 |
 |
- Search
| Psychiatry Investig > Volume 6(4); 2009 > Article |
Abstract
Objective
Recent neuroimaging studies have suggested that brain changes occur in subjects at ultra-high risk (UHR) for psychosis while experiencing prodromal symptoms, among which depression may increase the risk of developing a psychotic disorder. The goal of this study is to examine brain metabolite levels in the anterior cingulate cortex, the left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex and the left thalamus in subjects at UHR for psychosis and to compare brain metabolite levels between the UHR subjects with comorbid major depressive disorder and healthy controls.
Methods
Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy was used to examine brain metabolite levels. Twenty UHR subjects and 20 age- and intelligence quotient (IQ)-matched healthy controls were included in this study.
Recently, structural brain changes in subjects at ultra-high risk (UHR) for psychosis have been reported in several brain regions, including the hippocampus1,2 and anterior cingulate cortex (ACC).3 However, the inconsistency of previous findings suggests us that subtle structural changes might occur before the onset of psychosis, which are not enough to be detected through the structural magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Therefore, in vivo proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H-MRS) would greatly enhance our understanding of potential early brain changes in UHR subjects by assessing several brain chemicals such as N-acetylaspartate (NAA), creatine (Cr), choline (Cho), myo-inositol (Ins), glutamine and glutamate.
Few MRS studies have examined subjects at UHR for psychosis. Wood et al.4 reported a significant increase in NAA/Cr and Cho/Cr ratios in the dorsolateral prefrontal region of the UHR group. Decreased NAA/Cr and NAA/Cho ratios in the left frontal lobe and decreased NAA/Cr ratios in the ACC were also reported in UHR subjects.5 Recently, Aydin et al.6 reported decreased NAA levels and prolonged T2 relaxation time of tissue water in the genu of the corpus callosum in the UHR cases as well as in the first-episode patients of developing schizophrenia. In addition, there was a report that brain metabolite such as NAA was correlated with duration of prodromal symptoms in the first-episode patients of developing schizophrenia.13
On the other hand, depression is particularly common prodromal symptom in schizophrenia7 and may increase the risk of developing a psychotic disorder.8,9 In several MRS studies examining patients with major depressive disorder (MDD), brain metabolite abnormalities were reported in several brain regions.10,11 In addition, reduced activation of the dorsolateral prefrontal regions was observed in subjects at high genetic risk of schizophrenia with depressive symptoms.12 These findings suggest us that it is important to consider the influence of depression on brain metabolites status when examining neurochemical abnormalities in subjects at UHR for psychosis.
In this study, we primarily examined absolute value of brain metabolites in the ACC, the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC), and the left thalamus in subjects at UHR for psychosis. In addition, we examined differences in brain metabolites among UHR subjects with comorbid MDD, UHR subjects without MDD, and healthy subjects and investigated the correlation of brain metabolite levels with duration of prodromal symptoms. We used the absolute concentrations of metabolites in this study since relative concentrations using total Cr as an internal standard might result in false interpretation of data if Cr changed under certain conditions.14
The subjects enrolled in this study were part of a prospective, longitudinal project investigating individuals at high risk for psychosis at the Seoul Youth Clinic.
The UHR group consisted of 20 subjects. UHR was determined based on the Comprehensive Assessment of At-Risk Mental States (CAARMS) criteria.15 Individuals were considered as being at UHR if they met the criteria for UHR for psychosis and at least one of following: attenuated psychotic symptoms (APS), brief, limited intermittent psychotic symptoms (BLIPS), or trait plus state risk factors (T & S RF). Eighteen subjects met the intake criteria for APS and three met the T & S RF criteria. In addition, one subject met both the APS and T & S RF criteria. Eleven subjects in the UHR group (55%) were diagnosed with comorbid MDD, eight with anxiety disorder, and one with bipolar disorder, as determined via the Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-IV Axis I section (SCID).16 Nine subjects were receiving psychotropic drugs at baseline (low-dose atypical antipsychotics, n=8; antidepressant, n=1).
The healthy control group consisted of 20 subjects who were age- and intelligence quotient (IQ)-matched to the UHR group. All were healthy adults aged 16-30 years with no lifetime history of any psychiatric disorder or treatment, and no first- to third-degree relatives with psychiatric disorders. These subjects were recruited via an Internet advertisement or through the social networks of hospital staff.
Exclusion criteria of the present study included a known history of psychotic illness lasting longer than 1 week, substance abuse or dependence, neurological disease, or brain injury; evidence of medical illness that could manifest psychiatric symptoms; and intellectual disability (IQ<70). All subjects provided written informed consent, and parental consent was obtained for subjects younger than 18 years of age. This study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Institutional Review Board of Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
Procedures for clinical interview and assessment are described in our previous report.17 At intake, all potential subjects participated in an intensive clinical interview with two experienced psychiatrists who used the SCID16 to identify past and current psychiatric illnesses. The UHR subjects were assessed using the CAARMS to ensure that the intake criteria were met. In addition, psychotic features were evaluated using a modified 24-item version of the Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale (BPRS; rating items 1-7)18 and the Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS).19 The Hamilton Rating Scale for Depression (HAM-D),20 and the Hamilton Rating Scale for Anxiety (HAM-A)21 were also used to assess depressive and anxiety symptoms, respectively. The Korean version of the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale (K-WAIS) was administered to all subjects to obtain an estimated IQ.22
All MRI and MRS experiments were performed using a Siemens 1.5-T system (Avanto, Germany) with a standard head coil. Foam padding and a forehead-restraint strap were used to limit head movement during the scan. T1-weighted images in three orthogonal planes were used for positioning volumes of interest (VOIs). All subjects were advised of the importance of remaining motionless during the procedure.
For 1H-MRS volume location and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) correction of MRS quantification, an axial three-dimensional T1-weighted magnetization-prepared rapid acquisition gradient echo sequence was acquired (MPRAGE, 160 slices, TR/TE=1130/4.76 ms, inversion time=600 ms, matrix=256×208, FOV=173×230 mm2, flip angle=15°, number of slice=160, voxel size=0.90×0.90×0.90 mm3). Other T1 images were acquired for location information of the coronal and sagittal views (TR=1,020 ms, TE=4.7 ms, matrix=256×240, FOV=230×230 mm2, flip angle=15°).
Spectra consisting of 16 water-unsuppressed and 128 water-suppressed averages were acquired using a pointed resolved spin echo spectroscopy pulse sequence (TR=6,000 ms, TE=40 ms, scan time=13 min/spectrum), which was selected to increase the reliability of glutamate+glutamine (Glx) in 1.5-T.23 The raw data from each acquisition consisted of 2,048 points at a bandwidth of 2,500 Hz. The automatic shimming procedure built into the Siemens system was performed for each scan. The total examination time was approximately 60 min (Figure 1).
Three VOIs were obtained from the ACC, the left DLPFC, and the left thalamus (Figure 1). A 2×2×2 cm3 VOI in the ACC was aligned perpendicularly to the tip of the genu of the corpus callosum and centered at the interhemispheric fissure. The midpoint of the left dorsolateral prefrontal voxel (2×1.5×2 cm3) was positioned 7.5 mm anterior to the genu of the corpus callosum, and the VOI in the left thalamus was 1.5×2×2 cm3. Each VOI was carefully located on an axial slice to maximize the gray matter content for homogenous VOI selection by review of sagittal and coronal images.
Spectroscopic data (range, 4.2-1.0 ppm) were analyzed using LCModel (Ver 6.1-0), which has previously been used to identify low-concentration or overlapping metabolites.24 To ensure that high-quality spectra were obtained, we verified that the full-width half-maximum for NAA peak was less than 0.08 ppm; if not, we reacquired MRS data from the region. Absolute quantifications were obtained through repeated trials using a calibration phantom with 50 mM NAA in a 250-cm3 spherical flask.
The segmentation of the MRI data into gray matter, white matter, and CSF components was accomplished using in-house software employing a fuzzy C-means algorithm.25 We also corrected metabolite concentrations (C0) for partial volume effects due to CSF by determining the fractional content of the CSF in the VOI (FCSF) and applying the following correction: C=C0×[1/(1-FCSF)].
Demographic information was compared using chi-square analyses, t-tests, and one-way analyses of variance (ANOVAs). Metabolite parameters were compared between groups via analysis of covariance, with age as a covariate in each region. Pearson's correlation analysis was used to measure the association between duration of prodromal symptoms and brain metabolite levels. Post hoc comparison was done with Tukey's test. The level of significance was set at p<0.05. Statistical Package for Social Science (SPSS)(version 14.0; SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) was used for all analyses.
No significant differences were observed between the UHR and healthy control groups in terms of age, sex ratio, or IQ. Mean age was 21.80±3.11 years for the UHR group and 22.0±4.11 years for the healthy controls (t=0.695, p=0.491). The sex ratio (male/female) was 11/9 for the UHR group and 8/12 for healthy controls (χ2=0.902, p=0.342), and IQ scores were 110.25±14.39 for the UHR subjects and 112.05±9.74 for the healthy controls (t=0.463, p=0.646). Table 1 provides information on the demographic and clinical characteristics among UHR subjects with MDD, UHR subjects without MDD, and healthy controls. Compared to the UHR subjects without MDD, UHR subjects with MDD scored significantly higher on the PANSS total, BPRS, and HAM-D (Table 1).
No significant differences were observed in the absolute values of any metabolite in the ACC, left DLPFC, or left thalamus between the UHR group and healthy controls. However when we reanalyzed brain metabolite values according to MDD comorbidity among UHR subjects, a significant group effect was identified for Ins concentration in the left thalamus among UHR subjects with MDD, UHR subjects without MDD, and healthy controls (F=3.825, p=0.031). Tukey's post hoc test revealed a significant increase in Ins concentrations among UHR subjects with MDD relative to healthy controls (p=0.021; Figure 2) in the left thalamus. There were no significant differences in any other metabolite level in any brain region among UHR subjects with MDD, UHR subjects without MDD, or healthy controls (Table 2).
To control the effect of medications in the UHR group, we performed additional analysis in drug-naïve UHR subjects (n=11). This analysis revealed that Ins concentrations increased significantly in the left thalamus of drug-naïve UHR subjects compared to healthy controls (Ins: F=5.032, p=0.033). Upon further analysis, however, a significant comorbidity effect was observed for Ins concentrations in the left thalamus among drug-naïve UHR subjects with MDD, those without MDD, and healthy controls (Ins: F=3.656, p=0.039), although the sample size was small. Tukey's post hoc test revealed that drug-naïve UHR subjects with MDD (n=6) showed increased Ins levels in the left thalamus compared to healthy controls (Ins: 3.55±0.75 versus 2.58±0.71, p=0.019).
Using Pearson's correlation analysis, we found a significant positive correlation between Cho concentrations in the left thalamus and the duration of prodromal symptoms in the UHR group (r=0.495, p=0.027). In addition, we observed a trend toward positive correlation between thalamic Ins levels and the duration of prodromal symptoms in the UHR group (r=0.412, p=0.071). However, when the analysis was limited to UHR subjects with MDD, no significant correlation was observed between brain metabolite levels and clinical data.
In the present study, no differences in brain metabolite levels within the ACC, left DLPFC, or left thalamus were observed between UHR subjects and healthy controls. However, a significant increase in Ins levels was observed in the left thalamus in UHR subjects with comorbid MDD compared to healthy controls. To our knowledge, this is the first report demonstrating alterations in brain metabolite levels in UHR subjects with comorbid MDD using 1H-MRS.
The level of brain metabolites obtained by MRS provides us much valuable information with the function of the brain in vivo, which is one of major strengths that MRS studies have. Although there are more than 6 brain metabolites that can be assessed by MRS, we investigated 6 molecules including NAA, Cho, Cr, Ins, and Glx, which have been examined in previous MRS studies of subjects at UHR or high genetic risk of psychosis and patients with schizophrenia.5,13,26-28 NAA levels may represent sensitive means of monitoring neuronal cellular function.29,30 Cho levels can be used as an indicator of membrane turnover. Cr levels represent cellular energy metabolism. Ins is found primarily in glial cells and can be used as a marker of glial cell function.31 Increased Glx concentrations are reported to be related with excitotoxicitiy.27
Contrary to previous MRS studies, 1H-MRS did not reveal any significant alteration in brain metabolite levels in the UHR group. The results of two previous studies investigating brain metabolites in UHR subjects were inconsistent in this regard. For example, Jessen et al.5 reported that NAA/Cr ratios decreased in the frontal lobe, whereas Wood et al.4 reported increased NAA/Cr ratios in the frontal lobe. In addition, these studies did not account for between-group age differences, medications, or comorbidity. In this study, we addressed the potential confounding effects of medication by performing an additional analysis in drug-naïve UHR subjects (n=11), which revealed a significant increase in Ins concentrations in the left thalamus compared to healthy controls. However, these differences were influenced by the presence of comorbid MDD; only drug-naïve UHR subjects with MDD showed higher Ins than healthy controls.
Depression is one of the most frequent prodromal symptoms and the occurrence of depressive symptoms appears to have prognostic implications for the type and severity of symptoms in first-episode psychosis.7 Moreover, Yung et al.8 reported that severe depression was a predictor of psychosis. Of particular interest, we observed a significant increase in Ins concentrations in the left thalamus in UHR subjects with MDD compared to healthy controls. The thalamus is an important component of the limbic system that plays a role in the processing of emotion, and thalamic dysfunction is involved in the pathophysiology of MDD.32-35 Structurally, Young et al.33 reported that the number of neurons in the thalamus increased in patients with MDD compared to healthy controls. Functionally, thalamic metabolism36 and restingstate thalamic functional connectivity34 increased significantly in patients with MDD. To date, however, only few MRS studies have examined the role of the thalamus in MDD,37,38 instead, the majority of studies focused on the DLPFC, ACC or basal ganglia. In the present study, increased thalamic Ins concentrations suggest that the disruption of secondary messenger systems may occur in UHR subjects with MDD. Ins is an important constituent of the phosphatidylinositol (PI) secondary messenger system. Given that the human brain obtains most of its Ins supply from resynthesis through the PI cycle and that diverse receptors are coupled to the PI cycle,39 alterations in the Ins level may influence specific neuronal ganglia. In addition, dysfunction in the coupling metabolism of the receptor-secondary messenger system complex may provide an important biological substrate to UHR subjects experiencing prodromal depressive symptoms. Ins may also be a useful glial marker40 and stored in glial cells before its consumption in the PI cycle of neurons.41 Therefore, alterations in the Ins level may represent astroglial dysfunction that can be one of the possible biological mechanism of prodromal depressive symptoms in UHR subjects, although this hypothesis still need to be more investigated to be verified.
There were significant differences in PANSS total and BPRS scores between UHR subjects with MDD and those without MDD. To exclude the possible effect of PANSS total score difference on increased Ins concentrations in the UHR group with MDD, after stratifying the UHR group according to mean PANSS total score, no significant difference in Ins levels in the left thalamus was observed between UHR subjects with high PANSS total scores (PANSS score ≥56, n=11), UHR subjects with low scores, and healthy controls (F=1.847, p=0.172). Therefore, comorbid MDD may account for the observed increase in Ins concentrations in UHR subjects.
A trend toward a positive correlation between thalamic Ins levels and the duration of prodromal symptoms, and a significant positive correlation between Cho concentrations in the thalamus and the duration of prodromal symptoms were observed in the UHR group. As Cho is a primary constituent of cell membrane phospholipids, increased Cho levels can be interpreted as increased membrane turnover. Théberge et al.13 found a positive correlation between Cho levels in the left ACC and left thalamus and the duration of untreated psychosis, supporting the concept that Cho functions as a disease activity marker. Similarly, our results may indicate that disease-related processes, such as increased membrane turnover, may be occurring in UHR subjects, although we did not observe a significant difference in Cho concentrations between the UHR group and the healthy controls.
Our study has some important limitations. First, we were unable to include patients with schizophrenia. But although comparing brain metabolite values between UHR subjects and patients with schizophrenia was impossible, alterations in Ins levels according to comorbid MDD among UHR subjects would be convincing of elucidating the effect of depressive symptoms on brain of individuals at UHR for psychosis. Second, our sample size was small. Additional analysis to control the effect of comorbid MDD and medication might have possibilities to lower the statistical power. However, the other MRS studies about the UHR subjects and first episode schizophrenia also had a limitation with the number of subjects due to the rarity of the subject group.4,42 Therefore, a longitudinal follow-up investigation with a larger sample size is required in the future. In addition, comorbid anxiety disorder and bipolar disorder were not excluded in this study. Alteration of brain metabolites such as lactate, GABA, Ins is reported in subjects with anxiety disorder and bipolar disorder.40,43
In summary, our results demonstrate that increased thalamic Ins concentrations are associated with prodromal depressive symptoms in UHR subjects. More MRS studies in UHR subjects with longitudinal design will be needed to discover a biomarker of vulnerability to psychosis.
Acknowledgments
This paper was supported by a grant (M10644020003-08N4402-00310) from the Cognitive Neuroscience Program of the Korean Ministry of Science and Technology of the Republic of Korea.
References
1. Borgwardt SJ, Riecher-Rössler A, Dazzan P, Chitnis X, Aston J, Drewe M, et al. Regional gray matter volume abnormalities in the at risk mental state. Biol Psychiatry 2007;61:1148-1156. PMID: 17098213.


2. Velakoulis D, Wood SJ, Wong MT, McGorry PD, Yung A, Phillips L, et al. Hippocampal and amygdala volumes according to psychosis stage and diagnosis: a magnetic resonance imaging study of chronic schizophrenia, first-episode psychosis, and ultra-high-risk individuals. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2006;63:139-149. PMID: 16461856.


3. Yücel M, Wood SJ, Phillips LJ, Stuart GW, Smith DJ, Yung A, et al. Morphology of the anterior cingulate cortex in young men at ultra-high risk of developing a psychotic illness. Br J Psychiatry 2003;182:518-524. PMID: 12777343.


4. Wood SJ, Berger G, Velakoulis D, Phillips LJ, McGorry PD, Yung AR, et al. Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy in first episode psychosis and ultra high-risk individuals. Schizophr Bull 2003;29:831-843. PMID: 14989417.



5. Jessen F, Scherk H, Träber F, Theyson S, Berning J, Tepest R, et al. Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy in subjects at risk for schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 2006;87:81-88. PMID: 16842971.


6. Aydin K, Ucok A, Guler J. Altered metabolic integrity of corpus callosum among individuals at ultra high risk of schizophrenia and first-episode patients. Biol Psychiatry 2008;64:750-757. PMID: 18486106.


7. Häfner H, Löffler W, Maurer K, Hambrecht M, an der Heiden W. Depression, negative symptoms, social stagnation and social decline in the early course of schizophrenia. Acta Psychiatr Scand 1999;100:105-118. PMID: 10480196.


8. Yung AR, Phillips LJ, Yuen HP, McGorry PD. Risk factors for psychosis in an ultra high-risk group: psychopathology and clinical features. Schizophr Res 2004;67:131-142. PMID: 14984872.


9. Johnstone EC, Ebmeier KP, Miller P, Owens DG, Lawrie SM. Predicting schizophrenia: findings from the Edinburgh High-Risk Study. Br J Psychiatry 2005;186:18-25. PMID: 15630119.


10. Farchione TR, Moore GJ, Rosenberg DR. Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging in pediatric major depression. Biol Psychiatry 2002;52:86-92. PMID: 12113999.


11. Caetano SC, Fonseca M, Olvera RL, Nicoletti M, Hatch JP, Stanley JA, et al. Proton spectroscopy study of the left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in pediatric depressed patients. Neurosci Lett 2005;384:321-326. PMID: 15936878.


12. Whalley HC, Mowatt L, Stanfield AC, Hall J, Johnstone EC, Lawrie SM, et al. Hypofrontality in subjects at high genetic risk of schizophrenia with depressive symptoms. J Affect Disord 2008;109:99-106. PMID: 18164074.


13. Théberge J, Al-Semaan Y, Drost DJ, Malla AK, Neufeld RW, Bartha R, et al. Duration of untreated psychosis vs. N-acetylaspartate and choline in first episode schizophrenia: a 1H magnetic resonance spectroscopy study at 4.0 Tesla. Psychiatry Res 2004;131:107-114. PMID: 15313517.


14. Gruber S, Frey R, Mlynárik V, Stadlbauer A, Heiden A, Kasper S, et al. Quantification of metabolic differences in the frontal brain of depressive patients and controls obtained by 1H-MRS at 3 Tesla. Invest Radiol 2003;38:403-408. PMID: 12821853.


15. Yung AR, Yuen HP, McGorry PD, Phillips LJ, Kelly D, Dell'Olio M, et al. Mapping the onset of psychosis: the Comprehensive Assessment of At-Risk Mental States. Aust N Z J Psychiatry 2005;39:964-971. PMID: 16343296.


16. First MB, Spitzer RL, Gibbon M, Williams JBW. Structured clinical interview for DSM-IV axis I disorder. 1996,New York: New York State Psychiatric Institute.
17. Choi JS, Kang DH, Park JY, Jung WH, Choi CH, Chon MW, et al. Cavum septum pellucidum in subjects at ultra-high risk for psychosis: compared with first-degree relatives of patients with schizophrenia and healthy volunteers. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 2008;32:1326-1330. PMID: 18513845.



18. Lukoff D, Liberman RP, Nuechterlein KH. Symptom monitoring in the rehabilitation of schizophrenic patients. Schizophr Bull 1986;12:578-602. PMID: 3810065.



19. Kay SR, Fiszbein A, Opler LA. The positive and negative syndrome scale (PANSS) for schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 1987;13:261-276. PMID: 3616518.



20. Hamilton M. Development of a rating scale for primary depressive illness. Br J Soc Clin Psychol 1967;6:278-296. PMID: 6080235.


21. Hamilton M. The assessment of anxiety states by rating. Br J Med Psychol 1959;32:50-55. PMID: 13638508.


22. Yum TH, Park YS, Oh KJ, Lee YH. The manual of Korean-Wechsler adult intelligence scale. 1992,Seoul: Korean Guidance Press.
23. Jang DP, Lee JM, Lee E, Park S, Kim JJ, Namkoong K, et al. Interindividual reproducibility of glutamate quantification using 1.5-T proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Magn Reson Med 2005;53:708-712. PMID: 15723390.


24. Provencher SW. Estimation of metabolite concentrations from localized in vivo proton NMR spectra. Magn Reson Med 1993;30:672-679. PMID: 8139448.


25. Yoon U, Lee JM, Kim JJ, Lee SM, Kim IY, Kwon JS, et al. Modified magnetic resonance image based parcellation method for cerebral cortex using successive fuzzy clustering and boundary detection. Ann Biomed Eng 2003;31:441-447. PMID: 12723685.


26. Auer DP, Wilke M, Grabner A, Heidenreich JO, Bronisch T, Wetter TC. Reduced NAA in the thalamus and altered membrane and glial metabolism in schizophrenic patients detected by 1H-MRS and tissue segmentation. Schizophr Res 2001;52:87-99. PMID: 11595395.


27. Yoo SY, Yeon S, Choi CH, Kang DH, Lee JM, Shin NY, et al. Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy in subjects with high genetic risk of schizophrenia: investigation of anterior cingulate, dorsolateral prefrontal cortex and thalamus. Schizophr Res 2009;111:86-93. PMID: 19406622.


28. Tibbo P, Hanstock C, Valiakalayil A, Allen P. 3-T proton MRS investigation of glutamate and glutamine in adolescents at high genetic risk for schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 2004;161:1116-1118. PMID: 15169703.


29. Dager SR, Steen RG. Applications of magnetic resonance spectroscopy to the investigation of neuropsychiatric disorders. Neuropsychopharmacology 1992;6:249-266. PMID: 1632893.

30. Michaelis T, Merboldt KD, Bruhn H, Hänicke W, Frahm J. Absolute concentrations of metabolites in the adult human brain in vivo: quantification of localized proton MR spectra. Radiology 1993;187:219-227. PMID: 8451417.


31. Soares DP, Law M. Magnetic resonance spectroscopy of the brain: review of metabolites and clinical applications. Clin Radiol 2009;64:12-21. PMID: 19070693.


32. Neumeister A, Nugent AC, Waldeck T, Geraci M, Schwarz M, Bonne O, et al. Neural and behavioral responses to tryptophan depletion in unmedicated patients with remitted major depressive disorder and controls. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2004;61:765-773. PMID: 15289275.


33. Young KA, Holcomb LA, Yazdani U, Hicks PB, German DC. Elevated neuron number in the limbic thalamus in major depression. Am J Psychiatry 2004;161:1270-1277. PMID: 15229061.


34. Greicius MD, Flores BH, Menon V, Glover GH, Solvason HB, Kenna H, et al. Resting-state functional connectivity in major depression: abnormally increased contributions from subgenual cingulate cortex and thalamus. Biol Psychiatry 2007;62:429-437. PMID: 17210143.



35. Young KA, Bonkale WL, Holcomb LA, Hicks PB, German DC. Major depression, 5HTTLPR genotype, suicide and antidepressant influences on thalamic volume. Br J Psychiatry 2008;192:285-289. PMID: 18378990.


36. Drevets WC. Neuroimaging studies of mood disorders. Biol Psychiatry 2000;48:813-829. PMID: 11063977.


37. Smith EA, Russell A, Lorch E, Banerjee SP, Rose M, Ivey J, et al. Increased medial thalamic choline found in pediatric patients with obsessive-compulsive disorder versus major depression or healthy control subjects: a magnetic resonance spectroscopy study. Biol Psychiatry 2003;54:1399-1405. PMID: 14675804.


38. Vythilingam M, Charles HC, Tupler LA, Blitchington T, Kelly L, Krishnan KR. Focal and lateralized subcortical abnormalities in unipolar major depressive disorder: an automated multivoxel proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy study. Biol Psychiatry 2003;54:744-750. PMID: 14512215.


39. Kim H, McGrath BM, Silverstone PH. A review of the possible relevance of inositol and the phosphatidylinositol second messenger system (PI-cycle) to psychiatric disorders--focus on magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) studies. Hum Psychopharmacol 2005;20:309-326. PMID: 15880397.


40. Malhi GS, Valenzuela M, Wen W, Sachdev P. Magnetic resonance spectroscopy and its applications in psychiatry. Aust N Z J Psychiatry 2002;36:31-43. PMID: 11929436.


41. Frey R, Metzler D, Fischer P, Heiden A, Scharfetter J, Moser E, et al. Myo-inositol in depressive and healthy subjects determined by frontal 1H-magnetic resonance spectroscopy at 1.5 tesla. J Psychiatr Res 1998;32:411-420. PMID: 9844958.


42. Wood SJ, Berger GE, Wellard RM, Proffitt TM, McConchie M, Berk M, et al. Medial temporal lobe glutathione concentration in first episode psychosis: a 1H-MRS investigation. Neurobiol Dis 2009;33:354-357. PMID: 19118629.


43. Silverstone PH, McGrath BM, Kim H. Bipolar disorder and myo-inositol: a review of the magnetic resonance spectroscopy findings. Bipolar Disord 2005;7:1-10. PMID: 15654927.


FIGURE 1
Location of volumes of interest (VOIs) for magnetic resonance spectroscopy and their sample spectra. A: The anterior cingulate cortex. B: The left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex. C: The left thalamus.
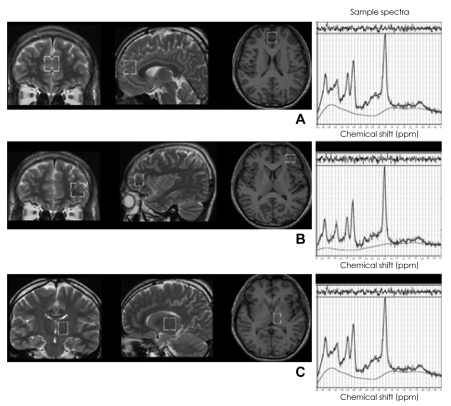
FIGURE 2
Absolute concentrations of myo-inositol in the left thalamus among the UHR group with MDD, those without MDD, and control group. *p=0.021. UHR: ultra-high risk, MDD: major depressive disorder.
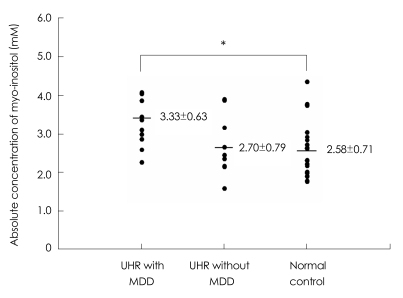
TABLE 1
Demographic and clinical characteristics in ultra-high risk subjects and healthy controls

Data are given as mean±SD. *p<0.05. UHR: ultra-high risk, MDD: major depressive disorder, IQ: intelligence quotient, PANSS: Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale, BPRS: Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale, HAM-D: Hamilton Depression Rating Scale, HAM-A: Hamilton Anxiety Rating Scale, CAARMS: Comprehensive A ssessment of At-Risk Mental States







