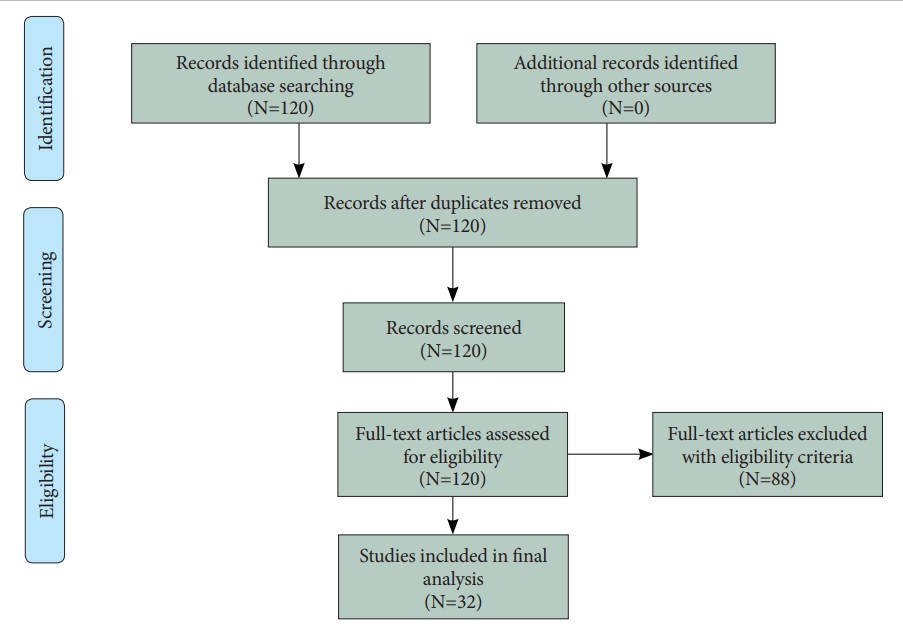
|
 |
- Search
| Psychiatry Investig > Volume 19(8); 2022 > Article |
|
Abstract
Notes
Availability of Data and Material
The datasets generated or analyzed during the study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: Kwang-Sig Lee, Byung-Joo Ham. Data curation: Kwang-Sig Lee, Byung-Joo Ham. Formal analysis: Kwang-Sig Lee, ByungJoo Ham. Funding acquisition: Byung-Joo Ham. Investigation: Kwang-Sig Lee, Byung-Joo Ham. Methodology: Kwang-Sig Lee, Byung-Joo Ham. Project administration: Kwang-Sig Lee, Byung-Joo Ham. Resources: Byung-Joo Ham. Software: Kwang-Sig Lee, Byung-Joo Ham. Supervision: Kwang-Sig Lee, Byung-Joo Ham. Validation: Kwang-Sig Lee, Byung-Joo Ham. Visualization: Kwang-Sig Lee, Byung-Joo Ham. Writing—original draft: Kwang-Sig Lee, Byung-Joo Ham. Writing—review & editing: KwangSig Lee, Byung-Joo Ham.
Funding Statement
This study was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (NRF-2020M3E5D9080792).
Table 1.
Different machine learning methods would be appropriate (i.e., would show the best performance measures) for different types of data for the early diagnosis of depression: 1) logistic regression, the random forest, the support vector machine and/or the artificial neural network in the case of numeric data; 2) the random forest in the case of genomic data; 3) the random forest and/or the support vector machine in the case of radiomic data; and 4) the random forest in the case of social-network-service data. Their performance measures reported varied within 60.1-100.0 for accuracy, 68.8-95.0 for sensitivity, 76.0-94.0 for specificity, and 64.0-96.0 for the AUC. ANN, artificial neural network; AR, augoregressive; AUC, area under the receiver operating characteristic curve; DT, decision tree; EEG, electroencephalogram; EN, elastic net; GB, gradient boosting; LR, logistic regression; NB, naïve bayes; RF, random forest; RMSE, root mean squared error; SNS, social network service; SNP, single nucleotide polymorphism; SVM, support vector machine
Table 2.
The following predictors would be important variables for the early diagnosis of depression: comorbid psychopathology, symptom-related disability, treatment credibility, access to therapists, time spent using certain internet-intervention modules; pain-fatigue (symptom intensity scale), comorbidity; 30 microbial markers (gut microbiota); psychological elasticity, income level; upper body movements-postures; brain connectivity within posterior cingulate cortex, within insula, between posterior cingulate cortex and insula/hippocampus-amygdala, between insula and precuneus, between superior parietal lobule and medial prefrontal cortex; single-nucleotide polymorphisms (rs12248560, rs878567, rs17710780); cingulate isthmus asymmetry, pallidal asymmetry, ratio of the paracentral to precentral cortical thickness, ratio of lateral occipital to pericalcarine cortical thickness; self-assessed cardiac-related fear, sex, number of words to answer the first homework assignment for internet-delivered psychotherapy. ANN, artificial neural network; AR, augoregressive; AUC, area under the receiver operating characteristic curve; DT, decision tree; EEG, electroencephalogram; EN, elastic net; GB, gradient boosting; LR, logistic regression; NB, naïve bayes; RF, random forest; RMSE, root mean squared error; SNS, social network service; SNP, single nucleotide polymorphism; SVM, support vector machine
REFERENCES