|
 |
- Search
| Psychiatry Investig > Volume 9(2); 2012 > Article |
Abstract
Objective
Lamotrigine is a widely used medication for psychiatric disorders and epilepsy, but the adverse effects of this drug in adolescent Korean patients have not yet been investigated. In the present study, we sought to compare the incidence and impact of lamotrigine-induced skin rashes and different pattern of adverse events in psychiatric and nonpsychiatric adolescent patients.
Methods
Using a retrospective cohort design, all of the charts were reviewed for adolescents (13 to 20 years old), treated with lamotrigine during the previous 2 years in the Child and Adolescent Psychiatric Clinic and Pediatric Neurologic Clinic of the Ulsan University Hospital in South Korea.
Results
Of the 102 subjects, 23 patients developed a skin rash. All of these rashes were observed within 7 weeks of the initiation of the lamotrigine therapy. Only one subject developed a serious rash, which was diagnosed as Stevens-Johnson syndrome. Although the psychiatric subjects were administered statistically lower doses of lamotrigine during weeks 1 through 5 and at week 12, the likelihood of developing a rash was not significantly different between the psychiatric and nonpsychiatric patients.
Lamotrigine (LTG) is an anticonvulsant medication that has been used widely for adult and pediatric seizure disorders. LTG is approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the maintenance treatment of bipolar disorder in adults and as an adjunctive therapy in epilepsy.1 This drug has also been used in youths with psychiatric disorders as a mood stabilizer.2 The common side effects of LTG include dizziness, ataxia, headache, tremor, blurred vision, and diplopia.3 Approximately 8% of patients who are administered LTG develop a benign maculopapular rash during the first 4 months of treatment.4 In adults, the incidence of serious rashes was 0.08% when LTG was used as the initial monotherapy and was 0.13% when this drug was used as an adjunctive therapy.4 Lamotrigine carries a U.S. Food and Drug Administration-mandated black box warning concerning the increased risk of rashes in children under the age of 16 years.1 Skin rashes are a major cause of treatment discontinuation for this medication. These skin reactions range, with increasing severity, from common and mild maculopapular rashes to Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS) and toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN). Although these reactions are rare, they are more common in children than in adults, and it is difficult to predict whether a rash will progress to SJS or TEN.3-5 Serious reactions are rare but may be life-threatening.6
The pathogenesis of skin reactions appears to be multifactorial and has, in many cases, been explained using the hapten hypothesis of drug hypersensitivity, which implies that metabolic and immunological mechanisms are involved. The immune response is initiated by reactive metabolites that are combined with self proteins. An imbalance between the metabolic bioactivation and detoxification of the drug may lead to an accumulation of reactive metabolites, which may bind irreversibly to endogenous proteins.7 T-cell lymphocyte clones may react to these drug-modified proteins, or to the parental drug itself, and cause delayed immune responses in the skin, whereas immediate IgE responses are responsible for urticaria, angioedema, and anaphylaxis.8 Among the traditional antiepileptic drugs, the aromatic compounds phenytoin and carbamazepine have been associated with relatively high incidences of cutaneous reactions in up to 10% of patients.9-11 Lamotrigine has also been shown to frequently cause this type of skin reaction.12,13
Studies using LTG for epilepsy indicate that the risk factors that are associated with serious rashes and lamotrigine treatment include a young age, a large starting dose, a rapid dose escalation, and the combination of LTG and valproate.3-5,12,14 In previous studies, females were found to be at a higher risk of developing an LTG-induced rash than males.12,15 Clinicians now initiate LTG treatment using a slow titration schedule. These dosing changes have reduced the incidence of serious rashes in pediatric LTG use to approximately 1%.16 However, compared with the pediatric use of LTG, the use of this drug in children and adolescent psychiatric patients is much more limited, even though this medication exhibits a possible efficacy for mood symptoms.2
In the present study, we aimed to study the safety and tolerability of lamotrigine in adolescents with psychiatric disorders who were experiencing a depressive symptoms, with a focus on the risk factors that were associated with rash development. We compared the incidence and impact of lamotrigine-induced skin rashes and pattern of adverse events in our sample with pediatric seizure disorder patients.
This retrospective cohort study enrolled consecutive 106 adolescents (13 to 20 years old) who had been first treated with lamotrigine during the previous 2 years in the Child and Adolescent Psychiatric Clinic and Pediatric Neurologic Clinic of the Ulsan University Hospital in South Korea. Inclusion criteria were patients being prescribed Lamotrigine for the first time during the study period. Among them, four patients with seizure disorder having concurrent psychiatric disorders were excluded. The study protocol was approved by the Institutional Review Board of the Ulsan University Hospital.
The data were collected by the investigators, M.D. H. J. Tak, using chart reviews, which gathered the following data: age, sex, DSM-IV diagnosis, ICD-10 diagnosis, and concurrent medications (i.e., antipsychotics, mood stabilizers, antidepressants, and stimulants). The presence of any adverse effects was also noted.
Diagnoses for the psychiatric patients were made by a child psychiatrist, S. Y. Bhang., using clinical interviews that were based on the DSM-IV TR criteria and on all of the available collateral information. For the pediatric patients, the seizure disorders were diagnosed by pediatric neurologist, G. Y. Lee, using the ICD-10 criteria.
Any comment of side effect in the medical record was collected. The expression such as "rash", "eruptions", and "urticaria" was considered as having rash, but "Pruritis" or "itching" sensation was not included. In this study, we defined "serious rash" as a condition that is life threatening, requiring hospitalization, Stevens Johnson syndrome or erytherma multiforme.
The continuous measures were compared using an independent t-test to determine whether there were significant differences in the demographic and dosage data between the patients who developed a rash and those who did not. An independent t-test was also used to compare the data of the psychiatric and nonpsychiatric patients. Unless otherwise specified, the data are presented as the means±standard deviations.
A chi-square test was used to analyze the frequency of the other adverse events. To define the factors that affected the onset of a rash, we also performed chi-square tests to evaluate valproate co-administration and the LTG dose across the weeks of treatment. The data were analyzed using SPSS version 17.0.
Of the 102 subjects, 65 (64%) were psychiatric patients, and 37 (36%) were pediatric patients. Among these 102 patients, 43 (42%) were males, and 59 (58%) were females. The average age of the subjects was 17.18 (range=13 to 20, SD=1.864) years (Table 1). The primary DSM-IV diagnoses for the psychiatric participants included bipolar disorder (n=39), major depressive disorder (n=12), schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder (n=13), and an eating disorder (n=1). The remaining 37 pediatric patients were diagnosed with seizure disorders (Table 1).
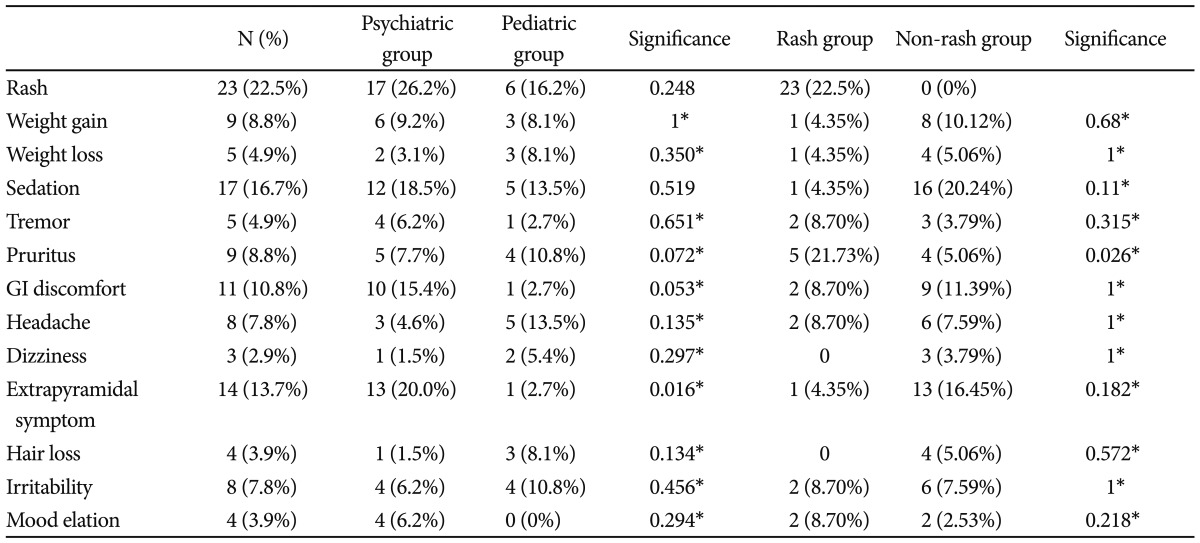
Twenty-three patients (22% of all of the participants) developed a rash during the course of the study period (Table 2). The incidence of a rash was not different between the males (n=9, 21% of males) and females (n=14, 24% of females) (p=0.738).
To evaluate the different rates of rash development between the psychiatric and nonpsychiatric patients' use of LTG, we conducted chi-square tests but found no statistically significant differences between the groups (p=0.248) (Table 2).
Seventeen psychiatric patients (73.9% of the total rash group) and 6 pediatric patients (26.1% of the total rash group) developed a rash. The psychiatric subjects were prescribed a statistically significant lower dose of LTG in weeks 1 through 5 and in week 12: 19.80 mg vs. 46.08 mg for the 1st week (p=0.002), 29.56 mg vs. 54.30 mg for the 2nd week (p=0.007), 43.75 mg vs. 84.04 mg for the 3rd week (p=0.000), 50.26 mg vs. 85.00 mg for the 4th week (p=0.019), 55.44 mg vs. 119.74 mg for the 5th week (p<0.001), and 88.63 mg vs. 174.42 mg for the 12th week (p=0.015).
To evaluate the effects of concurrent valproate and LTG use on rash development, we performed a chi-square test. There was no difference in the rate of rash development between the group that used valproate and the group that did not (p=0.304). Fourteen (21.5%) of psychiatric patients and 9 (24.3%) of seizure disorder patients had been taking valproate as a concurrent medication. The difference of the proportion was not statistically significant (Table 4).
In terms of the dosages of LTG, the mean initial dose of LTG in the valproate co-medication group (21.41±14.90 mg) was lower than that in the non-valproate group (31.64±35.11 mg), but this difference was not statistically significant. However, LTG dosages in the 2nd through the 5th weeks of treatment in the valproate group were statistically significantly lower than those in the non-valproate group: 23.52 mg vs. 42.85 mg for the 2nd week (p=0.023), 40.37 mg vs. 64.28 mg for the 3rd week (p=0.006), 48.42 mg vs. 69.05 mg for the 4th week (p=0.026), and 57.65 mg vs. 90.62 mg for the 5th week (p=0.006).
All of the rashes that were observed occurred within 7 weeks (n=23, 100%) of the treatment initiation in our subjects. The mean time interval to the rash onset from the starting time of the LTG treatment was 2.7 weeks (range=1 to 7 weeks, SD=1.428). The LTG dose in week 3 (mean 39.84±21.02 mg vs. 63.10±50.73 mg) and the mean peak dose (71.19±73.12 mg vs. 128.48±87.01 mg) were found to be statistically significantly lower in the group that developed a rash than in the group that did not develop a rash (Table 3). The incidence of pruritus was significantly different between the rash group (n=5, 21.7%) and the non-rash group (n=4, 5.1%). The patients with pruritus were likely to develop a rash. Before and after the development of the rashes, 5 patients experienced pruritic sensations (p=0.026). In addition, 4 patients suffered from pruritus without a rash during LTG treatment. However, the incidences of the other side effects of LTG were not different between the groups (Table 2). A 15-year-old male with a seizure disorder (n=1, 0.98% of all subjects) developed a serious rash, which was diagnosed as Stevens-Johnson syndrome and required hospitalization for 2 weeks. He was taking valproate 750 mg, and lamotrigine was added to his treatment regimen to further control his seizures. The rash appeared during the 3rd week of the lamotrigine treatment at a dose of 100 mg. After the hospitalization, the rash remitted completely with no long-term complications. Two subjects began steroid treatment for 2 weeks and another subject began antihistamine medication for days after development of rash.
At week-12, the number of subjects of non-rash group who continued the lamotrigine medication was 55 (69% of baseline) (Table 3). Two main reasons why non-rash group discontinued the medication at week-12 were lack of efficacy and poor compliance.
Twenty one patients (91.3%) discontinued the use of lamotrigine after the onset of a rash. Two (8.7%) patients continued the medication. Among the discontinuation patients, 18 (78.2%) subjects stopped the lamotrigine immediately after the onset of rash, 3 (13%) patients discontinued the drug gradually after trying to manage the rash through dose reduction. Two patients rechallenged LTG after discontinuing the use of the medication for 2 months for one patient, and 2.5 years for the other. These two patients had no reappearance of rash after restarting the LTG.
Overall, rash was the most common side effect, which was followed by sedation (n=17, 16.7%), extrapyramidal symptoms (EPS) (n=14, 13.7%), gastrointestinal discomfort (n=11, 10.8%), weight gain (n=9, 8.8%), and weight loss (n=5, 4.9%) (Table 2). The rates of EPS were higher in the psychiatric group (n=13, 20%) compared to the nonpsychiatric group (n=1, 2.7%) (p=0.016). None of the other side effects, besides rash and EPS, exhibited significant differences between the psychiatric and nonpsychiatric groups (Table 2). Among the 14 patients who developed EPS, 13 were taking concurrent antipsychotic medications.
The present study is the first to compare the side effects of LTG in adolescent epilepsy patients and adolescent psychiatric patients. This retrospective cohort study was conducted with patients who were aged 13 to 20 and who were newly prescribed LTG for the same 2-year period.
Lamotrigine has therapeutic effects in pediatric patients with bipolar disorder. Lamotrigine is an antiglutamatergic agent that decreases the activity of glutamate, an excitatory neurotransmitter, thus relieving depression while not affecting mania in patients with bipolar disorder.17 Therefore it is an emerging option for treatment of depression in pediatric bipolar disorder.18 A community study that examined the pattern of medication use in children and adolescents who were treated for bipolar disorder found that 15% of these patients were treated with new generation antiepileptic drugs before standard mood stabilizers.19 Lamotrigine monotherapy has been shown to be effective in maintaining depressive symptom control in pediatric bipolar disorder.2,20,21 As illustrated by these studies, LTG appears to be effective in treating depressive symptoms in adolescent psychiatric disorders.
As adjunctive therapy in pediatric patients with epilepsy, 11.5% of patients aged 2 to 16 years who received LTG discontinued treatment because of an adverse reaction.1 The reaction that was most commonly associated with treatment discontinuation was a rash.1,20 The incidence of a serious rash that was associated with hospitalization and the discontinuation of lamotrigine in the pediatric patients (2 to 16 years of age) was 0.8% (16 of 1983).1 In our study, only one patient had a serious rash and required hospitalization, which confirms the safety of LTG that has been shown in previous studies. However, compared with these previous studies, the incidence rate of a benign rash (n=22, 21.56% of all participants) in our present study was the highest, despite the slow titration of the medication in psychiatric patient group. In previous study on Korean adults, they report 12.5% and 12.7% of the rash incidence.22,23 In one study on Chinese adult epileptic patients prescribed with lamotrigine reported that 4.7% of the participants experienced rash.24 In children with bipolar spectrum disorder, 38.4% (n=15/39) of youth developed skin lesion and among them, 17.9% (n=7/39) patients developed rash.21 In one study for bipolar manic and hypomanic adolescent patient, 6.4% developed rash.2
Lamotrigine is metabolized exclusively by glucuronidation, and valproate inhibits the glucuronidation of this drug and decreases its clearance by approximately 50%.3 The addition of valproate to a patient's treatment regimen may significantly elevate LTG levels and may increase the likelihood of development of life-threatening SJS3 as a result of this drug's inhibition of uridine diphosphate glucuronyltransferase.25 However, valproate was not identified as a risk factor in our study, which was likely due to careful LTG dosing in accordance with current guidelines, especially for the psychiatric patients.
It is already recognized that drug-induced skin reactions, in general, are more frequent in women than in men.15,26 This gender difference has been reported previously for LTG.12 In our study, there were no gender differences in the rash development. In a recent study, significant gender difference was not reported for LTG rashes.13
Common side effects of lamotrigine include dizziness, ataxia, headache, tremor, blurred vision, and diplopia.3 In our sample, sedation, extrapyramidal symptoms and gastrointestinal symptoms were common side effects; weight gain, weight loss, tremor, pruritus, headache, dizziness, hair loss, irritability, and mood elevation were also noted (Table 2). No other side effects were found to result in the discontinuation of LTG in our study. Except for rash, LTG is generally well tolerated as an anticonvulsant and as an antidepressant mood stabilizer.27
For the nonpsychiatric seizure patients, the pediatrician titrated lamotrigine dose more rapidly than manufacturer's advice because of clinical demand for seizure control. In spite of this, the incidence of rash between psychiatric and nonpsychiatric patients was not statistically different. This supports that lowering starting dosage of lamotrigine can reduce the incidence of serious rash but not the overall incidence of lamotrigine related rash.12
Compared to previous reports, which did not report the existence of EPS, the EPS rate was significantly high for the psychiatric patients in the present study. One explanation for this relatively high EPS rate is the co-medication of these patients with antipsychotics (n=13, 92.85% of 14 EPS reporting subjects). Another explanation may be that the adolescent population often displays a higher level of sensitivity to medication toxicity than adults.28 Compared to adults, adolescents have a higher risk of dystonic reactions with the use of antipsychotic agents.29,30
The major limitation of the present study is that it is based on a retrospective analysis. The precious estimates of rash rates can be obtained from prospective clinical studies, which do allow for a careful follow-up with the patients and do provide detailed descriptions of all of the emerging adverse events. Second, our study sample was derived from one university hospital clinic, a factor which may have limited the representativeness of our data. Multicenter studies are required to generalize the findings of a study to heterogeneous patient populations with diverse clinical presentations. In addition, we did not examine the patients' histories for prior rashes that were developed as a result of previous medications, including other antiepileptic drugs. A history of rash from other antiepileptic drugs is a risk factor for developing rash to LTG.13 Third, the clinical response of depressive symptoms was not evaluated. Other limitations include the small number of patients in some of the subgroups, and the possible presence of a physician bias during the determination of whether or not a rash was related to a given medication. Controlled and prospective longitudinal studies that use larger samples of patients are needed to further investigate the predictors of LTG associated rash.
The present study is the first to investigate lamotrigine in adolescent psychiatric disorders and in epilepsy in Korea. The main aim of the present study was to determine the tolerability and safety of LTG in this population. The results of the current study support our hypothesis that LTG is tolerable in this special population.2 Despite the many limitations of this retrospective study, our observations show that LTG is tolerable and has a relatively low incidence of serious rash.
References
1. GlaxoSmithKline. Prescribing Information: Lamictal.[Online]. 2009,GlaxoSmithKline.
2. Pavuluri MN, Henry DB, Moss M, Mohammed T, Carbray JA, Sweeney JA. Effectiveness of lamotrigine in maintaining symptom control in pediatric bipolar disorder. J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol 2009;19:75-82. PMID: 19232025.



3. Martin A, Volkmar FR, Lewis M. Lewis's Child and Adolescent Psychiatry: A Comprehensive Textbook. 2007,4th Edition. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
4. Sadock BJ, Kaplan HI, Sadock VA. Kaplan & Sadock's Synopsis of Psychiatry: Behavioral Sciences/Clinical Psychiatry. 2007,Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
5. Guberman AH, Besag FM, Brodie MJ, Dooley JM, Duchowny MS, Pellock JM, et al. Lamotrigine-associated rash: risk/benefit considerations in adults and children. Epilepsia 1999;40:985-991. PMID: 10403224.


6. Mockenhaupt M, Messenheimer J, Tennis P, Schlingmann J. Risk of Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis in new users of antiepileptics. Neurology 2005;64:1134-1138. PMID: 15824335.


7. Leeder JS. Mechanisms of idiosyncratic hypersensitivity reactions to antiepileptic drugs. Epilepsia 1998;39(Suppl 7):S8-S16. PMID: 9798756.


9. Rapp RP, Norton JA, Young B, Tibbs PA. Cutaneous reactions in head-injured patients receiving phenytoin for seizure prophylaxis. Neurosurgery 1983;13:272-275. PMID: 6225961.


10. Brodie MJ, Overstall PW, Giorgi L. The UK Lamotrigine Elderly Study Group. Multicentre, double-blind, randomised comparison between lamotrigine and carbamazepine in elderly patients with newly diagnosed epilepsy. Epilepsy Res 1999;37:81-87. PMID: 10515178.


11. Chadwick D. Vigabatrin European Monotherapy Study Group. Safety and efficacy of vigabatrin and carbamazepine in newly diagnosed epilepsy: a multicentre randomised double-blind study. Lancet 1999;354:13-19. PMID: 10406359.


12. Wong IC, Mawer GE, Sander JW. Factors influencing the incidence of lamotrigine-related skin rash. Ann Pharmacother 1999;33:1037-1042. PMID: 10534214.


13. Hirsch LJ, Weintraub DB, Buchsbaum R, Spencer HT, Straka T, Hager M, et al. Predictors of Lamotrigine-associated rash. Epilepsia 2006;47:318-322. PMID: 16499755.


14. Chou JC, Fazzio L. Maintenance treatment of bipolar disorder: Applying research to clinical practice. J Psychiatr Pract 2006;12:283-299. PMID: 16998416.


15. Caranasos GJ, Stewart RB, Cluff LE. Drug-induced illness leading to hospitalization. JAMA 1974;228:713-717. PMID: 4406257.


16. Messenheimer JA. Rash in adult and pediatric patients treated with lamotrigine. Can J Neurol Sci 1998;25:S14-S18. PMID: 9827240.


17. Schatzberg AF. Employing pharmacologic treatment of bipolar disorder to greatest effect. J Clin Psychiatry 2004;65(Suppl 15):15-20. PMID: 15554791.

18. Kowatch RA, DelBello MP. Pharmacotherapy of children and adolescents with bipolar disorder. Psychiatr Clin North Am 2005;28:385-397. PMID: 15826738.


19. Bhangoo RK, Lowe CH, Myers FS, Treland J, Curran J, Towbin KE, et al. Medication use in children and adolescents treated in the community for bipolar disorder. J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol 2003;13:515-522. PMID: 14977464.


20. Chang K, Saxena K, Howe M. An open-label study of lamotrigine adjunct or monotherapy for the treatment of adolescents with bipolar depression. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 2006;45:298-304. PMID: 16540814.


21. Biederman J, Joshi G, Mick E, Doyle R, Georgiopoulos A, Hammerness P, et al. A prospective open-label trial of lamotrigine monotherapy in children and adolescents with bipolar disorder. CNS Neurosci Ther 2010;16:91-102. PMID: 20415838.



22. Chang JS, Joe SH, Cha BS, Moon ES, Ha TH, Yoon IY, et al. Lamotrigine augmentation in patients with treatment-resistant major depressive disorder: a naturalistic study. Korean J Psychopharmacol 2008;19:276-282.
23. Woo YS, Bahk WM, Jon DI, Joo YH, Kim W, Seo JS, et al. Rash in adult patients receiving lamotrigine to treat bipolar I disorder in Korea: a multicenter, prospective, naturalistic, open-label trial. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 2009;33:1147-1152. PMID: 19540298.


24. Zeng K, Wang X, Xi Z, Yan Y. Adverse effects of carbamazepine, phenytoin, valproate and lamotrigine monotherapy in epileptic adult Chinese patients. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 2010;112:291-295. PMID: 20071075.


25. Alvestad S, Lydersen S, Brodtkorb E. Rash from antiepileptic drugs: influence by gender, age, and learning disability. Epilepsia 2007;48:1360-1365. PMID: 17484761.


26. Tran C, Knowles SR, Liu BA, Shear NH. Gender differences in adverse drug reactions. J Clin Pharmacol 1998;38:1003-1009. PMID: 9824780.


27. Stahl SM. Stahl's Essential Psychopharmacology: Neuroscientific Basis and Practical Applications. 2008,3rd Edition. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
28. Choonara I, Gill A, Nunn A. Drug toxicity and surveillance in children. Br J Clin Pharmacol 1996;42:407-410. PMID: 8904610.



29. Rodnitzky RL. Drug-induced movement disorders in children and adolescents. Expert Opin Drug Saf 2005;4:91-102. PMID: 15709901.


30. Aguilar EJ, Keshavan MS, Martinez-Quiles MD, Hernandez J, Gomez-Beneyto M, Schooler NR. Predictors of acute dystonia in first-episode psychotic patients. Am J Psychiatry 1994;151:1819-1821. PMID: 7977894.