with antidepressant responses to selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and mirtazapine (NaSSA: noradrenergic and specific serotonergic antidepressant).29 This finding indicates the possibility that the AUTS2 gene might be closely related to the activity of serotonergic and noradrenergic systems. Originally, Cloninger proposed that the three heritable dimensions of personality, i.e., novelty seeking, harm avoidance, and reward dependence, are linked to dopaminergic, serotonergic and noradrenergic neurons, respectively.1530 Therefore, the polymorphisms rs7785360 and rs12698828 might be more likely associated with personality traits, while it is not clear whether these polymorphisms affect AUTS2 gene expression. However, a previous study has suggested that important elements for regulation of gene expressionis contained within introns.31 In fact, since the polymorphism rs6943555 has been reported to affect gene expression,1114 such intronic polymorphisms in the AUTS2 gene might be important to elucidate the relationship with human personality traits. As further evidence of this, a recent study revealed that the intronic haplotypes in the AUTS2 gene including rs6943555 are related to heroin dependence.12 In addition, our previous study also reported that the haplotype consisting of the intronic polymorphisms rs6943555 and rs9886351 might affect the pathogenesis of alcohol dependence.17 Thus, although an effect of the rs6943555-rs9886351 haplotypes on the development of personality traits was not observed in this study, it would be interesting for further analysis to be focused on AUTS2 haplotypes in future research.
The genotype and allele frequencies of the polymorphism AUTS2 rs6943555 might differ among races.1117 Genotype and allele frequencies of this polymorphism in this study were not significantly different compared to that of our previous study (male: 23, female: 52, mean age: 35.36┬▒9.06) (genotype: Žć2 (2)=0.271, p=0.873; allele: Žć2 (1)=0.557, p=0.455).17 In addition, the A/A genotype (11.6%) and A allele frequencies (34.7%) in our subjects showed very little difference from those in Han Chinese subjects [Zhang et al.: male: 192, female: 243, mean age: 37.6┬▒10.8; Chen et al.: male: 390 (genotyping in 373 males), mean age: 42.8┬▒14.4; Dang et al.: male: 355, female: 61, mean age: 37.13┬▒5.23] (A/A genotype: 8.31-13.0%; A allele: 29.3-35.8%).10-12 On the other hand, in Polish Caucasian subjects (male: 1819, female: 2042, mean age: 45.72┬▒14.91) the A/A genotype accounts for only 4.7% and the A allele 21%.13 The genotype and allele frequencies of the polymorphism AUTS2 rs6943555 in Polish Caucasian subjects show significant differences from those in the Japanese population examined in this study [genotype: Žć2 (2)=39.4, p<0.01; allele: Žć2 (1)=40.1, p<0.01].13 However, because the number of subjects in this study was far fewer than that in Chojnicka's study of Polish Caucasians,13 such a difference in methodology will should be considered. Likewise, the age ranges of the subjects in Chojnicka's13 and our studies (20.46┬▒1.15) were also greatly different, although a significant difference in genotype [Žć2 (2)=48.4, p<0.01] and allele [Žć2 (1)=46.9, p<0.01] frequencies of the polymorphism rs6943555 between Chojnicka's and Chen's11 studies that have roughly the same age range was also observed. Therefore, if the different results to our study are confirmed in further studies, such differences in genotype and allele frequencies among races might be one of the reasons.
It must be considered that there are several limitations in this study. First, the sample size of all the subjects (n=190) in our study was small and consequently the statistical power was low. We have calculated whether the number of samples is appropriate in this study by using the G*Power version 3.1.9.2 (http://www.gpower.hhu.de/). The effect size in the two-way analysis of variance [3 (genotype)├Ś2 (gender)] was set to 0.25 (medium effect),32 and statistical power was 0.8.32 Consequently, when analyzing the main effect of the genotype on TCI dimension (╬▒=0.05), the required number of samples was calculated to be 158 subjects (approximately 27 subjects per group). However, the required number of samples per group could not be obtained (e.g., the number of males with the A/A genotype of the polymorphism rs6943555 was 10 subjects). Second, to study the relationship between the AUTS2 gene polymorphisms and personality traits, we used only the shortened version of TCI as a self-report questionnaire. In addition, to clarify the effects of these polymorphisms on personality traits, it is necessary to use various self-report personality questionnaires with different characteristics.33 However, the high validity and reliability of the Japanese version of the TCI-125 items with a 4-point answer scale has been confirmed in Japanese university students (mean age: 20.37).18 Third, in order to exclude the influence of the results for students with mental health problems, we performed the PHQ-9. Because the PHQ9 is a self-report questionnaire that evaluates only depressive disorders,34 there is a possibility that it could not exclude subjects with other mental health problems such as anxiety disorders. Meanwhile, it has been reported that the PHQ-9 exhibits higher sensitivity and specificity in comparison with other self-report questionnaires for depression screening.35 Therefore, by excluding subjects with depressive symptoms that are observed at high frequency in university students,19 the possibility that more reliable results can be obtained is suggested.
In conclusion, our study suggests that the polymorphism AUTS2 rs6943555 is not associated with personality traits, as assessed by the TCI, in Japanese university students. Additionally, there was no significant association between the rs6943555-rs9886351 haplotypes and personality traits. Further large-scale studies with more subjects using not only the TCI but also other self-report questionnaires are needed, and it would be valuable also to clarify the relationship between the other important AUTS2 polymorphisms (including haplotypes) and human personality traits.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by a research project grant awarded by the Azabu University.
References
1. Ebstein RP, Benjamin J, Belmaker RH. Personality and polymorphisms of genes involved in aminergic neurotransmission. Eur J Pharmacol 2000;410:205-214. PMID: 11134670.


2. Kusumi I, Masui T, Kakiuchi C, Suzuki K, Akimoto T, Hashimoto R, et al. Relationship between XBP1 genotype and personality traits assessed by TCI and NEO-FFI. Neurosci Lett 2005;391:7-10. PMID: 16154272.


4. Huang XL, Zou YS, Maher TA, Newton S, Milunsky JM. A de novo balanced translocation breakpoint truncating the autism susceptibility candidate 2 (AUTS2) gene in a patient with autism. Am J Med Genet A 2010;152A:2112-2114. PMID: 20635338.


5. Ben-David E, Granot-Hershkovitz E, Monderer-Rothkoff G, Lerer E, Levi S, Yaari M, et al. Identification of a functional rare variant in autism using genome-wide screen for monoallelic expression. Hum Mol Genet 2011;20:3632-3641. PMID: 21680558.



6. Elia J, Gai X, Xie HM, Perin JC, Geiger E, Glessner JT, et al. Rare structural variants found in attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder are preferentially associated with neurodevelopmental genes. Mol Psychiatry 2010;15:637-646. PMID: 19546859.


7. McCarthy SE, Gillis J, Kramer M, Lihm J, Yoon S, Berstein Y, et al. De novo mutations in schizophrenia implicate chromatin remodeling and support a genetic overlap with autism and intellectual disability. Mol Psychiatry 2014;19:652-658. PMID: 24776741.



8. Hattori E, Toyota T, Ishitsuka Y, Iwayama Y, Yamada K, Ujike H, et al. Preliminary genome-wide association study of bipolar disorder in the Japanese population. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 2009;150B:1110-1117. PMID: 19259986.


9. Hori K, Nagai T, Shan W, Sakamoto A, Taya S, Hashimoto R, et al. Cytoskeletal regulation by AUTS2 in neuronal migration and neuritogenesis. Cell Rep 2014;9:2166-2179. PMID: 25533347.


10. Zhang B, Xu YH, Wei SG, Zhang HB, Fu DK, Feng ZF, et al. Association study identifying a new susceptibility gene (AUTS2) for schizophrenia. Int J Mol Sci 2014;15:19406-19416. PMID: 25347278.



11. Chen YH, Liao DL, Lai CH, Chen CH. Genetic analysis of AUTS2 as a susceptibility gene of heroin dependence. Drug Alcohol Depend 2013;128:238-242. PMID: 22995765.


12. Dang W, Zhang Q, Zhu YS, Lu XY. The evidence for the contribution of the autism susceptibility candidate 2 (AUTS2) gene in heroin dependence susceptibility. J Mol Neurosci 2014;54:811-819. PMID: 25398668.


13. Chojnicka I, Gajos K, Strawa K, Broda G, Fudalej S, Fudalej M, et al. Possible association between suicide committed under influence of ethanol and a variant in the AUTS2 gene. PLoS One 2013;8:e57199. PMID: 23437340.



14. Schumann G, Coin LJ, Lourdusamy A, Charoen P, Berger KH, Stacey D, et al. Genome-wide association and genetic functional studies identify autism susceptibility candidate 2 gene (AUTS2) in the regulation of alcohol consumption. Proc Natl AcadSci U S A 2011;108:7119-7124.

15. Cloninger CR. A unified biosocial theory of personality and its role in the development of anxiety states. Psychiatr Dev 1986;4:167-226. PMID: 3809156.

16. Cloninger CR, Svrakic DM, Przybeck TR. A psychobiological model of temperament and character. Arch Gen Psychiatry 1993;50:975-990. PMID: 8250684.


17. Narita S, Nagahori K, Nishizawa D, Yoshihara E, Kawai A, Ikeda K, et al. Association between AUTS2 haplotypes and alcohol dependence in a Japanese population. Acta Neuropsychiatr 2016;28:214-220. PMID: 26763194.


18. Kijima N, Saito R, Takeuchi M, Yoshino A, Ono Y, Kato M, et al. CloningerŌĆÖs seven-factor model of temperament and character and Japanese version of Temperament and Character Inventory (TCI). Jpn J Psychiatr Diagn 1996;7:379-399.
19. OŌĆÖNeil MK, Mingie P. Life stress and depression in university students: clinical illustrations of recent research. J Am Coll Health 1988;36:235240

20. Spitzer RL, Kroenke K, Williams JB. Validation and utility of a self-report version of PRIME-MD: the PHQ primary care study. Primary Care Evaluation of Mental Disorders. Patient Health Questionnaire. JAMA 1999;282:1737-1744. PMID: 10568646.


21. Kroenke K, Spitzer RL, Williams JB. The PHQ-9: validity of a brief depression severity measure. J Gen Intern Med 2001;16:606-613. PMID: 11556941.



22. Kroenke K, Spitzer RL. The PHQ-9: a new depression diagnostic andseverity measure. Psychiatr Ann 2002;32:509-521.

23. Muramatsu K, Miyaoka H, Kamijima K, Muramatsu Y, Yoshida M, Otsubo T, et al. The patient health questionnaire, Japanese version: validity according to the mini-international neuropsychiatric interview-plus. Psychol Rep 2007;101:952-960. PMID: 18232454.



24. Arroll B, Goodyear-Smith F, Crengle S, Gunn J, Kerse N, Fishman T, et al. Validation of PHQ-2 and PHQ-9 to screen for major depression in the primary care population. Ann Fam Med 2010;8:348-353. PMID: 20644190.



25. Inagaki M, Ohtsuki T, Yonemoto N, Kawashima Y, Saitoh A, Oikawa Y, et al. Validity of the Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ)-9 and PHQ-2 in general internal medicine primary care at a Japanese rural hospital: a cross-sectional study. Gen Hosp Psychiatry 2013;35:592-597. PMID: 24029431.


26. Barrett JC, Fry B, Maller J, Daly MJ. Haploview: analysis and visualization of LD and haplotype maps. Bioinformatics 2005;21:263-265. PMID: 15297300.



27. Purcell S, Neale B, Todd-Brown K, Thomas L, Ferreira MA, Bender D, et al. PLINK: a tool set for whole-genome association and populationbased linkage analyses. Am J Hum Genet 2007;81:559-575. PMID: 17701901.



28. Oksenberg N, Ahituv N. The role of AUTS2 in neurodevelopment and human evolution. Trends Genet 2013;29:600-608. PMID: 24008202.


29. Myung W, Kim J, Lim SW, Shim S, Won HH, Kim S, et al. A genomewide association study of antidepressant response in Koreans. Transl Psychiatry 2015;5:e633. PMID: 26348319.



30. Cloninger CR. A systematic method for clinical description and classification of personality variants. A proposal. Arch Gen Psychiatry 1987;44:573-588. PMID: 3579504.


31. Mattick JS, Gagen MJ. The evolution of controlled multitasked gene networks: the role of introns and other noncoding RNAs in the development of complex organisms. Mol Biol Evol 2001;18:1611-1630. PMID: 11504843.



33. Tsai SJ, Wang YC, Hong CJ. Norepinephrine transporter and alpha (2c) adrenoceptor allelic variants and personality factors. Am J Med Genet 2002;114:649-651. PMID: 12210281.


34. Muramatsu K, Miyaoka H, Kamijima K, Muramatsu Y. The patient health questionnaire (PHQ)-9: a depression diagnostic and severity measure in primary care. Jpn J Psychiatr Treat 2008;23:1299-1306.
35. L├Čwe B, Spitzer RL, Gr├żfe K, Kroenke K, Quenter A, Zipfel S, et al. Comparative validity of three screening questionnaires for DSM-IV depressive disorders and physiciansŌĆÖ diagnoses. J Affect Disord 2004;78:131-140. PMID: 14706723.


Table┬Ā1
TCI dimension scores in all the subjects grouped as to the AUTS2 rs6943555 genotype

TCI dimension scores are showed as mean┬▒SD. *p<0.05, this significance was lost on Bonferroni correction (p>0.05). TCI: Temperament and Character Inventory, AUTS2: autism susceptibility candidate 2, NS: novelty seeking, HA: harm avoidance, RD: reward dependence, P: persistence, SD: self-directedness, C: cooperativeness, ST: self-transcendence
Table┬Ā2
TCI dimension scores in the subjects with PHQ-9 scores <10 grouped as to the AUTS2 rs6943555 genotype

TCI dimension scores are showed as mean┬▒SD. TCI: Temperament and Character Inventory, PHQ-9: Patient Health Questionnaire-9, AUTS2: autism susceptibility candidate 2, NS: novelty seeking, HA: harm avoidance, RD: reward dependence, P: persistence, SD: self-directedness, C: cooperativeness, ST: self-transcendence