 |
 |
- Search
| Psychiatry Investig > Volume 11(3); 2014 > Article |
Abstract
Objective
Cholinergic nicotinic receptor (CHRN) gene family has been known to mediate the highly additive effects of nicotine in the body, and implicated nicotine dependence (ND) and related phenotypes. Previous studies have found that CHRNA6-CHRNB3 cluster polymorphisms were significantly associated with the risk of ND and various tobacco behaviors. The aim of study was to evaluate the genetic association of CHRNB3 and CHRNA6 polymorphisms with the risk of ND based on the Fagerstrom Test for Nicotine Dependence (FTND) score and five subscales of nicotine dependence syndrome scale (NDSS) in Korean population.
Methods
Six SNPs in CHRNA6-CHRNB3 cluster were analyzed in 576 Korean subjects. Association analysis using logistic models and regression analysis with NDSS were performed.
Results
There was no association in the case-control analysis, whereas all six SNPs were significantly associated with drive factor among NDSS in subgroup based on the FTND score. CHRNB3 rs4954 and CHRNA6 rs16891604 showed significant associations with NDSSF1 (drive) in dominant models among moderate to severe ND among smokers after correction (pcorr=0.02 and 0.001, respectively), whereas other four SNPs showed significant associations among mild ND after correction (pcorr=0.03-0.02 in dominant model).
Conclusion
This study showed that the genetic influence of CHRNB3-CHRNA6 cluster polymorphisms are found in a ND endophenotype (drive) using NDSS subscales, rather than the risk of ND in Korean population. Our findings might be the first report for the association of CHRNB3-CHRNA6 cluster with ND-related phenotypes in Korean and might offer an approach to elucidating the molecular mechanisms of ND and ND-related phenotypes.
Cigarette smoking is a major health problem and a leading environmental risk factor for several diseases, such as pulmonary disease and cancer worldwide. Despite the increasing awareness of health-related consequences, a large number of smokers fail to stop smoking due to their nicotine dependence (ND).1 The genetic influences on nicotine dependence were established through twin studies,2,3,4 and genetic factors with heritability account for between 40-70% of the phenotypic variance.3,4,5,6
Cholinergic nicotinic receptor (CHRN) gene family code pentameric molecular assemblies of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR) subunits mediate the highly additive effects of nicotine in the body.7 According to the functional importance of nicotinic subunit genes, early genetic association studies of nicotine dependence have been focused on CHRNA4 and CHRNB2,7,8 and the significant associations of the CHRNA5-CHRNA3-CHRNB4 cluster, CHRNB3-CHRNA6 cluster and level of nicotine dependence have been recently reported.9,10 Besides these subunit genes, CHRNB3 and CHRNA5 have emerged as strong candidates for nicotine dependence in two recent reports of a genome-wide association and high-throughput candidate gene survey,9,10 and variants in or near CHRND-CHRNG, CHRNA7, and CHRNA10 show modest association with nicotine dependence risk in African-Americans.11 It has been also suggested that genetic variants in the CHRN gene family are associated with tobacco-related behaviors. CHRNA5 rs16969968 and rs588765 affect smoking quantity,12 and CHRNA4 variants have been associated with tobacco-related behaviors.8,13,14
CHRNB3 rs4950 and rs13280604 are significantly associated with the subjective response factors to initial tobacco use.15 Although studies on smoking and ND based on linkage scans and the candidate gene approach have yielded somewhat inconsistent results,16 genetic influences of the CHRN gene family have been replicated in separate community samples and other ethnic populations.11,15
The assessment of ND has relied largely on the use of the Fagerström Tolerance Questionnaire (FTQ) or the Fagerstrom Test for Nicotine Dependence (FTND).17,18 The Fagerström scales were originally developed as unidimensional measures of physical tolerance. There is no assessment of other important aspects of ND, such as craving, subjective compulsion to smoke, nicotine withdrawal, behavioral saliency, or behavioral automaticity, which are now regarded as core constructs. The nicotine dependence syndrome scale (NDSS) was developed using a multidimensional concept of ND, and includes scores on five subscales: Drive, Priority, Tolerance, Continuity, and Stereotypy.19
Previous studies have found that the CHRNA6-CHRNB3 cluster polymorphisms were significantly associated with the risk of ND and various tobacco behaviors,9,10,15,20 and these associations were replicated in a large meta-analysis in samples of European ancestry from the ENGAGE consortium.21 To the best of our knowledge, there is no genetic association study of the CHRNA6-CHRNB3 cluster with the risk of ND and the multidimensional nicotine dependence measure in the Asian population, especially in the Korean population. The aim of the current study was to evaluate the genetic association of CHRNB3 and CHRNA6 polymorphisms with the risk of ND based on the FTND score and five subscales of NDSS in the Korean population.
Nicotine-dependent patients in several community mental health centers and hospital nicotine dependence clinics were recruited. All (n=371) were diagnosed using the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fourth Edition (DSM-IV) criteria. The population controls (n=205) consisted of randomly selected students from Eulji University and Ulsan University of Korea. After a detailed explanation about the process of this study, informed consent was obtained. The Institutional Review Board of the hospital had approved the study. Clinical data from the K-NDSS tests (Korean version of NDSS) were obtained. The clinical profiles of the study subjects were summarized in Table 1.
Candidate SNPs were selected using the database in the Asian population from the International HapMap Project database (http://hapmap.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov). SNP selection was based on the following criteria; In the 80-kb region including the CHRNB3 and CHRNA6 genes, SNPs were selected taking into consideration their minor allele frequencies (MAFs; ≥5%) and linkage disequilibrium (LD) (only one SNP if there were in absolute; r2≥0.95).
For genotyping of the polymorphic sites, the amplifying primers and probes were designed for TaqMan (Supplementary Table 1, online). The PCRs were run on a TaqMan Universal Master Mix without UNG (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA) but with a PCR primer concentration of 900 nM and a TaqMan MGB-probe concentration of 200 nM. The reactions were carried out in a 384-well format in a total reaction volume of 5 uL with 20 ng of the genomic DNA. The plates then were placed in a thermal cycler (PE 9700, Applied Biosystems) and heated to 50℃ for 2 minutes and 95℃ for 10 minutes; this step was followed by 40 cycles of 95℃ for 15 seconds and 60℃ for 1 minute. Ten percent of the samples were randomly selected for repeated genotyping, and the results were 100% concordant. The TaqMan assay plates were then transferred to a Prism 7900HT instrument (Applied Biosystems), which we used to measure the fluorescence intensity in each well of the plate. The fluorescence data files from each plate were analyzed with automated software (SDS 2.1).
Haplotypes were inferred using the algorithm developed by the Broad Institute, Haploview.22 We examined Lewontin's D' (|D'|) and the linkage disequilibrium coefficient r2 between all pairs of biallelic loci.23 The allelic distributions of polymorphisms and haplotypes among patients with nicotine dependence and normal subjects were evaluated by logistic regression models calculating odd ratios (OR), 95% confidential intervals (CI) and corresponding P-values using age and sex as covariates. According to the FTND scores, the genotype distributions of patients with severe and mild nicotine dependence were also compared to that of non-smokers. A regression model was used for association analyses with five NDSS subscale factors, adjusting for age and sex as covariates. To correct for multiple testing, the effective number of independent markers was calculated using the software SNPSpD (http://genepi.qimr.edu.au/general/daleN/SNPSpD), which is based on the spectral decomposition (SpD) of matrices of pair-wise LD values between SNPs.24 The resulting number of independent marker loci of the CHRNB3-CHRNA6 region (3.499) was applied to correct for multiple testing. We analyzed all the subjects and the dichotomized subgroups; mild ND (FTND less than 4) and moderate-to-severe (FTND given 4 or more).
In this study, we examined the association of polymorphisms in the CHRNB3 and CHRNA6 gene region with the risk of nicotine dependence in Korean subjects (n=576). Asian genotype information on 72 SNPs in about 80 kb regions of the CHRNB3 and CHRNA6 gene were extracted from the International HapMap database, and six SNPs were finally selected, and then genotyped in 371 smokers and 205 non-smokers. The minor allele frequency and Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium are summarized in the Supplementary Table 2 (online). Linkage disequilibria among SNPs were measured by calculating Lewontin's D' and r2 values (Supplementary Figure 1, online), and rs13280604, rs1689161, rs9298628 and rs10109040 were tightly linked with one another. The haplotypes were constructed using six SNPs and only one haplotype (ht1) among three major haplotypes was used for further analyses because ht2 and ht3 were almost equivalent to rs16891604 and rs4954, respectively.
Initially, when the association analysis of six SNPs and a haplotype were examined using logistic regression models between smokers and non-smokers, no association was observed (Table 2). The genetic effects of polymorphisms on the five subscale factors of NDSS were analyzed using regression models. CHRNA3 rs4954 and CHRNA6 rs16891604 showed significant associations with NDSSF1 (drive) in dominant models among moderate-to-severe ND among smokers after correction (pcorr=0.02 and 0.001, respectively) (Table 3), whereas the other four SNPs were significantly associated with NDSSF1 among mild ND after correction (pcorr=0.04-0.03 in the codominant model and pcorr=0.03-0.02 in the dominant model) (Table 3). Overall associations showed that the drive subscale of ND was decreased in subjects with minor alleles, but CHRNB3 rs4954 showed an increase in the drive subscale. In the additional association analyses for the rest of the NDSSFs, no association was observed (Supplementary Table 3, online).
Drive, which is an essential factor in addiction and one of the NDSS factors, is defined as a presence of craving or withdrawal in the abstinence period. Using the regression analyses of subscales of NDSS among Korean smokers revealed that CHRNB3 and CHRNA6 polymorphisms were significantly associated with the drive subscale factor (Table 3). Interestingly, the genetic associations of four SNPs in CHRNB3 and CHRNA6 (rs13280604, rs16891651 in CHRNB3; and rs9298628, rs10109040 in CHRNA6) were found only in mild ND, whereas CHRNB3 rs4954 and CHRNA6 rs16891604 showed the associations in moderate-to-severe ND. The genetic effects in the dominant model of CHRNB3 rs4954 and CHRNA6 rs16891604 were opposite from each other, that is, CHRNB3 rs4954 increased the craving of smoking in moderate-to-severe ND subjects but CHRNA6 rs16891604 reduced it. Our results showed that none of the CHRNB3 and CHRNA6 polymorphisms affected the diagnosis of ND; however, CHRNB3 rs4954 and CHRNA6 rs16891604 might play an important role in the craving and withdrawal of smoking in the abstinence period of severe ND subjects, respectively. On the other hand, the rest 4 SNPs of CHRNB3 and CHRNA6, which showed tight linkage with one another, showed the genetic effect for the withdrawal of smoking. These results implicated that the genetic function of CHRNB3-CHRNA6 gene cluster polymorphisms might differ in accordance with the phase of ND. Although CHRNB3 rs4954 also showed the reduced effect of the drive subscale in mild ND, and this effect of CHRNB3 rs4954 might be due to its low number of subjects with minor homozygote. The limitations of the current study were the low number of subjects and the differences in the male/female ratio and average age between ND smokers and non-smokers. Although these limitations could affect our results by positive or negative false errors, our results might offer a plausible clue of the genetic factors related with ND-related endophenotypes. In fact, the statistical power in the case-control analysis was relatively low (46.70-72.95%) (Table 2), and the additional analysis of the risk of ND in male subjects showed that there was no big difference in the distribution and association results (Supplementary Table 4, online).
Several studies have shown that polymorphisms in the CHRNB3-CHRNA6 cluster are associated with the risk of ND and related phenotypes, such as smoking behaviors. CHRNB3 rs9298629 (absolute LD with rs9298628 in the current study) showed nominal association with the risk of ND in female Israelis.20 Associations of SNPs in the 5' region of CHRNB3 and 3' UTR of CHRNA6 with the risk of ND were also found in US-based samples and Australian-based European-Ancestry samples.9 Moreover, CHRNB3 rs4950 and rs13280604 were significantly associated with ND-related phenotypes, such as the subjective responses to nicotine.15 However, the association of previous studies showed somewhat different results to our results, especially the association results for the risk of ND. The analysis of the MAF and LD structure of 6 polymorphisms among three typical ethnic groups, including Asian, Caucasian and African data from 1000 genome databases (http://browser.1000genomes.org/index.html) revealed that the MAF of CHRNA6 rs16891604 was quite different from that of Caucasians and Africans (Supplementary Table 5, online), and that the LD structures of tested ethnic groups were quite different with one another (Supplementary Figure 2, online). Therefore, our results could be valuable because polymorphisms tested might be specific to ethnic group.
In a study of NDSS using a criterion-group design contrasting chippers and regular smokers, the drive subscale was the most robust correlate of group membership, with an odds ratio of 6.45, accounting for 54% of the variance. The area under the ROC curve for Drive was 0.92, again indicating a very high degree of discrimination.25 Therefore, the drive subscale may be the most important factor among the subscales of NDSS. Exploring the appropriate phenotype or endophenotype in a genetic study is essential; however, it is difficult to know in advance which phenotype might be associated with specific genes or SNPs. The use of multidimensional scales such as NDSS potentially aids in exploring the construct and nature of ND. In a recent Finnish cohort study, NDSS were used as an ND endophenotype measurement, and it was reported that the tolerance factor of the NDSS showed a suggestive association to CHRNB4 rs11636753, rs11634351, and rs1948.26
The nicotine dependence phenotype/endophenotype could be various and differ by gender. As mentioned in the limitations, our study did not have an even male/female ratio. In future research, age- and sex-matched genetic analysis is needed.
An a priori assumption of our study was the genetic influences of CHRNB3 and CHRNA6 for the risk of ND as well as ND-related endophenotype. Our results implicated that CHRNB3 and CHRNA6 polymorphisms might be genetic predispositions for the ND-related endophenotypes rather than the risk of ND in the Korean population. To the best of our knowledge, our results may be the first report investigating the association of the CHRNB3-CHRNA6 cluster with ND-related endophenotypes, including subscale factors of NDSS in the Korean population. The current study may be meaningful, although there were several limitations in our study (e.g., the small sample size and smaller portion of females among ND subjects than that of controls).
In conclusion, this study showed that the genetic influence of CHRNB3-CHRNA6 cluster polymorphisms are found in the ND endophenotype (drive) using NDSS subscales, rather than the risk of ND in the Korean population. These effects of multiple loci were different between mild and moderate-to-severe groups of ND. Our findings could offer an approach to elucidating the molecular mechanisms of ND and ND-related phenotypes in the Korean population.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a grant of the Ministry of Health and Welfare, Republic of Korea (A090058).
Supplementary Material
Supplementary Table 2
Allele frequency of CHRNB3 and CHRNA6 polymorphisms in Korean subjects
Supplementary Table 3
Regression analyses of CHRNB3 and CHRNA6 polymorphisms with NDSSF2, NDSSF3, NDSSF4 and NDSSF5 in smokers
Supplementary Table 4
Association analysis of CHRNB3 and CHRNA6 polymorphisms with the nicotine dependence in Korean male subjects
Supplementary Figure 1
Physical map of CHRNB3-CHRNA6 gene region. A: Gene map and SNPs in CHRNB3 and CHRNA6 on chromosome 8p11.2-21. Coding exons are marked by black blocks, and 5' and 3' UTRs by white blocks. B: Haplotypes of CHRNB3 and CHRNA6. Haplotypes with frequency >0.05 are used for further analysis. C: Linkage disequilibrium coefficient among CHRNB3 and CHRNA6S-NPs. CHRN: cholinergic nicotinic receptor, LD: linkage disequilibrium.
Supplementary Figure 2
Diagram of LD structures of Korean (A), Asian (Japanese+Chinese; B), Caucasian (C) and African (D) from 1000 genome database. LD: linkage disequilibrium.
References
2. Lessov CN, Martin NG, Statham DJ, Todorov AA, Slutske WS, Bucholz KK, et al. Defining nicotine dependence for genetic research: evidence from Australian twins. Psychol Med 2004;34:865-879. PMID: 15500307.


3. Swan GE, Carmelli D, Rosenman RH, Fabsitz RR, Christian JC. Smoking and alcohol consumption in adult male twins: genetic heritability and shared environmental influences. J Subst Abuse 1990;2:39-50. PMID: 2136102.


4. Maes HH, Sullivan PF, Bulik CM, Neale MC, Prescott CA, Eaves LJ, et al. A twin study of genetic and environmental influences on tobacco initiation, regular tobacco use and nicotine dependence. Psychol Med 2004;34:1251-1261. PMID: 15697051.


5. Rhee SH, Hewitt JK, Young SE, Corley RP, Crowley TJ, Stallings MC. Genetic and environmental influences on substance initiation, use, and problem use in adolescents. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2003;60:1256-1264. PMID: 14662558.


6. Li MD, Cheng R, Ma JZ, Swan GE. A meta-analysis of estimated genetic and environmental effects on smoking behavior in male and female adult twins. Addiction 2003;98:23-31. PMID: 12492752.


7. Lindstrom JM. Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors of muscles and nerves: comparison of their structures, functional roles, and vulnerability to pathology. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2003;998:41-52. PMID: 14592862.


8. Ehringer MA, Clegg HV, Collins AC, Corley RP, Crowley T, Hewitt JK, et al. Association of the neuronal nicotinic receptor beta2 subunit gene (CHRNB2) with subjective responses to alcohol and nicotine. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 2007;144B:596-604. PMID: 17226798.


9. Bierut LJ, Madden PA, Breslau N, Johnson EO, Hatsukami D, Pomerleau OF, et al. Novel genes identified in a high-density genome wide association study for nicotine dependence. Hum Mol Genet 2007;16:24-35. PMID: 17158188.


10. Saccone SF, Hinrichs AL, Saccone NL, Chase GA, Konvicka K, Madden PA, et al. Cholinergic nicotinic receptor genes implicated in a nicotine dependence association study targeting 348 candidate genes with 3713 SNPs. Hum Mol Genet 2007;16:36-49. PMID: 17135278.


11. Saccone NL, Schwantes-An TH, Wang JC, Grucza RA, Breslau N, Hatsukami D, et al. Multiple cholinergic nicotinic receptor genes affect nicotine dependence risk in African and European Americans. Genes Brain Behav 2010;9:741-750. PMID: 20584212.



12. Saccone NL, Culverhouse RC, Schwantes-An TH, Cannon DS, Chen X, Cichon S, et al. Multiple independent loci at chromosome 15q25.1 affect smoking quantity: a meta-analysis and comparison with lung cancer and COPD. PLoS Genet 2010;6.

13. Feng Y, Niu T, Xing H, Xu X, Chen C, Peng S, et al. A common haplotype of the nicotine acetylcholine receptor alpha 4 subunit gene is associated with vulnerability to nicotine addiction in men. Am J Hum Genet 2004;75:112-121. PMID: 15154117.



14. Li MD, Beuten J, Ma JZ, Payne TJ, Lou X, Garcia V, et al. Ethnic- and gender-specific association of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor alpha4 subunit gene (CHRNA4) with nicotine dependence. Hum Mol Genet 2005;14:1211-1219. PMID: 15790597.


15. Zeiger JS, Haberstick BC, Schlaepfer I, Collins AC, Corley RP, Crowley TJ, et al. The neuronal nicotinic receptor subunit genes (CHRNA6 and CHRNB3) are associated with subjective responses to tobacco. Hum Mol Genet 2008;17:724-734. PMID: 18055561.


16. Han S, Gelernter J, Luo X, Yang BZ. Meta-analysis of 15 genome-wide linkage scans of smoking behavior. Biol Psychiatry 2010;67:12-19. PMID: 19819424.



17. Fagerstrom KO. Measuring degree of physical dependence to tobacco smoking with reference to individualization of treatment. Addict Behav 1978;3:235-241. PMID: 735910.


18. Heatherton TF, Kozlowski LT, Frecker RC, Fagerstrom KO. The Fagerstrom Test for Nicotine Dependence: a revision of the Fagerstrom Tolerance Questionnaire. Br J Addict 1991;86:1119-1127. PMID: 1932883.


19. Shiffman S, Waters A, Hickcox M. The nicotine dependence syndrome scale: a multidimensional measure of nicotine dependence. Nicotine Tob Res 2004;6:327-348. PMID: 15203807.


20. Greenbaum L, Kanyas K, Karni O, Merbl Y, Olender T, Horowitz A, et al. Why do young women smoke? I. Direct and interactive effects of environment, psychological characteristics and nicotinic cholinergic receptor genes. Mol Psychiatry 2006;11:312-322. PMID: 16314871.


21. Thorgeirsson TE, Gudbjartsson DF, Surakka I, Vink JM, Amin N, Geller F, et al. Sequence variants at CHRNB3-CHRNA6 and CYP2A6 affect smoking behavior. Nat Genet 2010;42:448-453. PMID: 20418888.



22. Barrett JC, Fry B, Maller J, Daly MJ. Haploview: analysis and visualization of LD and haplotype maps. Bioinformatics 2005;21:263-265. PMID: 15297300.


23. Hedrick PW. Gametic disequilibrium measures: proceed with caution. Genetics 1987;117:331-341. PMID: 3666445.




24. Nyholt DR. A simple correction for multiple testing for single-nucleotide polymorphisms in linkage disequilibrium with each other. Am J Hum Genet 2004;74:765-769. PMID: 14997420.



25. Shiffman S, Sayette MA. Validation of the nicotine dependence syndrome scale (NDSS): a criterion-group design contrasting chippers and regular smokers. Drug Alcohol Depend 2005;79:45-52. PMID: 15943943.



26. Broms U, Wedenoja J, Largeau MR, Korhonen T, Pitkaniemi J, Keskitalo-Vuokko K, et al. Analysis of detailed phenotype profiles reveals CHRNA5-CHRNA3-CHRNB4 gene cluster association with several nicotine dependence traits. Nicotine Tob Res 2012;14:720-733. PMID: 22241830.



Table 2
Association analysis of CHRNB3 and CHRNA6 polymorphisms with the nicotine dependence in Korean subjects
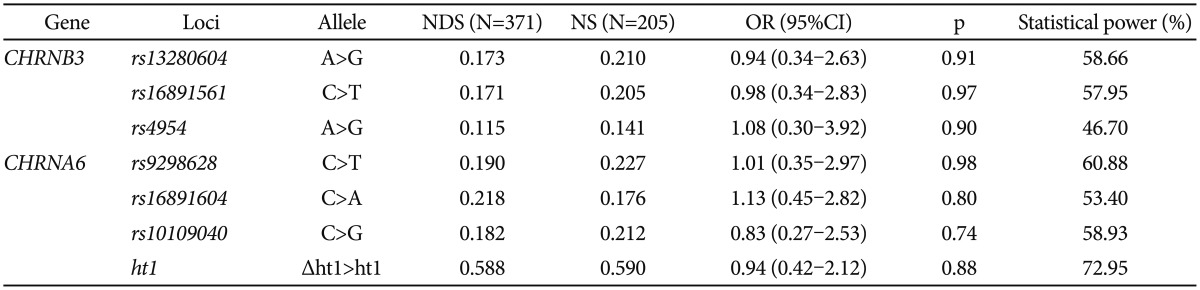
Table 3
Regression analyses of CHRNB3 and CHRNA6 polymorphisms with NDSSF1 (drive) among smokers
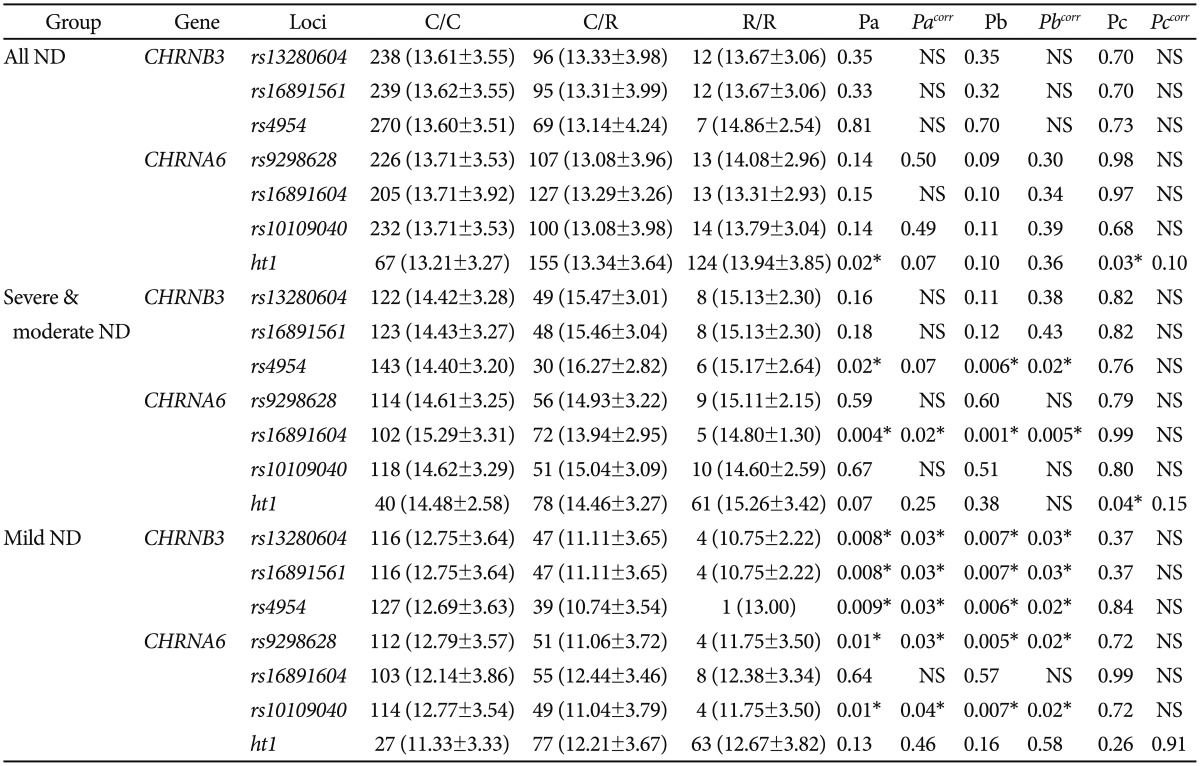
C/C, C/R and R/R represent major homozygotes, heterozygotes and minor homozygotes, respectively. Pa, Pb and Pc mean the p-values of codominant, dominant and recessive model, respectively. *p<0.05. ND: nicotine dependence, NS: non-smoker of population control, CHRN: cholinergic nicotinic receptor, NDSS: Nicotine Dependence Syndrome Scale







