|
 |
- Search
| Psychiatry Investig > Volume 7(2); 2010 > Article |
Abstract
Objective
Oxidative stress may be an important pathogenic mechanism in the obesity and metabolic syndrome. The aims of this study was to assess the possible association between the oxidative stress related Glutathione S-Transferase genes (GST-M1, GST-T1, and GST-P1) variants and the olanzapine-induced weight gain in Korean schizophrenic patients.
Methods
We categorized 78 schizophrenic patients into two groups the more than 7% weight gain from baseline (weight gain Ōēź7%) and the less weight gain (weight gain <7%) groups according to weight change between before and after long-term olanzapine treatment (440┬▒288 days). All participants were genotyped for the GST-M1, GST-T1 and GST-P1 genes. Differences in allele frequencies between cohorts with different body weight changes were evaluated by a chi-square analysis and Fisher's exact test. The multifactor dimensionality reduction (MDR) approach was used to analyze gene-gene interactions.
Results
Mean body weight gain was 5.42 kg. There was no difference in the null genotype distribution of GST-M1 and -T1 between subjects with body weight gain Ōēź7% compared to subjects with body weight gain <7% (p>0.05). No significant difference in GST-P1 genotype and allele frequencies were observed between the groups (p>0.05). MDR analysis did not show a significant interaction between the three GST gene variants and susceptibility to weight gain (p>0.05).
Weight gain, as an adverse reaction induced by the use of atypical antipsychotics, is well recognized and has become a serious problem. Weight gain is a major reason for discontinuation or noncompliance with atypical antipsychotics. Obesity and weight gain in adulthood have been associated with significant health complications such as type II diabetes, coronary heart disease, stroke, gallbladder disease, osteoarthritis, obstructive sleep apnea syndrome, respiratory problems and some types of cancer.1 Substantial weight gain may also adversely affect self-esteem, social functioning and physical activity.2 Furthermore, medication-induced weight gain has been associated with a lower quality of life,3,4 and is a leading barrier to continued compliance with psychiatric medications.5,6 In particular, the dibenzodiazepine-derived drugs, clozapine and olanzapine appear to have the greatest weight gain liability. Olanzapine is associated with significant weight gain comparable to that produced by clozapine.7
The underlying mechanisms by which these medications cause weight gain remain unclear. However, there are some pharmacological clues, such as those proposed to involve the histamine, serotonin (5-HT) and adrenergic receptors.8 In addition to these neurotransmitters, it has been reported that antipsychotic-induced weight gain is associated with a state of heightened oxidative stress.9,10 For example, several studies showed the positive correlation between indices of obesity, such as body mass index (BMI) and waist/hip ratio and the markers of oxidative stress such as reduced erythrocyte glutathione.11,12 There also has been much interested in the role of free radicals and oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of metabolic syndrome.11,12 It was reported that the oxidative stress was related to administration of antipsychotics, which increases dopamine turnover, and leads to excess production of oxidative metabolites in an animal study.13 Increased production of oxidative metabolites leads to the formation of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Furthermore, ROS-induced mitochondrial dysfunction can lead to disruptions of lipid metabolism, increasing the intracellular lipid content.14
Glutathione-S-transferase (GSTs) are enzymes that have ROS detoxification properties.15 GSTs also belong to a superfamily of polymorphic enzymes that catalyze the conjugation reaction between reduced glutathione and a variety of xenobiotics including carcinogens, environmental contamination, anticancer agents, antibiotics, and products of the oxidative process.16,17 The imbalance between ROS and antioxidants is related to insulin resistance in mice and humans.14,18 It has been proposed that increased oxidative stress also underlies the pathophysiology of metabolic syndrome.19,20 Therefore, functional polymorphisms of GSTs could be considered to be candidate genetic markers for a risk factor of weight gain or metabolic syndrome related to antipsychotic use.
GSTs can be categorized into four main classes: A, M, P, and T. Individuals who are homozygous for the null GST-M1 or null GST-T1 allele lack the respective enzyme function.21,22 GST-P1 is an important GST isoform. Depending on the GST-P1 polymorphisms, Ile-to-Val changes in the amino acid sequence of the protein may alter the activity of the enzyme. Recently there was the finding that GST-P1 Val variant possesses five-fold more enzymatic activity to some metabolites in GST-P1 Ile/Val or Ile/Ile.23 Therefore, we hypothesized that the null alleles of GST-M1, -T1, and the Ile allele of GST-P1 may increase the formation of ROS and then, the disruptions of lipid metabolism, increasing the intracellular lipid content, leading to the risk of weight gain. We sought to characterize the genetic polymorphisms in the GST-M1, T1, and -P1 genes in schizophrenic patients with and without weight gain in a genetically homogenous Korean population. To date there has been no study of antipsychotic-induced weight gain associated with GST genes yet. We therefore performed the first study of antipsychotic-induced weight gain associated with GST gene variants. We also investigated whether gene-gene interactions among GST-M1, -T1, and -P1 gene polymorphisms could be correlated with olanzapine-induced weight gain in our sample.
A total of 103 schizophrenic patients were enrolled from the three collaborating hospitals of Korea University Hospital. All subjects were examined by trained psychiatrists using the Korean version of the Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-IV, leading to a diagnosis based on DSM-IV criteria.24 Exclusion criteria included evidence of other psychiatric, medical, or neurological illness; family history of diabetes or eating disorder; and age over 65 or under 18 years. Application of these criteria resulted in the exclusion of 25 patients. All the subjects were ethnic Koreans, and some findings from these subjects have been reported previously.25-27 Written informed consents were obtained, and the study protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Korea University Hospital.
Seventy-eight subjects were weighed prior to starting olanzapine and again after long-term treatment at least 3 months (440┬▒288 days). The dosage was adjusted individually according to clinical judgment. We controlled the use of drugs other than olanzapine. Medications such as antipsychotics, mood stabilizers, and antidepressants were avoided during the study, because of their potential effects on weight change. However, we combined the use of benzodiazepines or anticholinergics as needed. No subject had received olanzapine or clozapine prior to the present study. The mean daily dose of olanzapine at the end-point examination was 14.05 mg (standard deviation=5.1 mg).
Other clinical variables that were measured in the study were gender, age, olanzapine treatment duration and dosages, and previous antipsychotics dosages (expressed as chlorpromazine equivalents). Changes in body weight and BMI during the treatment were also calculated.
Genetic polymorphism analyses for the GSTM1 and GSTT1 genes were determined using the multiplex polymerase chain reaction (PCR) with modifications of the previously described method.29 The appropriate fragment of the GST gene for the GSTM1 and GSTT1 alleles was amplified with specific primers from human genomic deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). The following primers were used in the PCR reaction: GSTM1, (sense) 5'-GAACTCCCTGAAAAGCTAAAGC-3' and (antisense) 5'-GTTGG-GCTCAAATATACGGTGG-3'; GSTT1, (sense) 5'-TTCCTTACTGGTCCTCACATCTC-3' and (antisense) 5'-TCACGGGATCATGGCCAGCA-3'. PCR was performed in a total volume of 30 L containing 100 ┬Ąg genomic DNA, 5 M of each primer, 2.5 mM deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates, 1.5 mM MgCl2, 100 mM Tris-HCL, and 1 U thermostable Taq DNA polymerase with a GeneAmp PCR system 2700 (Applied Biosystems, Foster, CA, USA). The amplification conditions were initial denaturation at 94Ōäā for 5 min, followed by 35 cycles of denaturation at 94Ōäā for 45 sec, annealing at 59Ōäā for 50 sec, extension at 72Ōäā for 1 min, and a final extension step at 72Ōäā for 10 min. The PCR amplification products (GSTM1: 215 bp, GSTT1: 480 bp) were then separated electrophoretically on an ethidium bromide-stained 2% agarose gel.
A PCR-based assay was used to detect the GSTP1 polymorphism on exon 5.30 The primer sequences for GSTP1 exon 5 were (sense) 5'-GAGGAAACTGAGACCCACTGAG-3' and (antisense) 5'-AGCCCCTTTCTTTGTTCAGCC-3'. A typical PCR reaction was performed in a 25 ┬ĄL volume containing 1├ŚPCR buffer, 3.0 mM MgCl2, 0.25 mM dNTPs, 1.5 units of Taq polymerase, and 0.3 mM of primers GSTP1 exon 5. The DNA chains were denatured by incubation at 94Ōäā for 5 min, followed by 35 cycles of 94Ōäā for 30 sec, then 60Ōäā for 30 sec, and 72 Ōäā for 30 sec, followed by a final extension step at 72Ōäā for 5 min. A 424-bp DNA fragment was amplified for exon 5 and followed by 3 h of digestion with 4 units of BsmAI for exon 5 (New England Biolabs, Beverly, MA, USA). The fragments were separated on a 3% agarose gel stained with ethidium bromide. The Ile/Ile, Ile/Val and Val/Val genotypes yielded two bands (292 and 132 bp), four bands (292, 222, 132 and 70 bp), and three bands (222, 132 and 70 bp), respectively.
Differences in allele frequencies between groups with different body weight changes were evaluated by a chi-square analysis and Fisher's exact test. The association of genotype with weight gain and change in BMI was tested with Student's t-test. All of the analyses were performed using standard software (Statistical Package for the Social Sciences for Windows), and p values smaller than 0.05 were considered statistically significant. The multifactor dimensionality reduction (MDR) approach was designed to detect gene-gene interactions in the presence or absence of main effects in case-control studies in human genetics.31,32 MDR has been shown to have high power for detecting interactions in a wide range of simulated data.33-35 MDR has also been used to identify interactions in common complex diseases.36-39 MDR is a non-parametric, model-free approach, making it a unique tool for identifying interactions. MDR categorizes all genetic data into 2 groups, "high risk" and "low risk", by comparing all single loci and all multilocus combinations and then categorizing each genotype as either "high risk" or "low risk" on the basis of the ratio of cases to controls having that genotype. MDR ultimately selects one genetic model, either single or multilocus, that predicts phenotype with the greatest success. To evaluate the predictive ability of the model, prediction error was calculated using 10-fold cross-validation. The result is a set of models, one for each model size considered. From these models, a final model is chosen on the basis of minimization of prediction error and maximization of cross-validation consistency (CVC) (number of times a particular set of factors is identified across the cross-validation subsets). Statistical significance is determined empirically by permuting the case and control labels 1,000 times. The use of permutations to generate p values eliminates the problem of multiple testing. The MDR analysis was carried out using version 1.1.0 of the MDR software package (http://www.epistasis.org).
There were no differences in age (45.24┬▒11.24 years vs. 47.41┬▒11.43 years, t=0.83, p=0.41), sex (male/female, 25/12 vs. 27/14, Žć2=0.26, p=0.87), initial body weight (67.07┬▒12.64 kg vs. 62.65┬▒11.82 kg, t=1.60, p=0.12), initial BMI (24.12┬▒3.82 kg/m2 vs. 22.97┬▒3.56 kg/m2, t=1.37, p=0.17), or olanzapine dosage (14.55┬▒5.46 mg vs. 13.68┬▒4.57 mg, t=0.76, p=0.49) between subjects with body weight gains of Ōēź7% and <7%.
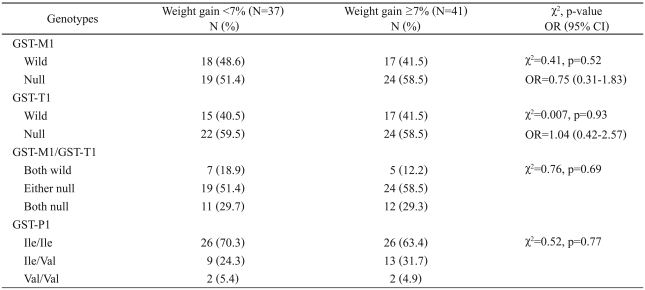
The distributions of the three GST genotypes in our sample are shown in Table 1. All groups were in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium with non-significant Žć2 values comparing the observed and expected genotype frequencies of each of the tested polymorphisms. There was no difference in the null genotype distribution of GST-M1 and -T1 in subjects with body weight gain Ōēź7% compared to subjects with body weight gain <7% (p>0.05)(Table 1). To investigate whether the profile of GST-M1/T1 genotypes might be associated with the risk of olanzapine-induced weight gain, we examined both genotypes in combination. There was no difference in the distribution of the null genotypes of both GST-M1 and GST-T1 between subjects with body weight gain Ōēź7% and subjects with body weight gain <7%.
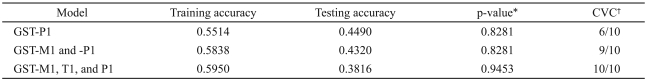
The observed frequencies of the GST-P1 Ile/Ile, Ile/Val, and Val/Val genotypes were 70.3, 24.3 and 5.4%, respectively, in 37 subjects with body weight gain <7%. In 41 subjects with body weight gain Ōēź7%, the corresponding frequencies of the GST-P1 genotypes were 63.4, 31.7 and 4.9%, respectively. No significant difference in genotype frequency was observed between the groups (Table 1). Table 2 shows the results of CVC, training accuracy and testing accuracy obtained from MDR analysis of the data. None of the models selected by MDR were statistically significant.
The mean gains in weight and BMI after long-term olanzapine treatment in our 78 Korean schizophrenic patients were 5.42 kg and BMI 1.99 kg/m2, respectively. However, we found no evidence of an association between the GST polymorphism and olanzapine-induced weight gain in Korean schizophrenic patients. All our subjects were inpatients and had taken olanzapine for at least 3 months. Although most of our subjects were chronic schizophrenic patients, they had never taken olanzapine or clozapine before participating our study.
Excessive levels of ROS play causative roles in the development of insulin resistance and diabetes.40,41 Recently, there has been much interest in the role of free radicals and oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of metabolic syndrome.11,12 Sagara42 found that some of the side effects of antipsychotic drug are related to oxidative stress and to the level of ROS that is controlled by antioxidant such as glutathione. Kuzuya et al.19 reported that there was the association between glutathione peroxidase 1 (GPX1) 198Leu variants and central obesity in men. They also reported that CT/TT genotypes were associated with the higher prevalence of metabolic syndrome in men. Therefore, they speculated that these association suggested that a weaker antioxidant defense system or greater oxidative stress might be a causative factor for obesity. In addition to GPX1, it was reported that defective glutathione peroxidase 3 (GPX3) expression in adipose tissue is associated with reduced systemic GPX activity and increased oxidative stress in obesity.20 Lee et al.20 proposed that local ROS accumulation in the adipose tissue of obesity could be expanded into systemic oxidative stress by the vicious cycle wherein increasing local ROS accumulation suppresses adipose GPX3 expression. Although there was no previous study reporting the association between the GSTs and weight gain and we also found no evidence of the association between the GST polymorphism of glutathione and olanzapine-induced weight gain, it is possible that glutathione and its related enzymes are associated with obesity and metabolic complication such as metabolic syndrome.
This study had several limitations. First, its long-term nature made complete control over the use of drugs impossible. Therefore, we could not exclude the effects of different dosages and combining medications (e.g., benzodiazepine and benztropine), although the drugs used (regarding olanzapine dosage) did not differ significantly among genotype groups. Furthermore, most patients had received other antipsychotics before olanzapine treatment, and hence we could not exclude the effects of prior medication. Second, the duration of medication was not the same for all subjects in our sample. However, we do not believe that this would have a significant effect, since the duration of olanzapine treatment did not differ between the genotype groups and we checked the final body weight at least 3 months later in all patients. Previous studies have found that weight was mainly gained during the first 6-8 weeks of olanzapine therapy.43 It is also reported that there was the association between the -759C/T polymorphism of the 5-HT2C receptor gene with early phase (after 4 weeks of treatment) weight gain induced by antipsychotic treatment in Korean schizophrenia patients.44 Third, the long-term nature of this study prevented us from assessing or controlling caloric intake (e.g., caloric count and meal refusals. Fourth, the relatively small sample limits the generalizability of our findings.
Future studies should employ larger samples and control the use of medication. In addition, the possible involvement of as-yet-uncovered gene(s) that influence susceptibility to olanzapine-induced weight gain should be evaluated, as well as the possibility of gene-gene and gene-environment interactions.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Korea Research Foundation Grant funded by the Korean Government (KRF-2008-313-E00333). PYM was supported by a 2008 Inje University research grant.
References
1. Allison DB, Mentore JL, Heo M, Chandler LP, Cappelleri JC, Infante MC, et al. Antipsychotic-induced weight gain: a comprehensive research synthesis. Am J Psychiatry 1999;156:1686-1696. PMID: 10553730.


2. Taylor DM, McAskill R. Atypical antipsychotics and weight gain--a systematic review. Acta Psychiatr Scand 2000;101:416-432. PMID: 10868465.


3. Allison DB, Mackell JA, McDonnell DD. The impact of weight gain on quality of life among persons with schizophrenia. Psychiatr Serv 2003;54:565-567. PMID: 12663847.


4. Strassnig M, Brar JS, Ganguli R. Body mass index and quality of life in community-dwelling patients with schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 2003;62:73-76. PMID: 12765746.


5. Perkins DO. Adherence to antipsychotic medications. J Clin Psychiatry 1999;60(Suppl 21):25-30. PMID: 10548139.
6. Vauth R, L├Čschmann C, R├╝sch N, Corrigan PW. Understanding adherence to neuroleptic treatment in schizophrenia├Ł. Psychiatry Res 2004;126:43-49. PMID: 15081626.


7. Jibson MD, Tandon R. New atypical antipsychotic medications. J Psychiatr Res 1998;32:215-228. PMID: 9793875.


8. Casey DE, Zorn SH. The pharmacology of weight gain with antipsychotics. J Clin Psychiatry 2001;62(Suppl 7):4-10. PMID: 11346195.
9. Pillai A, Parikh V, Terry AV Jr, Mahadik SP. Long-term antipsychotic treatments and crossover studies in rats: differential effects of typical and atypical agents on the expression of antioxidant enzymes and membrane lipid peroxidation in rat brain. J Psychiatr Res 2007;41:372-386. PMID: 16564057.


10. Walss-Bass C, Weintraub ST, Hatch J, Mintz J, Chaudhuri AR. Clozapine causes oxidation of proteins involved in energy metabolism: a possible mechanism for antipsychotic-induced metabolic alterations. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 2008;11:1097-1104. PMID: 18466668.



11. Palmieri VO, Grattagliano I, Portincasa P, Palasciano G. Systemic oxidative alterations are associated with visceral adiposity and liver steatosis in patients with metabolic syndrome. J Nutr 2006;136:3022-3026. PMID: 17116714.


12. Eriksson JW. Metabolic stress in insulin's target cells leads to ROS accumulation-a hypothetical common pathway causing insulin resistance. FEBS Lett 2007;581:3734-3742. PMID: 17628546.


13. Andreassen OA, J├Ėrgensen HA. Neurotoxicity associated with neuroleptic-induced oral dyskinesias in rats. Implications for tardive dyskinesia? Prog Neurobiol 2000;61:525-541. PMID: 10748322.


14. Fridlyand LE, Philipson LH. Reactive species and early manifestation of insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab 2006;8:136-145. PMID: 16448517.


15. Silva Mdo C, Gaspar J, Duarte Silva I, Faber A, Rueff J. GSTM1, GSTT1, and GSTP1 genotypes and the genotoxicity of hydroquinone in human lyphocytes. Environ Mol Mutagen 2004;43:258-264. PMID: 15141365.


16. Mannervik B. The isoenzymes of glutathione transferase. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol 1985;57:357-417. PMID: 3898742.


17. Hayes JD, Strange RC. Glutathione S-transferase polymorphisms and their biological consequences. Pharmacology 2000;61:154-166. PMID: 10971201.


18. Houstis N, Rosen ED, Lander ES. Reactive oxygen species have a causal role in multiple forms of insulin resistance. Nature 2006;440:944-948. PMID: 16612386.



19. Kuzuya M, Ando F, Iguchi A, Shimokata H. Glutathione peroxidase 1 Pro198Leu variant contributes to the metabolic syndrome in men in a large Japanese cohort. Am J Clin Nutr 2008;87:1939-1944. PMID: 18541588.


20. Lee YS, Kim AY, Choi JW, Kim M, Yasue S, Son HJ, et al. Dysregulation of adipose glutathione peroxidase 3 in obesity contributes to local and systemic oxidative stress. Mol Endocrinol 2008;22:2176-2189. PMID: 18562625.




21. Pemble S, Schroeder KR, Spencer SR, Meyer DJ, Hallier E, Bolt HM, et al. Human glutathione S-transferase ╬Ė(GSTT1): cDNA coloning and the characterization of a genetic polymorphism. Biochem J 1994;300:271-276. PMID: 8198545.



22. Seideg├źrd J, Pero RW, Markowitz MM, Roush G, Miller DG, Beattie EJ. Isoenzyme(s) of glutathione transferase (class Mu) as a marker for the susceptibility to lung cancer: a follow up study. Carcinogenesis 1990;11:33-36. PMID: 2295125.



23. Sundberg K, Johansson AS, Stenberg G, Widersten M, Seidel A, Mannervik B, et al. Differences in the catalytic efficiencies of allelic variants of glutathione transferase P1-1 towards carcinogenic diol epoxides of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Carcinogenesis 1998;19:433-436. PMID: 9525277.



24. Han OS, Hong JP. Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-IV Axis I Disorder-Korean Version. 2000,Seoul: Hana Medical Publishing.
25. Park YM, Chung YC, Lee SH, Lee KJ, Kim H, Byun YC, et al. Weight gain associated with the alpha2a-adrenergic receptor -1,291 C/G polymorphism and olanzapine treatment. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 2006;141B:394-397. PMID: 16583406.


26. Park YM, Cho JH, Kang SG, Choi JE, Lee SH, Kim L, et al. Lack of association between the -759C/T polymorphism of the 5-HT2C receptor gene and olanzapine-induced weight gain among Korean schizophrenic patients. J Clin Pharm Ther 2008;33:55-60. PMID: 18211617.


27. Kang SG, Lee HJ, Park YM, Choi JE, Han C, Kim YK, et al. Possible association between the -2548A/G polymorphism of the leptin gene and olanzapine-induced weight gain. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 2008;32:160-163. PMID: 17804136.


28. Park YM, Chung YC, Lee SH, Lee KJ, Kim H, Choi JE, et al. G-protein beta3 subunit gene 825C/T polymorphism is not associated with olanzapine-induced weight gain in Korean schizophrenic patients. Psychiatry Investig 2009;6:39-43.



29. Kang SG, Lee HJ, Choi JE, An H, Rhee M, Kim L. Association study between glutathione S-transferase GST-M1, GST-T1, and GST-P1 polymorphisms and tardive dyskinesia. Hum Psychopharmacol 2009;24:55-60. PMID: 19051221.


30. Zhong SL, Zhou SF, Chen X, Chan SY, Chan E, Ng KY, et al. Relationship between genotype and enzyme activity of glutathione S-transferases M1 and P1 in Chinese. Eur J Pharm Sci 2006;28:77-85. PMID: 16488119.


31. Hahn LW, Ritchie MD, Moore JH. Multifactor dimensionality reduction software for detecting gene-gene and gene-environment interactions. Bioinformatics 2003;19:376-382. PMID: 12584123.



32. Ritchie MD, Hahn LW, Roodi N, Bailey LR, Dupont WD, Parl FF, et al. Multifactor-dimensionality reduction reveals high-order interactions among estrogen-metabolism genes in sporadic breast cancer. Am J Hum Genet 2001;69:138-147. PMID: 11404819.



33. Motsinger AA, Ritchie MD. The effect of reduction in crossvalidation intervals on the performance of multifactor dimensionality reduction. Genet Epidemiol 2006;30:546-555. PMID: 16800004.


34. Ritchie MD, Hahn LW, Moore JH. Power of multifactor dimensionality reduction for detecting gene-gene interactions in the presence of genotyping error, missing data, phenocopy, and genetic heterogeneity. Genet Epidemiol 2003;24:150-157. PMID: 12548676.


35. Velez D, White BC, Motsinger AA, Bush WS, Ritchie MD, Williams SM, et al. A balanced accuracy function for epistasis modeling in imbalanced datasets using multifactor dimensionality reduction. Genet Epidemiol 2007;31:306-315. PMID: 17323372.


36. Brassat D, Motsinger AA, Caillier SJ, Erlich HA, Walker K, Steiner LL, et al. Multifactor dimensionality reduction reveals gene-gene interactions associated with multiple sclerosis susceptibility in African Americans. Genes Immun 2006;7:310-315. PMID: 16625214.




37. Motsinger AA, Brassat D, Caillier SJ, Erlich HA, Walker K, Steiner LL, et al. Complex gene-gene interactions in multiple sclerosis: a multifactorial approach reveals associations with inflammatory genes. Neurogenetics 2007;8:11-20. PMID: 17024427.


38. Agirbasli D, Agirbasli M, Williams SM, Phillips JA 3rd. Interaction among 5,10 methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase, plasminogen activator inhibitor and endothelial nitric oxide synthase gene polymorphisms predicts the severity of coronary artery disease in Turkish patients. Coron Artery Dis 2006;17:413-417. PMID: 16845248.


39. Hsieh CH, Liang KH, Hung YJ, Huang LC, Pei D, Liao YT, et al. Analysis of epistasis for diabetic nephropathy among type 2 diabetic patients. Hum Mol Genet 2006;15:2701-2708. PMID: 16893912.



40. R├Čsen P, Nawroth PP, King G, M├Čller W, Tritschler HJ, Packer L. The role of oxidative stress in the onset and progression of diabetes and its complications: a summary of a Congress Series sponsored by UNESCO-MCBN, the American Diabetes Association and the German Diabetes Society. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 2001;17:189-212. PMID: 11424232.


41. Packer L, Kraemer K, Rimbach G. Molecular aspects of lipoic acid in the prevention of diabetes complications. Nutrition 2001;17:888-895. PMID: 11684397.


42. Sagara Y. Induction of reactive oxygen species in neurons by haloperidol. J Neurochem 1998;71:1002-1012. PMID: 9721725.


43. Nasrallah H. A review of the effect of atypical antipsychotics on weight. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2003;28(Suppl 1):83-96. PMID: 12504074.

44. Ryu S, Cho EY, Park T, Oh S, Jang WS, Kim SK, et al. -759 C/T polymorphism of 5-HT2C receptor gene and early phase weight gain associated with antipsychotic drug treatment. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 2007;31:673-677. PMID: 17275977.