|
 |
- Search
| Psychiatry Investig > Volume 9(1); 2012 > Article |
Abstract
Objective
We investigated neuropsychological markers that can be used to discriminate pathological cognitive aging from normal cognitive aging.
Methods
We administered frontal lobe function tests including the Wisconsin Card Sorting Test (WCST), digit span test, lexical fluency test, fixed condition design fluency test, and Trail Making Test B (TMT-B) to 92 individuals with pathological cognitive aging (PCA) and 222 individuals with normal cognitive aging (NCA). We examined the main effects of participants' diagnoses (PCA, NCA) and age (65-69 years old, 70-74 years old and 75 years old or over) on their test performance using multivariate analysis of variance.
Results
The main effects of both the diagnosis (F=2.860, p=0.002) and the age group (F=2.484, p<0.001) were significant. The PCA group showed lower performance on the backward digit span test (F=14.306, p<0.001), fixed condition design fluency test (F=8.347, p=0.004) and also exhibited perseverative errors in the WCST (F=4.19, p=0.042) compared with the NCA group. The main effect of the diagnosis on the backward digit span test and the fixed condition design fluency test remained significant after Bonferroni correction. The main effect of age remained significant in the TMT-B (F=8.737, p<0.001) after Bonferroni correction. Other test scores were not influenced by diagnosis or age.
Pathological cognitive aging (PCA) is an umbrella term that covers a range of cognitive impairments beyond the normal range of age-associated cognitive decline. In contrast to crystallized intelligence that remains stable until at least the mid-70s, fluid intelligence that requires reasoning, problem solving, planning or organization1,2 begins to decline from middle age.3 Although it is notable that frontal lobe functioning declines in normal cognitive aging (NCA), frontal dysfunction is also common in PCA. However, we expect that the frontal dysfunctions associated with PCA may be qualitatively and/or quantitatively different from those that are associated with NCA since frontal lobe dysfunction was found in patients with early Alzheimer's disease (AD),4,5 was associated with the survival of AD patients,6 and could also discriminate incident AD patients from individuals with NCA better than could me-mory deficit.7,8 Moreover, frontal dysfunction has been reported to be a core cognitive feature of non-Alzheimer's dementia, e.g. vascular dementia.9 Therefore, frontal lobe dysfunction is likely to be an indicator of PCA in the elderly.
The frontal lobe is active in various cognitive functions: abstract thinking, reasoning, cognitive flexibility, working memory, planning, active problem solving, anticipation of potential behavioral consequences, organization, regulation of attention, self-monitoring of behavior, and the regulation of behavior.7,10 The aim of the present study is to find a useful cognitive marker that can discriminate PCA from NCA by comparing the frontal dysfunction associated with PCA with that present in NCA using comprehensive frontal lobe function tests.
This study was a part of the Korean Longitudinal Study on Health and Aging which was conducted in Seongnam, Korea.11 All subjects were randomly-sampled community-dwelling Koreans aged 65 years or more.
We operationally defined PCA as the mild cognitive impairment (MCI). Among the participants, 92 individuals had MCI (amnestic single domain type 15, amnestic multiple domain type 36, nonamnestic single domain type 24, nonamnestic multiple domain type 17) and 222 were cognitively normal. Those subjects who had major Axis I psychiatric disorders including dementia and depressive disorders were excluded. Those who had serious medical and neurological disorders that could affect their mental functioning and those whose education had lasted less than 7 years were also excluded. Individuals with minor physical abnormalities (e.g. diabetes with no serious complications, essential hypertension, mild hearing loss, etc) were not excluded. All subjects had adequate vision and hearing, although many wore glasses and some required a hearing aid.
All subjects were fully informed of the study protocol and provided written informed consent from themselves or their legal guardians.
Standardized clinical interviews and neurological and physical examinations were conducted by geriatric neuropsychiatrists with expertise in dementia research using the Korean version of the Consortium to Establish a Registry for Alzheimer's Disease Clinical Assessment Battery (CERAD-K-C),12 the Korean version of the Mini International Neuropsychiatric Interview.13 For diagnosing MCI, the Korean version of the CERAD Neuropsychological Assessment Battery (CERAD-K-N)14 was administered. The CERAD-K-N consists of nine cognitive tests: categorical verbal fluency test, modified Boston naming test, Mini-mental status examination (MMSE), word list learning test, word list recall test, word list recognition test, constructional praxis test, constructional recall test, and the trail making test A (TMT-A). For evaluating frontal lobe function, the Wisconsin Card Sorting Test (WCST),15 digit span test,16 lexical fluency test,17 fixed condition design fluency test,18 and the Trail Making Test B (TMT-B)19,20 were also conducted. In the design fluency test, subjects were instructed to invent as many different drawings as they could in 4 minutes using 4 lines. The drawings could not represent actual object, nor could they be derived from such objects.18 All neuropsychological tests were administered by trained neuropsychologists.
Participants' level of depression was evaluated using the Revised Korean version of the Geriatric Depression Scale (GDS-KR).21 The modified Hachinski Ischemic Score (MHIS)22 was used to assess cerebrovascular burden.
Assessments were performed at the Seoul National University Bundang Hospital (SNUBH). The respondents who could not visit the SNUBH took all assessments at home. The study protocol was approved by the Institutional Review Board of SNUBH.
Final diagnoses and the Clinical Dementia Rating (CDR) indices23 were determined by a panel comprising four research neuropsychiatrists. Two of the diagnostic panel members (KWK and DYL) were certified as CDR raters by the Memory and Aging Project of the Alzheimer's Disease Research Center, at the Washington University School of Medicine. Diagnoses of dementia and other major psychiatric disorders were made according to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders fourth edition criteria.24
MCI was diagnosed according to the consensus criteria from the International Working Group on Mild Cognitive Impairment.25,26 We determined the presence of objective cognitive impairment when a subject scored worse than -1.5 SD on the age-, gender-, and education-adjusted norms for Korean elders on any of the 8 neuropsychological tests excluding the MMSE of the CERAD-K-N. Intact or minimally impaired functional activity was defined as worth 1 point or less on the Blessed Dementia Scale included in the CERAD-K-C.
Descriptive statistics were calculated to determine the demographic and clinical characteristics of the subjects. The demographic and neuropsychological characteristics of the PCA and NCA groups were compared using Student's t tests and chi square tests. Two-way multivariate analysis of covariance was performed to examine the effects of diagnosis (PCA, NCA) and age (separated into categories of 65-69 years old, 70-74 years old and 75 years old or over) on frontal function test performance. GDS-KR scores and educational level were entered as covariates. All the statistical analyses were done using SPSS 17.0.
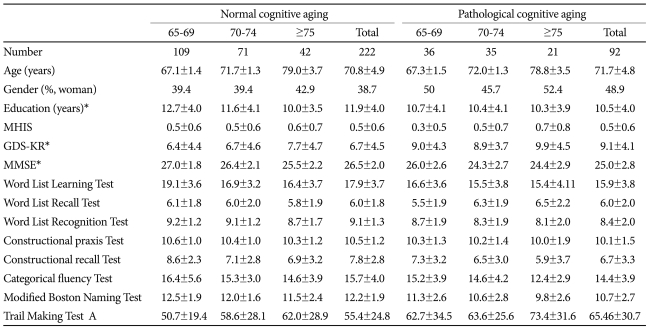
The demographic characteristics of the subjects are presented in Table 1. As expected, the PCA group showed lower performance in the MMSE, word list learning test, word list recognition test, and modified Boston naming test than the NCA group (t=5.374, p<0.001). Although subjects with depressive disorders were excluded from both groups, the PCA group showed higher GDS-KR scores than the NCA group (t=-4.450, p<0.001). The PCA group was also less educated than the NCA group (t=2.682, p=0.008). However, age (p=0.143), gender distribution (χ2=2.77, p=0.096) and MHIS (p=0.538) score were comparable between the two groups.
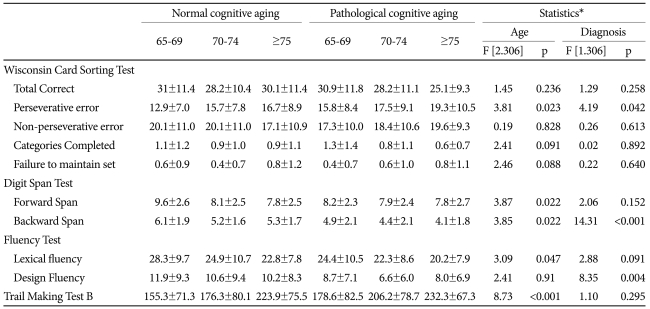
Table 2 summarizes the impact of the diagnosis (PCA, NCA) and age (65-69 years old, 70-74 years old and 75 years old or over) on frontal functions adjusting for the GDS-KR and the level of education. The main effects of both the diagnosis (F=2.860, p=0.002) and the age group (F=2.484, p<0.001) were significant. There was found to be no significant interaction between diagnosis and age (F=1.228, p=0.224). The PCA group performed less well in the backward digit span test (F=14.306, p<0.001) and fixed condition design fluency test (F=8.347, p=0.004) and had more perseverative errors in the WCST (F=4.19, p=0.042) compared with the NCA group. After Bonferroni correction, the main effect of the diagnosis remained significant only in the backward digit span test and the fixed condition design fluency test. The older individuals showed the lower performance and most perseverative errors in the WCST (F=3.81, p=0.023), digit span forward test (F=3.87, p=0.022), digit span backward test (F=3.85, p=0.022), lexical fluency test (F =3.09, p=0.047 and TMT-B (F=8.737, p<0.001). After Bonferroni correction, the main effect of age remained significant only in the TMT-B. Other test scores were not influenced by diagnosis or age.
We found that the performance of design fluency and backward digit span tests were associated with PCA after adjusting for the influences of age, level of education and depressive symptoms.
Impaired design fluency could be attributed to deficits in various cognitive functions such as general fluency, visuoconstructive ability, fine motor coordination, graphmotor speed, cognitive flexibility, the ability to create novel response without repetition, and the ability to switch between various strategies to maximize production of responses while at the same time avoiding response repetition.27-30 Yet since lexical and categorical verbal fluencies were comparable between the PCA group and the NCA group, it does not seem possible to attribute impaired design fluency to deficits in general fluency or the ability to switch between strategies. It also does not seem to be attributed to deficits in visuoconstructive ability, fine motor coordination or motor speed either because performances in the constructional praxis test and the TMT-A of the CERAD-K-N were comparable between the two groups.
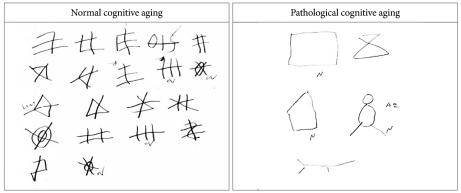
The design fluency test requires more divergent thinking than verbal fluency test.31 Although verbal fluency tests require the ability to produce words, the words that can be produced are not novel given that they are stored in the individual's existing lexicon or verbal knowledge. Therefore verbal fluency tests assess retrieval processes from lexical and semantic memory32 rather than productive thinking. By contrast, the design fluency test can examine the ability to create novel responses without repetition, and flexible thinking because it is de-signed to assess visual inventiveness which could not named (Figure 1).18 This creativity is fostered by the frontal lobe, particularly the prefrontal cortex.33,34 In this sense, the design fluency test may assess more specifically frontal lobe functioning than verbal fluency tests do. In addition, the design fluency test may be sensitive to changes in either the dominant or non-dominant hemisphere. In some previous studies, verbal fluency tasks were related to activation of the left frontal lobe wh-ereas the design fluency task was related to activation of both left and right frontal lobes.18,35
Since most dementing illnesses, including AD, show frontal dysfunctions in their early stages,4,36 using design fluency task that is specific to frontal function, sensitive to changes in both frontal lobes, and robust against the influence of aging may be a good neuropsychological marker for PCA.
Deficits in backward digit span were also associated with the PCA in the present study. This is consistent with earlier observations that a deficit in working memory is one of the earliest signs of dementia.37,38 However, the backward digit span test seemed to be less useful as a neuropsychological marker of PCA than the design fluency task given that its performance was considerably influenced by age and that there are many other sophisticated means of testing working memory, e.g. the word list learning test. The TMT-B is one of the most widely used tests for assessing frontal function. However, using the TMT-B to detect early changes in frontal function associated with PCA may not be the best option, because the effect of aging on the performance of TMT-B was significant in the present study. This observation was in line with the results from previous studies.39-41
Several limitations warrant consideration in generalizing our observations. First, the constructional praxis test in the CERAD-K-N is too simple to effectively identify subtle impairments in visuospatial ability. Therefore, although the performance of the constructional praxis test was comparable between the PCA and NCA groups in the present study, further studies are needed into whether the impaired design fluency may be attributed to deficits in visuoconstructional ability. Second, PCA was simply decided by the individual's having MCI. Although MCI is regarded as a high risk condition of dementia and other cognitive disorders, about two-thirds of MCI sufferers do not progress to having dementia or other cognitive disorders.42,43 Lastly, due to the cross-sectional nature of the present study, a prospective longitudinal study is warranted that can determine whether impaired design fluency can predict incident PCA such as dementia.
Despite these limitations, the conclusion remains that the design fluency task is a simple and sensitive neuropsychological marker to detect pathological cognitive aging.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a grant from the Korean Health Technology R&D Project, Ministry for Health, Welfare, & Family Affairs, Republic of Korea (Grant No. A092077).
References
1. Rabbitt P. Frontal brain changes and cognitive performance in old age. Cortex 2005;41:238-240. PMID: 15714914.


2. Duncan J, Burgess P. Fluid intelligence after frontal lobe lesions. Neuropsychologia 1995;33:261-268. PMID: 7791994.


3. Lezak MD, Howieson DB, Loring DW. Neuropsychological Assessment. 2004,Oxford: Oxford University Press.
4. Mosconi L. Brain glucose metabolism in the early and specific diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease. FDG-PET studies in MCI and AD. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2005;32:486-510. PMID: 15747152.



5. Laakso MP, Soininen H, Partanen K, Helkala EL, Hartikainen P, Vainio P, et al. Volumes of hippocampus, amygdala and frontal lobes in the MRI-based diagnosis of early Alzheimer's disease: correlation with memory functions. J Neural Transm Park Dis Dement Sect 1995;9:73-86. PMID: 7605591.


6. Zhou B, Zhao Q, Teramukai S, Ding D, Guo Q, Fukushima M, et al. Executive function predicts survival in Alzheimer disease: a study in Shanghai. J Alzheimers Dis 2010;22:673-682. PMID: 20847419.


7. Bisiacchi PS, Borella E, Bergamaschi S, Carretti B, Mondini S. Interplay between memory and executive functions in normal and pathological aging. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol 2008;30:723-733. PMID: 18608665.


8. Rapp MA, Reischies FM. Attention and executive control predict Alzheimer disease in late life: results from the Berlin Aging Study (BASE). Am J Geriatr Psychiatry 2005;13:134-141. PMID: 15703322.


9. Traykov L, Baudic S, Raoux N, Latour F, Rieu D, Smagghe A, et al. Patterns of memory impairment and perseverative behavior discriminate early Alzheimer's disease from subcortical vascular dementia. J Neurol Sci 2005;229-230:75-79. PMID: 15760623.


10. Grigsby J, Kaye K, Shetterly SM, Baxter J, Morgenstern NE, Hamman RF. Prevalence of disorders of executive cognitive functioning among the elderly: findings from the San Luis Valley Health and Aging Study. Neuroepidemiology 2002;21:213-220. PMID: 12207148.


11. Park JH, Lim S, Lim JY, Kim KI, Han MK, Yoon IY, et al. An overview of the Korean Longitudinal Study on Health and Aging (KLoSHA). Psychiatry Investig 2007;4:84-95.
12. Lee JH, Lee KU, Lee DY, Kim KW, Jhoo JH, Kim JH, et al. Development of the Korean version of the Consortium to Establish a Registry for Alzheimer's Disease Assessment Packet (CERAD-K): clinical and neuropsychological assessment batteries. J Gerontol B Psychol Sci Soc Sci 2002;57:P47-P53. PMID: 11773223.



13. Yoo SW, Namkoong K, Kim SJ, Kim CH, Chae JH, Oh KS, et al. Validity of Korean version of the Mini-international Neuropsychiatric interview. Anxiety Mood 2006;2:50-55.
14. Lee DY, Lee KU, Lee JH, Kim KW, Jhoo JH, Kim SY, et al. A normative study of the CERAD neuropsychological assessment battery in the Korean elderly. J Int Neuropsychol Soc 2004;10:72-81. PMID: 14751009.


15. Heaton RK, Chelune GJ, Talley JL, Kay GG, Curtiss G. Wisconsin Card Sorting Test Manual: Revised and Expanded. 1993,Odessa: Psychological Assessment Resources.
16. Wechsler D. Technical Manual for the Wechsler Adult Intelligence and Memory Scale. 1997,Third Edition. New York: The Psychological Corporation.
17. Benton AL, Hamsher K de S. Multilingual Aphasia Examination. 1976,Iowa City: University of Iowa.
18. Jones-Gotman M, Milner B. Design fluency: the invention of nonsense drawings after focal cortical lesions. Neuropsychologia 1977;15:653-674. PMID: 896022.


19. Seo EH, Lee DY, Kim KW, Lee JH, Jhoo JH, Youn JC, et al. A normative study of the Trail Making Test in Korean elders. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry 2006;21:844-852. PMID: 16955436.


20. Spreen O, Strauss E. A Compendium of Neuropsychological Test: Administration, Norms, and Commentary. 1991,New York: Oxford University Press.
21. Kim JY, Park JH, Lee JJ, Huh Y, Lee SB, Han SK, et al. Standardization of the korean version of the geriatric depression scale: reliability, validity, and factor structure. Psychiatry Investig 2008;5:232-238.



22. Hachinski VC, Iliff LD, Zilhka E, Du Boulay GH, McAllister VL, Marshall J, et al. Cerebral blood flow in dementia. Arch Neurol 1975;32:632-637. PMID: 1164215.


23. Hughes CP, Berg L, Danziger WL, Coben LA, Martin RL. A new clinical scale for the staging of dementia. Br J Psychiatry 1982;140:566-572. PMID: 7104545.


24. American Psychiatric Association. Task Force on DSM-IV. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders: DSM-IV. 1994,Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association.
25. Petersen RC. Mild cognitive impairment as a diagnostic entity. J Intern Med 2004;256:183-194. PMID: 15324362.


26. Winblad B, Palmer K, Kivipelto M, Jelic V, Fratiglioni L, Wahlund LO, et al. Mild cognitive impairment--beyond controversies, towards a consensus: report of the International Working Group on Mild Cognitive Impairment. J Intern Med 2004;256:240-246. PMID: 15324367.


27. Varney NR, Roberts RJ, Struchen MA, Hanson TV, Franzen KM, Connell SK. Design fluency among normals and patients with closed head injury. Arch Clin Neuropsychol 1996;11:345-353. PMID: 14588939.



28. Ruff RM, Allen CC, Farrow CE, Niemann H, Wylie T. Figural fluency: differential impairment in patients with left versus right frontal lobe lesions. Arch Clin Neuropsychol 1994;9:41-55. PMID: 14589511.



29. Mickanin J, Grossman M, Onishi K, Auriacombe S, Clark C. Verbal and nonverbal fluency in patients with probable Alzheimer's disease. Neuropsychology 1994;8:385-394.

30. Bigler ED, Schultz R, Grant M, Knignt G, Lucas J, Roma M, et al. Design fluency in dementia of the Alzheimers type: preliminary findings. Neuropsychology 1988;2:127-133.

31. Bigler ED. Design fluency in dementia of Alzheimer's type, multi-infarct dementia and dementia associated with alcoholism. Appl Neuropsychol 1995;2:7-14. PMID: 16318546.


32. Raboutet C, Sauzeon H, Corsini MM, Rodrigues J, Langevin S, N'Kaoua B. Performance on a semantic verbal fluency task across time: Dissociation between clustering, switching, and categorical exploitation processes. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol 2010;32:268-280. PMID: 19657912.


33. Flaherty AW. Brain illness and creativity: mechanisms and treatment risks. Can J Psychiatry 2011;56:132-143. PMID: 21443820.


34. de Souza LC, Volle E, Bertoux M, Czernecki V, Funkiewiez A, Allali G, et al. Poor creativity in frontotemporal dementia: a window into the neural bases of the creative mind. Neuropsychologia 2010;48:3733-3742. PMID: 20868703.


35. Fama R, Sullivan EV, Shear PK, Cahn-Weiner DA, Marsh L, Lim KO, et al. Structural brain correlates of verbal and nonverbal fluency measures in Alzheimer's disease. Neuropsychology 2000;14:29-40. PMID: 10674796.



36. Stokholm J, Vogel A, Gade A, Waldemar G. Heterogeneity in executive impairment in patients with very mild Alzheimer's disease. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 2006;22:54-59. PMID: 16682794.


37. Huntley JD, Howard RJ. Working memory in early Alzheimer's disease: a neuropsychological review. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry 2010;25:121-132. PMID: 19672843.


38. Kalbe E, Kessler J, Calabrese P, Smith R, Passmore AP, Brand M, et al. DemTect: a new, sensitive cognitive screening test to support the diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment and early dementia. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry 2004;19:136-143. PMID: 14758579.


39. Perry ME, McDonald CR, Hagler DJ Jr, Gharapetian L, Kuperman JM, Koyama AK, et al. White matter tracts associated with set-shifting in healthy aging. Neuropsychologia 2009;47:2835-2842. PMID: 19540862.



40. Zakzanis KK, Mraz R, Graham SJ. An fMRI study of the Trail Making Test. Neuropsychologia 2005;43:1878-1886. PMID: 16168730.


41. Salthouse TA, Fristoe NM. Process analysis of adult age effects on a computer-administered trail making test. Neuropsychology 1995;9:518-528.

42. Han JW, Lee SB, Kim TH, Park JH, Lee JJ, Huh YS, et al. Functional Impairment in the diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord 2011;25:225-229. PMID: 21285856.


43. Mitchell AJ, Shiri-Feshki M. Rate of progression of mild cognitive impairment to dementia--meta-analysis of 41 robust inception cohort studies. Acta Psychiatr Scand 2009;119:252-265. PMID: 19236314.