|
 |
- Search
| Psychiatry Investig > Volume 7(4); 2010 > Article |
Abstract
Objective
The Structured Interview for Prodromal Syndrome (SIPS) from Yale University is intended to diagnose prodromal syndrome of psychosis and to measure the severity of prodromal symptoms. Here, a Korean version of SIPS is presented, and its reliability, validity, and factor structures are examined using a representative Korean sample.
Methods
The Korean version of SIPS was administered to 40 participants over a period of 1 year. The inter-rater reliability and internal consistency of the SIPS were then evaluated. In addition, its factor structure was investigated using principal-axis factor analysis. Concurrent validity was explored using Pearson correlation coefficients with the Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS).
Results
Of the 40 subjects, 12.5% developed psychotic disorders during the 1-year follow-up period. Inter-rater reliability was good (intra-class correlations=0.96), and internal consistency was acceptable (Cronbach's alpha=0.83). A three-factor resolution displayed the best simple structure and accounted for 52.6% of all item variance. Factors 1 and 2 showed strong correlations with negative symptoms and cognitive dysfunction, respectively, on the PANSS. Factor 3 was not correlated with any factor on the PANSS.
Schizophrenia is a common form of chronic mental disorder with a lifetime risk of approximately 1%.1,2 Once symptoms are present, it is difficult to return to a pre-morbid state. Decreased duration of untreated psychosis represents an extremely important intervention because of reduction in unnecessary suffering and possibility to improve long-term outcome.3,4 For these reasons, active involvement in the treatment of psychosis is most beneficial prior to the onset of schizophrenia, i.e., in the prodromal state. Rather than 'prodrome,' McGorry and Singh5 have suggested that the term 'at risk mental state' (AR-MS) be used to describe a sub-threshold syndrome that can be regarded as a risk factor for subsequent psychosis.
To investigate prodromal syndromes and measure the severity of associated symptoms, the Personal Assessment and Crisis Evaluation Clinic in Melbourne, Australia, has developed the Comprehensive Assessment of At-Risk Mental States (CAARMS).6 Similarly, the Prevention through Risk Identification, Management, and Education (PRIME) prodromal research team at Yale University has developed the Structured Interview for Prodromal Syndromes (SIPS).7 There are some differences between these two scales with respect to the criteria for prodrome. However, the SIPS provides operational definitions for three prodromal syndromes: Brief Intermittent Psychotic Symptom syndrome (BIPS), Attenuated Positive Symptom syndrome (APS), and Genetic Risk and Deterioration syndrome (GRD), and the CAARMS has similar designations.
BIPS is defined as exhibiting one or more symptoms from the positive items on the Scale of Prodromal Symptoms (SOPS) in the psychotic range, with the symptom(s) having begun within the past 3 months, and exhibiting the symptoms for several minutes per day at a frequency of at least once per month. Thus, subjects meeting the BIPS criteria display recently emergent, brief, and intermittent psychotic symptoms. APS is characterized by the presence of one or more of the positive items on the SOPS scale in the prodromal range, with the symptom(s) having appeared within the past year, or showing attenuated psychotic symptoms at one or more points within the past year, and exhibiting the symptoms at least once per week during the past month. These subjects report experiencing mild or attenuated positive symptoms in the form of unusual thought content (delusional ideas, persecutory ideas, or grandiose ideas), perceptual abnormalities, and disorganized speech. GRD subjects have shown a significant drop in functioning, defined by at least a 30% drop in the Global Assessment of Functioning (GAF) scale over the past year, and who have a genetic risk in the form of a first-degree relative exhibiting any psychotic or schizotypal personality disorder.
The SIPS is a structured diagnostic interview used to diagnose the above three prodromal syndromes that was developed by Miller et al.8 and McGlashan et al.9 Several reports have confirmed the validity of the SIPS in the diagnosis of prodromal syndrome for psychosis. Miller et al.7 found the positive predictive value to be 50% at 12 months and 67% at 24 months among 14 prodromal subjects evaluated using the SOPS. The North American Prodrome Longitudinal Study found that, of 377 prodromal patients who were excluded from GRD status, 40% converted to a fully psychotic illness during a period of 30 months.10 The Prevention Program for Psychosis (P3) reported the conversion rate to psychosis in Spain was 18% and 23% at the 1-year and 3-year follow-ups, respectively.11 These findings suggest that the SIPS might be useful for the diagnosis of prodromal syndromes as well as for measuring the severity of prodromal symptoms.
Several studies have investigated the reliability and validity of the SIPS, but these have only been conducted using the English and Spanish versions.7,12 The accurate evaluation of the prodromal symptoms of psychosis necessitates appropriate assessment tools that not only utilize the native language, but that also consider the language and culture inherent in the instrument. Such tools require validation; thus, a complete Korean version of the SIPS was developed. In the present study, the usefulness of the Korean version of the SIPS in screening the Korean population for prodromal symptoms was assessed and its reliability and validity were evaluated.
The subjects made initial contact with the Seoul Youth Clinic (SYC) by telephone or through an Internet website (http://neuroimage.snu.ac.kr/youth/index.html). Following a telephone interview by a clinical nurse specialist, a screening interview was conducted by two experienced psychiatrists. Potential subjects ranged from 15 to 33 years of age; patients were excluded if they had 1) a past history of medical/neurological illness that could manifest as psychiatric symptoms, 2) a history of taking antipsychotics/mood stabilizers for longer than 1 week, or 3) low intelligence (intelligence quotient <70). A total of 40 subjects were enrolled in this study.
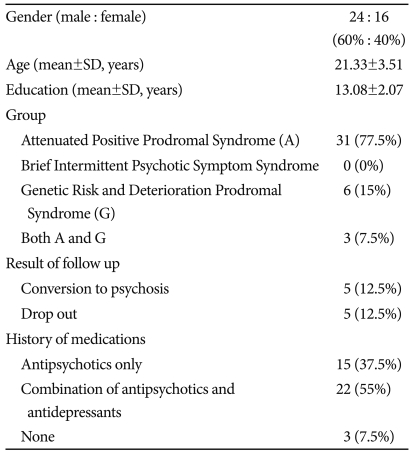
These subjects were part of a prospective, longitudinal project at the SYC from May 2006 to July 2009 that investigated individuals with prodromal symptoms of psychosis.13 The sociodemographic characteristics of the subjects are shown in Table 1. Participants had a mean age of 21.33±3.51 years, and 24 (60%) subjects were male. Individuals were considered prodromal if they met the criteria for at least one of three groups at intake: 1) APS, n=31, 2) BIPS, n=0, or 3) GRD, n=6. Three subjects met the intake criteria for both the APS and GRD groups. At intake, all subjects were assessed using the SIPS, Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS),14 and Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-IV.15 Psychotic features were evaluated monthly using the PANSS and at 6 months and 1 year using the SIPS. Of the 40 subjects who were prodromal at baseline, five dropped out, and five developed a psychotic disorder. In addition, of the 40 subjects, 15 were taking antipsychotics, 22 were taking antipsychotics and antidepressants, and three subjects were not taking medication.
Written informed consent was obtained from all subjects. Parental consent was obtained for subjects younger than 18 years of age. This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board at Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
The SIPS includes the SOPS, the Schizotypal Personality Disorder Checklist,16 a family history questionnaire,17 and a modified version of the GAF.18 In addition, the SIPS contains operational definitions of the three prodromal syndromes (Criteria of Prodromal Syndromes) and psychosis onset (Presence of Psychotic Syndrome). The SOPS is a 19-item scale designed to measure the severity of prodromal symptoms and is composed of four subscales for five attenuated positive symptoms, six negative symptoms, four disorganization symptoms, and four general symptoms. The seven-point scales cover severity of symptoms for the attenuated psychotic range and other symptoms. The seven-point scales used to score each item assess the severity of symptoms for the attenuated psychotic range as well as other symptoms. The positive symptoms rated on the SOPS are one aspect of a prodromal diagnosis, whereas the negative, disorganization, and general symptoms rated on the SOPS are helpful to evaluate the overall severity of symptoms once the diagnosis is established. The SOPS is analogous to the PANSS and the Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale, although the latter two instruments are severity rating scales used for patients who are fully psychotic rather than for those who are sub-psychotic or show attenuated symptoms.
With the permission of the author (Thomas H. McGlashan), three experienced psychiatrists translated the SIPS (version 3.1) into Korean. The Korean version of SIPS was then back-translated by a bilingual individual, and modifications were made. The final version was reviewed by the original translators.
The PANSS is a 30-item scale used to measure symptom severity for patients with schizophrenia and is composed of three subscales: the positive symptoms (7 items, including delusions and hallucinations), negative symptoms (7 items, including blunted affect and social withdrawal), and general psychopathology (14 items for general symptoms, including anxiety and depression) scales. Each of the items is scored on a 7-point Likert-type scale (1=absent and 7=extreme) representing increasing levels of psychopathology. The Korean version of PANSS has demonstrated good concurrent validity with other scales and inter-rater and test-retest reliability.14
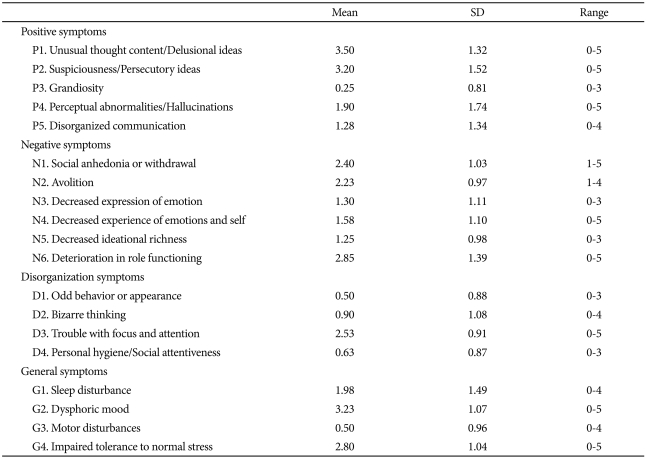
The mean ratings for the SOPS subscale were 2.03 for positive symptoms, 1.93 for negative symptoms, 1.14 for disorganized symptoms, and 2.13 for general symptoms. Of the 19 symptoms featured, 16 had means below the total-scale midpoint of 3.0 (Table 2). For three symptoms, grandiosity, impairment in personal hygiene or social attentiveness, and motor disturbances, most subjects (≥70%) were rated as displaying no pathology.
Two psychiatrists independently rated 20 cases, and the inter-rater reliability of the Korean version of SOPS scores was evaluated using the Intraclass Correlations Coefficient.19 The inter-rater reliability of the SOPS total score was 0.96 and those of four subscales (positive, negative, disorganization, and general symptoms) were 0.84, 0.97, 0.86, and 0.92, respectively. Thus, inter-rater reliability was in the excellent range for the total score and for all subscales.20
The Cronbach's alpha coefficient for the SOPS total score was 0.83, with an alpha level of 0.50 for the positive symptoms subscale, 0.78 for the negative symptoms subscale, 0.56 for the disorganization symptoms subscale, and 0.48 for the general symptoms subscale.21
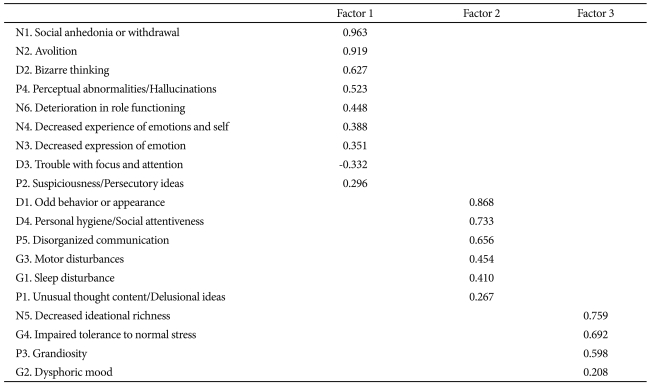
Principal axis factor analysis was employed to explore the factor structures of the Korean version of SOPS. The initial exploratory factor analysis used an oblique (promax) rotation and generated six factors with eigenvalues greater than one. The number of factors was determined based on 1) a scree test,22 2) the interpretability of the factor structures,23 3) model fit indices,24 and 4) Thurstone's criteria.25 These criteria require a minimum number of items with salient loadings (≥0.30) on more than one factor, a minimum number of items that do not have salient loadings on any factor, and a minimum number of items having three or more salient loadings per factor. Based on these criteria, a three-factor resolution displayed the best simple structure and accounted for 52.6% of the all item variance (Table 3). Taking salient loadings as those ≥0.30, Factor 1 had five of the six SOPS negative symptoms (the exception was 'decreased ideational richness'). Two disorganization symptoms, including 'bizarre thinking' and 'trouble with focus and attention,' loaded onto Factor 1 along with 'perceptual abnormalities/hallucination' and 'suspiciousness/persecutory ideas.' Two disorganized symptoms as well as 'disorganized communication' (classified as a positive symptom in SOPS) loaded on Factor 2. In addition, two general symptoms, 'motor disturbances' and 'sleep disturbance,' loaded on Factor 2 along with 'unusual thought content/delusional ideas.' Finally, a positive symptom, 'grandiosity,' a negative symptom, 'decreased ideational richness,' and two general symptoms, 'impaired tolerance to normal stress' and 'dysphoric mood,' loaded on Factor 3.
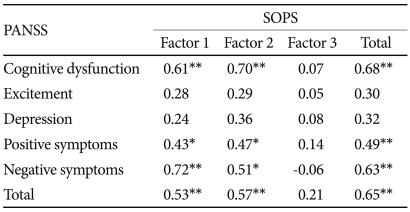
To evaluate the concurrent validity of the Korean version of SIPS, a Pearson's correlation analysis was performed between each SOPS sub-scores (the three factors extracted in the present study) and the five factors of the PANSS that have been noted in previous studies.14,26 PANSS factors included cognitive dysfunction, excitement, depression, positive symptoms, and negative symptoms. A Bonferroni correction placed significance at p=0.006. Factor 1 was significantly correlated with negative symptoms (r=0.72, p<0.001), cognitive dysfunction (r=0.61, p<0.001), positive symptoms (r=0.43, p<0.005), and PANSS total score (r=0.53, p<0.001)(Table 4). Factor 2 was significantly associated with cognitive dysfunction (r=0.70, p<0.001), negative symptoms (r=0.51, p<0.005), positive symptoms (r=0.47, p<0.005), and PANSS total score (r=0.57, p<0.001)(Table 4). Factor 3 did not show significant correlation with any of the PANSS subscale scores (Table 4). The SOPS total score was significantly correlated with cognitive dysfunction (r=0.68, p<0.001), positive symptoms (r=0.49, p<0.005), negative symptoms (r=0.63, p<0.001), and PANSS total score (r=0.65, p<0.001).
Currently, the SIPS and CAARMS scales are utilized to diagnose prodromal syndrome for psychosis and to measure the severity of prodromal symptoms. The present study examined the reliability, concurrent validity, and factor structure of the Korean version of SIPS. In the SYC, 40 subjects diagnosed as prodromal were closely monitored for more than 1 year. Of these 40 subjects, 12.5% developed psychotic disorders. Although previous studies have shown conversion rates to psychosis of approximately 40-50%,7,27 other studies with a greater number of participants have reported conversion rates of 10-20%.10,11,28,29 This is similar to the conversion rates seen in the present study.
The inter-rater reliability for the SOPS total score was 0.96, and those for all subscales (positive, negative, disorganization, and general symptoms) were above 0.80. These were within a good range and consistent with a previous report stating that excellent inter-rater reliability value is 0.95 for the total score and above 0.75 for all four subscales.7 With regard to internal consistency, the Cronbach's alpha coefficient for the SOPS total score and for negative symptoms was good (0.83 and 0.78, respectively), and the coefficients for the positive and disorganization subscales were low but acceptable (all >0.5). The Cronbach's alpha coefficient for the general symptoms subscale was somewhat lower (0.48). Decrease internal consistency of the general symptoms subscale might be influenced by the composition with four item and relatively smaller sample size of the subject. The Cronbach's alpha coefficient for the general symptoms subscale in the P3 study was low (0.574) similar to the present study. However, the value of the Cronbach's alpha coefficient for the negative symptoms subscale was high and similar to the P3 results in Spain.12 The SOPS was developed to define and rate the severity of the prodromal state of psychosis and was designed using the PANSS, with modifications of the positive symptom scales.8 The fact that the Korean version of the SOPS has good internal consistency for the negative symptoms subscale coincides with other reports suggesting that the internal coherence of negative symptoms is better than that of other subscales among patients with schizophrenia examined using PANSS.30,31
Similar to the previous studies,12,32 results from the factor analysis of our subjects identified three factors. However, whereas a previous study classified the analysis into negative, general, and positive symptoms,32 here, Factor 1 was shown to be a comparatively homogeneous component for negative symptoms, and Factors 2 and 3 appeared to be relatively heterogeneous in this study. The homogeneity of the negative symptoms in prodromal subjects in this study is also similar to findings in other studies that used PANSS to evaluate patients with schizophrenia, which have identified negative symptoms as the major component.33-35 However, the heterogeneity of the other two factors is thought to be due to the small sample size of this study (n=40), similar to that in the P3 study (n=30).12 In addition to the small sample size, the different characteristics of participants resulted in a greater number of GRD subjects (15%) in this study compared with their proportion in other studies (5% in the PRIME study and 6.6% in the P3 study).12,32 Five items of the negative symptoms ('social anhedonia or withdrawal,' 'avolition,' 'deterioration in role functioning,' 'decreased experience of emotions and self,' and 'decreased expression of emotion') were also included in Factor 1 in other studies. As 'avolition' is the cardinal symptom among negative aspects in schizophrenia, 'it has regularly loaded heavily on Factor 1 among prodromal subjects.
A valid scale should be highly correlated with a different scale measuring the same phenomenon. However, because no Korean version of a scale designed to diagnose and evaluate prodrome exists as yet, correlations among the five factors (cognitive, excitement, depression, positive, and negative) were evaluated using the Korean version of PANSS.14 Factor 1 of the SOPS showed the strongest correlation with negative symptoms of PANSS (r=0.72, p<0.001). Factor 2 showed the strongest correlation with cognitive dysfunction (r=0.70, p<0.001). Factor 3 was not correlated with any factor of PANSS. Consequently, Factor 1, Factor 2, and Factor 3 are thought to reflect negative symptoms, cognitive dysfunction, and general symptoms (non-specific symptoms), respectively.
The present study has some limitations. Most importantly, as this study utilized only prodromal subjects and did not include participants who failed to meet the criteria for psychosis, it does not have predictive validity. However, the 14 subjects who had high genetic risk and family histories of schizophrenia but showed no significant decline in functioning did not develop any psychotic disorders as assessed by the SIPS. Based on this indirect evidence, the predictive validity of SIPS may be considered good. Second, the small sample size is another limiting factor. The present results should be seen as preliminary, and the findings should be replicated using more subjects evaluated by the Korean version of SIPS. However, one must consider the difficulty of gathering and monitoring possible prodromal subjects for more than 1 year in a single center.
Despite these limitations and the need for further research using factor analysis with more subjects, the Korean version of SIPS demonstrates adequate reliability and appears to be helpful in the diagnosis and evaluation of prodrome in Korea. The collection of data from larger sample sizes is required so that the SIPS can be widely and extensively used in prodrome research.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a grant of the Korea Healthcare technology R&D project, Ministry for Health, Welfare and Family Affairs, Republic of Korea (A090096). We give special thanks to Thomas H. McGlashan for the permission to use the Structured Interview for Prodromal Syndrome. Soo Jin Kwon and Go Eun Jang contributed to regular contacts with subjects and Junehee Son contributed to back-translation of the Korean version of SIPS.
References
1. Perälä J, Suvisaari J, Saarni SI, Kuoppasalmi K, Isometsä E, Pirkola S, et al. Lifetime prevalence of psychotic and bipolar i disorders in a general population. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2007;64:19-28. PMID: 17199051.


2. Regier DA, Narrow WE, Rae DS, Manderscheid RW, Locke BZ, Goodwin FK. The de facto US mental and addictive disorders service system. Epidemiologic catchment area prospective 1-year prevalence rates of disorders and services. Arch Gen Psychiatry 1993;50:85-94. PMID: 8427558.


3. Harrigan SM, McGorry PD, Krstev H. Does treatment delay in first-episode psychosis really matter? Psychol Med 2003;33:97-110. PMID: 12537041.


4. Norman RM, Malla AK. Duration of untreated psychosis: a critical examination of the concept and its importance. Psychol Med 2001;31:381-400. PMID: 11305847.


5. McGorry PD, Singh BS. Schizophrenia: risk and possibility of prevention, in Handbook of Studies on Preventive Psychiatry. 1995,Amsterdam: Elsevier Science.
6. Yung AR, Yuen HP, McGorry PD, Phillips LJ, Kelly D, Dell'Olio M, et al. Mapping the onset of psychosis: the Comprehensive Assessment of At-Risk Mental States. Aust N Z J Psychiatry 2005;39:964-971. PMID: 16343296.


7. Miller TJ, McGlashan TH, Rosen JL, Cadenhead K, Cannon T, Ventura J, et al. Prodromal assessment with the structured interview for prodromal syndromes and the scale of prodromal symptoms: predictive validity, interrater reliability, and training to reliability. Schizophr Bull 2003;29:703-715. PMID: 14989408.



8. Miller TJ, McGlashan TH, Woods SW, Stein K, Driesen N, Corcoran CM, et al. Symptom assessment in schizophrenic prodromal states. Psychiatr Q 1999;70:273-287. PMID: 10587984.


9. McGlashan TH, Miller TJ, Woods SW, Hoffman RE, Davidson L. A scale for the assessment of prodromal symptoms and states. 2001,Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic Publishers.
10. Woods SW, Addington J, Cadenhead KS, Cannon TD, Cornblatt BA, Heinssen R, et al. Validity of the prodromal risk syndrome for first psychosis: findings from the North American Prodrome Longitudinal Study. Schizophr Bull 2009;35:894-908. PMID: 19386578.




11. Lemos-Giráldez S, Vallina-Fernández O, Fernández-Iglesias P, Vallejo-Seco G, Fonseca-Pedrero E, Paíno-Piñeiro M, et al. Symptomatic and functional outcome in youth at ultra-high risk for psychosis: a longitudinal study. Schizophr Res 2009;115:121-129. PMID: 19786339.


12. Lemos S, Vallina O, Fernández P, Ortega JA, García P, Gutiérrez A, et al. [Predictive validity of the Scale of Prodromal Symptoms (SOPS)]. Actas Esp Psiquiatr 2006;34:216-223. PMID: 16823681.

13. Yoo SY, Lee KJ, Kang DH, Lee SJ, Ha TH, Wee W, et al. Characteristics of subjects at clinical high risk for schizophrenia: natural follow up study in 'Seoul Youth Clinic'-pilot study. J Korean Neuropsychiatr Assoc 2007;46:19-28.
14. Yi JS, Ahn YM, Shin HK, An SK, Joo YH, Kim SH, et al. Reliability and validity of the Korean version of the Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale. J Korean Neuropsychiatr Assoc 2001;40:1090-1105.
15. First MB, Spitzer RL, Gibbon M, Wiliams JB. Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-IV Axis I Disorders. 1997,New York: Biometrics Research.
16. American Psychiatric Association. DSM-IV: Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 1994,4th edition. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association.
17. Andreasen NC, Endicott J, Spitzer RL, Winokur G. The family history method using diagnostic criteria. Reliability and validity. Arch Gen Psychiatry 1977;34:1229-1235. PMID: 911222.


18. Hall RC. Global assessment of functioning. A modified scale. Psychosomatics 1995;36:267-275. PMID: 7638314.


19. McGraw KO, Wong SP. Forming Inferences About Some Intraclass Correlation Coefficients. Psychol Methods 1996;1:30-46.

20. Fleiss JL. Analysis of data from multiclinic trials. Control Clin Trials 1986;7:267-275. PMID: 3802849.


21. Nunnally JC, Bernstein IH. Psychometric theory. 1994,New York: McGraw-Hill.
23. Gorsuch RL. Factor Analysis. 1983,Hillsdale: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
24. Muthen LK, Muthen BO. How to use a Monte Carlo study to decide on sample size and determine power. Struct Equ Modeling 2002;9:599-620.

25. Thurstone LL. Multiple-factor analysis. 1947,Chicago, IL: Chicago Press.
26. Lindenmayer JP, Grochowski S, Hyman RB. Five factor model of schizophrenia: replication across samples. Schizophr Res 1995;14:229-234. PMID: 7766534.


27. Yung AR, Phillips LJ, Yuen HP, Francey SM, McFarlane CA, Hallgren M, et al. Psychosis prediction: 12-month follow up of a high-risk ("prodromal") group. Schizophr Res 2003;60:21-32. PMID: 12505135.


28. Yung AR, Yuen HP, Berger G, Francey S, Hung TC, Nelson B, et al. Declining transition rate in ultra high risk (prodromal) services: dilution or reduction of risk? Schizophr Bull 2007;33:673-681. PMID: 17404389.




29. Cannon TD, Cadenhead K, Cornblatt B, Woods SW, Addington J, Walker E, et al. Prediction of psychosis in youth at high clinical risk: a multisite longitudinal study in North America. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2008;65:28-37. PMID: 18180426.



30. Peralta V, Cuesta MJ. Psychometric properties of the positive and negative syndrome scale (PANSS) in schizophrenia. Psychiatry Res 1994;53:31-40. PMID: 7991730.


31. von Knorring L, Lindström E. The Swedish version of the Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS) for schizophrenia. Construct validity and interrater reliability. Acta Psychiatr Scand 1992;86:463-468. PMID: 1281960.


32. Hawkins KA, McGlashan TH, Quinlan D, Miller TJ, Perkins DO, Zipursky RB, et al. Factorial structure of the Scale of Prodromal Symptoms. Schizophr Res 2004;68:339-347. PMID: 15099615.


33. Kawasaki Y, Maeda Y, Sakai N, Higashima M, Urata K, Yamaguchi N, et al. Evaluation and interpretation of symptom structures in patients with schizophrenia. Acta Psychiatr Scand 1994;89:399-404. PMID: 8085470.


34. Lindenmayer JP, Bernstein-Hyman R, Grochowski S, Bark N. Psychopathology of Schizophrenia: initial validation of a 5-factor model. Psychopathology 1995;28:22-31. PMID: 7871117.


35. Lancon C, Auquier P, Nayt G, Reine G. Stability of the five-factor structure of the Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS). Schizophr Res 2000;42:231-239. PMID: 10785581.