 |
 |
- Search
| Psychiatry Investig > Volume 14(3); 2017 > Article |
Abstract
Objective
Executive dysfunction might be an important determinant for response to pharmacotherapy in obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), and could be sustained independently of symptom relief. The anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) has been indicated as a potential neural correlate of executive functioning in OCD. The present study examined the brain-executive function relationships in OCD from the ACC-based resting state functional connectivity networks (rs-FCNs), which reflect information processing mechanisms during task performance.
Methods
For a total of 58 subjects [OCD, n=24; healthy controls (HCs), n=34], four subdomains of executive functioning were measured using the Rey-Osterrieth Complex Figure Test (RCFT), the Stroop Color-Word Test (SCWT), the Wisconsin Card Sorting Test (WCST), and the Trail Making Test part B (TMT-B). To probe for differential patterns of the brain-cognition relationship in OCD compared to HC, the ACC-centered rs-FCN were calculated using five seed regions systemically placed throughout the ACC.
Results
Significant differences between the OCD group and the HCs with respect to the WCST perseverative errors, SCWT interference scores, and TMT-B reaction times (p<0.05) were observed. Moreover, significant interactions between diagnosis×dorsal ACC [S3]-based rs-FCN strength in the right dorsolateral prefrontal cortex for RCFT organization summary scores as well as between diagnosis×perigenual ACC [S7]-based rs-FCN strength in the left frontal eye field for SCWT color-word interference scores were unveiled.
Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) is a relatively common and chronically disabling disorder with an average life-time prevalence of 2-3%.1 A neuroanatomical model of OCD proposes that clinical symptoms of obsessive thoughts, compulsive acts, and neurocognitive deficits are related to dysfunction in several parallel-running sub-networks that collectively comprise the cortico-striato-thalamo-cortical (CSTC) loop.23 Executive dysfunction in OCD encompasses visuoconstructive organization [measured using the Rey-Osterrieth Complex Figure Test (RCFT)] as well as cognitive flexibility and response control, which could be subdivided into subdomains of selective attention and response inhibition [measured using the Stroop Color-Word Test (SCWT)], decision making with set-shifting and strategic planning [measured using the Wisconsin Card Sorting Test (WCST)], and set-shifting with visuomotor sequencing [measured using the Trail Making Test part B (TMT-B)].4567 Executive dysfunction might be an important determinant for pharmacotherapeutic treatment responses in OCD, and could be sustained independently of symptom relief after pharmacotherapy.89 Therefore, a finer delineation of the neural foundations for impaired executive performance in OCD is critical for improved prognoses.10
The anterior cingulate cortex (ACC), a prefrontal cortical component of the CSTC loop,111213 has been indicated as a potential neural correlate of executive functioning in healthy subjects (HC) as well as subjects with OCD.614 The ACC undergoes a higher-than-average degree of cortical surface area expansion during neurodevelopment and maturation,15 with parallel development of a fine-grained resting-state functional connectivity network (rs-FCN) along the histologically heterogeneous rostro-caudal and dorso-ventral axes of the ACC subregions.161718 This creates a set of matured integrative hubs,17 including the caudal ACC (motoric executive control),19 the dorsal ACC (selective attention, response inhibition and set-maintenance),2021 the supragenual ACC (conflict detection/resolution and error processing),2223 the rostral ACC (mentalizing/decoding of external cues),24 and the subgenual ACC (emotional recognition/regulation as a prerequisite of cognitive control).2526 Indeed, the rs-FCN describes patterns of functional coherence between distributed brain regions during task-free status, reflecting a human information processing mechanism, such as executive functioning during task performance.2027
Several rs-FCN studies assessing OCD have focused on finding the core pathophysiology of OC symptomatology, as reflected in pattern changes within the orbitofrontal cortex (OFC)-based rs-FCN and the default mode network (DMN). The OFC shows increased amplitude of low-frequency fluctuation (ALFF; a measure of spontaneous regional neuronal activity),11 elevated degree centrality,28 and increased rs-FCN with the ventral2930 and dorsal16 caudate. Conversely, the posterior cingulate cortex (PCC)-based midline core subsystem of the DMN in OCD demonstrates decreased rs-FCN strength with the ventral/dorsal ACC, dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC), and putamen.3132 Additionally, the inter-modular rs-FCN between the salience network (SN)33 and DMN is also reduced in OCD.2834 Moreover, the fronto-parietal top-down control network reveals excessive local clustering between the ACC, precuneus, and temporo-parietal junction.35 However, to our knowledge, there have been few studies elucidating the network-based neural underpinnings of executive dysfunction subdomains in OCD as indicated in the ACC-centered rs-FCN.
The goal of present study was to illustrate the differential impact of ACC-based inter-modular communication between the DMN,36 SN,33 executive control network (ECN)37 or dorsal attention network (DAN)38 based on executive functioning performance when comparing OCD with HC. Specifically, between-group comparisons of ACC-based rs-FCN between OCD and HC groups using five ACC sub-regions were examined based on the following brain-cognition relationships: caudal ACC (hub region of somatomotor network)-based rs-FCN vs. set-shifting with visuomotor sequencing (TMT-B),39 dorsal ACC (hub region of SN)-based rs-FCN vs. visuospatial organization (RCFT organization score),404142 supragenual ACC (hub region of ECN)-based rs-FCN vs. setshifting with strategic planning (WCST perseverative error),434445 and rostral ACC (hub region of DMN)-based rs-FCN vs. response inhibition (SCWT incongruent trial reaction time).54647
Twenty-four patients (17 males and 7 females) who fulfilled DSM-IV criteria for OCD, and who were diagnosed based on DSM-IV criteria (4th edition, text revision; DSM-IV-TR), were recruited between March 2007 and May 2009 from the OCD clinic at Seoul National University Hospital. Eighteen patients were drug-naive, and the remaining six had been drug-free for at least four weeks at the time of study inclusion. Thirty-four sex- and age-matched HCs were also recruited. The non-patient version of the Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-IV (SCID-NP) was used to assess psychiatric disorders in HCs. Exclusion criteria included a lifetime history of major psychiatric disorders other than OCD, significant head injury, seizure disorder, or intellectual disability. A total of 22 OCDs and 22 HCs were previously included in a task-negative rs-FCN study.32 The Institutional Review Board at Seoul National University Hospital approved the current study, and written informed consent was obtained from all subjects after the procedures had been fully explained.
The severity of subjects' obsessive-compulsive symptomatology was measured using the 10-item clinician-rated Yale-Brown Obsessive Compulsive Scale (Y-BOCS).48 The Beck Depression Inventory (BDI)49 and the Beck Anxiety Inventory (BAI)50 were also administered to measure the severity of accompanying depressive mood and anxiety, respectively. The Korean version of the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale (K-WAIS)51 was administered to measure subjects' intelligence quotient (IQ). Demographic and clinical data from the OCD and HC groups were compared using independent t-tests for continuous variables and chi-squared tests for categorical variables using the Matlab Statistics Toolbox (ver. R2014a; MathWorks Inc., Natick, MA, USA).
The RCFT5253 has been widely used to evaluate visuospatial constructional ability and non-verbal memory.54 Comprehensive RCFT performances scoring, using the Boston Qualitative Scoring System (BQSS),55 produced an Organization Summary Score, an arithmetic sum of the copy condition Fragmentation score (information integration) and Planning score (overall planning ability based on the order, placement and overall integrity of the depicted elements).54
The Stroop effect is defined as the extent of delay in naming the color of an incongruent color word relative to naming the color of a congruent color word or of a neutral non-color word.56 Since the SCWT color-word page provides conflicting visual stimuli to measure selective attention and response inhibition, we used the reaction time required to complete the reading of the SCWT color-word page as an interference score.57
The WCST58 evaluates cognitive capacity related to abstract reasoning, concept formation, and conceptual flexibility.59 For the present study, the perseverative error score determined by the subject sorting the cards according to a previously successful principle or persisting with an initially erroneous guess during subsequent sorts60 was selected as an appropriate measure of executive functioning.61
The TMT-B62 from the Halstead-Reitan Neuropsychological Test Battery requires task-switching ability and working memory in the characteristic context of visuomotoric tracking.3963 Subjects were asked to connect numbered and lettered circles printed consecutively on a worksheet by alternating the two sequences as fast as possible.
All resting-state functional brain images were acquired using a 1.5 T MAGNETOM Avanto scanner (Siemens, Erlangen, Germany). The resting-state fMRI scanning procedure consisted of 120 volumes covering the whole brain, acquired in 25 contiguous axial slices approximately parallel to the anteriorposterior commissure plane with interleaved multi-slice echo-planar imaging during 4.68 min (TR=2.34 s, TE=52 ms, field of view=22 cm, flip angle=90°, voxel size=3.44×3.44×5 mm, slice thickness=5 mm, no inter-slice gap). During these resting-state experiments, subjects lay in the dark with their eyes closed and were instructed to relax as much as possible and think about nothing in particular. Additionally, T1-weighted high-resolution structural images, obtained using a magnetization-prepared rapid acquisition gradient echo sequence (TR=1.16 s, TE=4.76 ms, field of view=23 cm, flip angle=15°, voxel size=0.45×0.45×0.90 mm, slice thickness=0.9 mm, no interslice gap), were acquired in 176 contiguous axial slices to coregister and normalize the echo-planar images to the Montreal Neurologic Institute (MNI) template.
Functional data were preprocessed using SPM8 software (http://www.fil.ion.ucl.ac.uk/spm). The initial four volumes of the functional images were removed to eliminate any non-equilibrium effects of magnetization. Preprocessing steps consisted of slice-timing correction for interleaved acquisition, head motion correction, spatial normalization into standard stereotactic MNI space with re-sampling to 3-mm cubic voxels, and spatial smoothing using a Gaussian kernel of 6-mm full width at half-maximum. For the resting-state functional connectivity analysis, additional preprocessing steps consisting of de-trending, temporal band-pass filtering (0.01 Hz<f<0.08 Hz), and regressing out of the first temporal derivatives (including the head motion parameters, global signals, and signals stemming from cerebral white matter and cerebrospinal fluid) were serially conducted using the resting-state fMRI Data Analysis Toolkit (REST version 1.8, http://resting-fmri.sourceforge.net).64
We examined the rs-FCN of five selected seed regions of interest (ROIs) systematically placed throughout the right ACC in two arrays designated as superior (S) and inferior (I).1765 The five ACC seeds selected for this study represent samples of five subdomains of executive functioning associated with the ACC: the caudal ACC seed S1 (motoric executive control;19 MNI coordinates: x=5, y=-10, z=47), the dorsal ACC seed S3 (selective attention, response inhibition, and setmaintenance;2021 x=5, y=14, z=42), the supragenual ACC seed S5 (conflict detection/resolution and error processing;2223 x=5, y=34, z=28), the perigenual ACC seed S7 (mentalizing/decoding of external cues;24 x=5, y=47, z=11), and the subgenual ACC seed I9 (emotional recognition/regulation as a prerequisite of cognitive control;2526 x=5, y=25, z=-10). Using the “functional connectivity” function of REST, we examined rs-FC maps of the five predefined ACC seed ROIs for each subject. Each spherical seed had a radius of 3 mm in a 3×3×3 mm voxel-sized space. For each participant, we calculated the mean time series of each seed ROI by averaging across all voxels within the seed, to calculate the map of Pearson correlation coefficients for mean time series between seed ROI-versus-voxel of gray matter across the cerebral hemisphere. Finally, the correlation coefficient maps were converted into z maps using Fisher's z transformations to improve normality.64
To reveal within-group functional connectivity patterns (Figure 1), we entered each single-subject intrinsic network component into a voxel-wise one-sample t-test in SPM8 and created statistical z maps of the intrinsic networks based on each of the five ACC seeds (p<0.001 and cluster threshold (k)≥10 for multiple comparisons, which corresponds to the corrected threshold of p<0.05 as determined by 3dClustSim in AFNI [https://afni.nimh.nih.gov/]). Subsequent two-sample t-tests in SPM8 with a binary inclusive mask encompassing the within-group level rs-FCN for two groups were conducted for five kinds of ACC-based rs-FCNs (p<0.001 and k≥10) (Figure 2).
Furthermore, between-group comparison for the differential pattern of correlations between four pairs of ACC-based rs-FCN strength and degree of executive functioning (Figure 3) including the caudal ACC S1-based rs-FCN vs. TMT-B reaction time,3966 the dorsal ACC S3-based rs-FCN vs. RCFT organization summary score,46 the supragenual ACC S5-based rs-FCN vs. WCST perseverative errors,4567 and the perigenual ACC S7-based rs-FCN vs. SCWT color-word interference score,54768 were tested using the general linear model (GLM) in SPM8 [while covarying for age and sex; using an inclusive binary mask of the group-level rs-FCN map; results significant at p<0.0125 (=0.05/4) and k (cluster size) ≥10].69 For identification of probabilistic cytoarchitecture as well as Brodmann area (BA) per local global maxima, SPM Anatomy toolbox version 2.070 and Talairach Client version 2.4.3 (http://www.talairach.org/manual.html) were used.
Subject demographic and clinical characteristics ts are presented in Table 1. We found no significant differences between the groups regarding age, sex, education, IQ, and RCFT organization summary scores. In contrast, significant differences were observed between the OCD group and the HCs with respect to the WCST perseverative errors, SCWT colorword interference scores, and TMT-B reaction times (p<0.05, two-tailed).
Caudal seed S1 in subjects with OCD (Figure 1) correlated with a network of right ventral MCC and left ventral ACC (BA 24), the right primary somatosensory (BA 3) and motor (BA 4) cortices, the bilateral supplementary motor areas (SMA; BA 6) and insula (BA 13), the right claustrum and precuneus (BA 7), the right supramarginal gyrus (BA 40), and the DLPFC (BA 9). Of note, the ACC S1-based rs-FCN in the right ventral MCC (BA 24) was weaker in OCD compared to HC (Figure 2). However, no significant interaction between diagnosis (OCD vs. HC)×ACC S1-based rs-FCN strength for TMT-B reaction times was detected.
Seed S3, which resides in the dorsal ACC, demonstrated significant rs-FCN in the bilateral insula (BA 13) and DLPFC (BA 9), left supramarginal gyrus (BA 40), right ventral MCC (BA 24) and SMA, bilateral premotor cortex, right pulvinar nucleus of the thalamus and bilateral claustrum, left pars orbitalis (BA 47) and superior temporal gyri (BA 22/38/41), left dorsal PCC (BA 31) and right frontopolar cortex (BA 10), as well as the left putamen and amygdala in OCD (Figure 1). Specifically, the ACC S3-based rs-FCN in the left DLPFC (BA 8; middle frontal gyrus) was attenuated in OCD compared to HC (Figure 2).
Moreover, a significant interaction between diagnosis×ACC S3-based rs-FCN strength in the right DLPFC (BA 9) for RCFT organization summary scores was revealed (p<0.001, k≥10) (Figure 3, Table 2); a portion of the ACC seed S3-based rs-FCN in the right DLPFC correlated inversely with RCFT organization summary scores in HC [r (partial correlation coefficient while covarying for age and sex)=-0.466, p=0.007] but not in OCD [r=0.479, p=0.024>0.013 (=0.05/4)].
The supragenual ACC seed region S5 showed significant rs-FC with bilateral DLPFC (BA 9/46) and supramarginal gyri (BA 40), left insula (BA 13), bilateral claustrum and right thalamus, right frontopolar cortex (BA 10), left ventral PCC and precuneus (BA 23/7), bilateral premotor cortex (BA 6), and right associative visual cortex (BA 19) in OCD (Figure 1). Compared to HC, subjects with OCD showed stronger ACC S5-based rs-FCN in the left DLPFC (BA 46) and right pars opercularis (BA 44) (Figure 2). Conversely, no significant interaction between diagnosis×ACC S5-based rs-FCN strength for WCST perseverative errors was found.
Perigenual ACC seed S7 in OCD revealed rs-FCN with the left medial prefrontal and orbitofrontal cortices (BA 10/11), left retrosplenial (BA 30) and right dorsal (BA 31) PCC, bilateral angular (BA 39) and middle/inferior temporal gyri (BA 20/21/22), pars orbitalis (BA 47), bilateral caudate body and right thalamus, right DLPFC (BA 9), bilateral premotor cortex (BA 6) and frontal eye field (FEF; BA 8; superior lateral or medial frontal cortices) in OCD (Figure 1). It is noteworthy that the ACC S7-based rs-FCN in the left caudate body and dorsal ACC (BA 32) and in the right ventral ACC (BA 24) were weaker in subjects with OCD compared to HC (Figure 2).
Moreover, a significant interaction between diagnosis×ACC S7-based rs-FCN strength in the left FEF for SCWT color-word interference scores (Figure 3, Table 2) was also demonstrated (p<0.001, k>10); reductions in ACC seed S7-based rs-FCN in the left FEF correlated inversely with the SCWT color-word interference score in HC (r=-0.595, p=0.0004) but not in OCD [r=0.425, p=0.049>0.013 (=0.05/4)].
Seed I9, located in the subgenual ACC, was associated with an extensive pattern of correlated activity in the bilateral frontopolar cortices and OFC (BA 10/11), right subgenual ACC (BA 25) and pars orbitalis (BA 47) in subjects with OCD (Figure 1); the pattern of ACC I9-based rs-FCN was not significantly different from the HC group (Figure 2).
To the best of our knowledge, there has been a distinct lack of prior research investigating the network-based neural underpinnings of executive dysfunction in OCD as reflected in the ACC-centered rs-FCNs. In the current study, five seeds in the right ACC, a central component of the CSTC loop, revealed distinct patterns of rs-FCNs in subjects with OCD, in agreement with prior research with HC.17 Conversely, the OCD group revealed differences in rs-FCN strength between the ACC sub-regions and the left DLPFC, right pars opercularis, right ventral ACC, and the left caudate nucleus. When selected dysfunction of brain rs-FCN occurs as a result of disorder-related pathological process, among others, the hierarchical structure of the functional brain network (including the focus of primal regional functional connectivity modulating successful or maladaptive cognitive performance) could be changed.71
This study showed changes in characteristic intra-/intermodular ECN connectivity in OCD (Figure 2). Increased rs-FCN strength between the right supragenual ACC (S5) and the left DLPFC (BA 46), reminiscent of the neural response during working memory task performance with increased task load,37 demonstrated an elevation of intra-modular ECN network connectivity in OCD.72 Additionally, decreased rs-FCN between the right dorsal ACC (S3) and left DLPFC (BA 8), as well as increased rs-FCN between the right supragenual ACC (S5) and right inferior frontal gyrus (BA 44), uncovered not only decreased inter-modular rs-FCN between the SN and ECN, but also increased inter-modular rs-FCN between the ECN and ventral attention network (VAN) in OCD, respectively.3373 The aforementioned inter-modular ECN connectivity with the SN and VAN could be related to maladaptive cognitive performance in OCD, including intractable preoccupations, distractions related to one's obsessions, and frequent failures with flexible adaptation toward increased cognitive load during working memory or executive planning.37747576
This study illustrated a significant interaction between diagnosis×ACC S7-based rs-FCN strength in the left FEF for SCWT color-word interference scores (Figure 3). In other words, an inverse correlation between the intensity of rostral ACC-based rs-FCN in the left FEF with SCWT color-word interference scores in HC (r=-0.595, p=0.0004) lost its effectiveness in OCD (r=0.425, p=0.049>0.013). This implies a differential impact of inter-modular connectivity between the DMN and DAN for higher-ordered cognitive strategies related to visuo-spatial constructional ability according to OCD or HC group membership. Only when the primal executive functioning of selective attention and response inhibition is sufficient (which is the case for HC, and not for OCD),77 attentional status optimization per se, in relation to the stronger inter-modular network connectivity between the DAN and DMN could minimize the Stroop interference effect. This would be able to facilitate SCWT color-word page reading performance.7879
Although the degree of visuoconstructive organizational strategy use during RCFT figure copying did not show statistically significant difference between the two groups of OCD and HC,80 this study disclosed a characteristic role of intermodular rs-FCN between the ECN and SN.33 This was mainly composed of the dorsal ACC and DLPFC (Figure 3) for strategic decoding of RCFT stimuli against the cognitive conflict of “whether to memorize in visual details or to reconstruct the whole framework” in HC (r=-0.466, p=0.007).8182 This might result in the “zooming-in” of attentional focus for HC.8384 However, few MRI studies to date have unveiled the neural correlates of organizational strategies as measured using the RCFT;85 thus, the present results require cautious interpretation, warranting further studies.
A few limitations should be acknowledged. We did not consider OCD symptom subtypes8687 in our rs-FCN analyses. However, if we accept the notion of OCD as one disease entity with a common pathophysiology encompassing several symptom subtypes,29 our investigation of rs-FCNs might successfully reflect a common pathophysiology. Additionally, since our goal was to elucidate finer network-based neural underpinnings of executive dysfunction in OCD from the perspective of ACC sub-regions, we were not able to conduct a broader exploration of functional brain networks that would enable a priori screening of multi-hub regions related to neurocognitive performance in OCD.
The present findings, obtained using a well-developed methodology, revealed the importance of the ACC as a central executor in CSTC loops among subjects with OCD.65 Using the rs-FCN approach, the patterns of which resemble the topographic activation patterns of the same regions during task performance,20 we provided evidence of a significant diagnosis×strength of ACC-based rs-FCN interaction in the correlation between executive functioning and ACC-based rs-FCN. The strategic decoding of visuospatial stimuli such as RCFT was dependent on the inter-modular network connectivity between dorsal ACC versus right DLPFC, with minimization of color-word interference effect during SCWT mainly loaded on the optimal strength of inter-modular network connectivity between the left FEF versus perigenual ACC. These finely delineated, network-based neural foundations for diverse facets of executive dysfunction in OCD could become a potential target for future treatment. The aim of such interventions should be improvements in global domains of functioning that is broader than simple clinical symptom relief.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) Grant funded by the Korean Government (MSIP): No. NRF-2015R1A5A7037676.
References
1. Ruscio AM, Stein DJ, Chiu WT, Kessler RC. The epidemiology of obsessive-compulsive disorder in the National Comorbidity Survey Replication. Mol Psychiatry 2010;15:53-63. PMID: 18725912.


2. Milad MR, Rauch SL. Obsessive-compulsive disorder: beyond segregated cortico-striatal pathways. Trends Cogn Sci 2012;16:43-51. PMID: 22138231.


3. Saxena S, Bota RG, Brody AL. Brain-behavior relationships in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Semin Clin Neuropsychiatry 2001;6:82-101. PMID: 11296309.


4. Cavedini P, Zorzi C, Piccinni M, Cavallini MC, Bellodi L. Executive dysfunctions in obsessive-compulsive patients and unaffected relatives: searching for a new intermediate phenotype. Biol Psychiatry 2010;67:1178-1184. PMID: 20381015.


5. Glascher J, Adolphs R, Damasio H, Bechara A, Rudrauf D, Calamia M, et al. Lesion mapping of cognitive control and value-based decision making in the prefrontal cortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2012;109:14681-14686. PMID: 22908286.



6. Pauls DL, Abramovitch A, Rauch SL, Geller DA. Obsessive-compulsive disorder: an integrative genetic and neurobiological perspective. Nat Rev Neurosci 2014;15:410-424. PMID: 24840803.


7. Shin NY, Lee TY, Kim E, Kwon JS. Cognitive functioning in obsessive-compulsive disorder: a meta-analysis. Psychol Med 2014;44:1121-1130. PMID: 23866289.


8. D'Alcante CC, Diniz JB, Fossaluza V, Batistuzzo MC, Lopes AC, Shavitt RG, et al. Neuropsychological predictors of response to randomized treatment in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 2012;39:310-317. PMID: 22789662.


9. Lewin AB, Larson MJ, Park JM, McGuire JF, Murphy TK, Storch EA. Neuropsychological functioning in youth with obsessive compulsive disorder: an examination of executive function and memory impairment. Psychiatry Res 2014;216:108-115. PMID: 24508366.


10. Banks GP, Mikell CB, Youngerman BE, Henriques B, Kelly KM, Chan AK, et al. Neuroanatomical characteristics associated with response to dorsal anterior cingulotomy for obsessive-compulsive disorder. JAMA Psychiatry 2015;72:127-135. PMID: 25536384.


11. Hou J, Wu W, Lin Y, Wang J, Zhou D, Guo J, et al. Localization of cerebral functional deficits in patients with obsessive-compulsive disorder: a resting-state fMRI study. J Affect Disord 2012;138:313-321. PMID: 22331021.


12. Rotge JY, Guehl D, Dilharreguy B, Tignol J, Bioulac B, Allard M, et al. Meta-analysis of brain volume changes in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Biol Psychiatry 2009;65:75-83. PMID: 18718575.


13. Yucel M, Harrison BJ, Wood SJ, Fornito A, Wellard RM, Pujol J, et al. Functional and biochemical alterations of the medial frontal cortex in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2007;64:946-955. PMID: 17679639.


14. Shenhav A, Botvinick MM, Cohen JD. The expected value of control: an integrative theory of anterior cingulate cortex function. Neuron 2013;79:217-240. PMID: 23889930.



15. Fjell AM, Westlye LT, Amlien I, Tamnes CK, Grydeland H, Engvig A, et al. High-expanding cortical regions in human development and evolution are related to higher intellectual abilities. Cereb Cortex 2015;25:26-34. PMID: 23960203.



16. Fitzgerald KD, Welsh RC, Stern ER, Angstadt M, Hanna GL, Abelson JL, et al. Developmental alterations of frontal-striatal-thalamic connectivity in obsessive-compulsive disorder. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 2011;50:938-948.e3. PMID: 21871375.



17. Kelly AM, Di Martino A, Uddin LQ, Shehzad Z, Gee DG, Reiss PT, et al. Development of anterior cingulate functional connectivity from late childhood to early adulthood. Cereb Cortex 2009;19:640-657. PMID: 18653667.



18. Palomero-Gallagher N, Mohlberg H, Zilles K, Vogt B. Cytology and receptor architecture of human anterior cingulate cortex. J Comp Neurol 2008;508:906-926. PMID: 18404667.



19. Paus T. Primate anterior cingulate cortex: where motor control, drive and cognition interface. Nat Rev Neurosci 2001;2:417-424. PMID: 11389475.


20. Dosenbach NU, Fair DA, Cohen AL, Schlaggar BL, Petersen SE. A dual-networks architecture of top-down control. Trends Cogn Sci 2008;12:99-105. PMID: 18262825.



21. Sreenivasan KK, Curtis CE, D'Esposito M. Revisiting the role of persistent neural activity during working memory. Trends Cogn Sci 2014;18:82-89. PMID: 24439529.



22. Amodio DM. The neuroscience of prejudice and stereotyping. Nat Rev Neurosci 2014;15:670-682. PMID: 25186236.


23. Mansouri FA, Buckley MJ, Tanaka K. Mnemonic function of the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in conflict-induced behavioral adjustment. Science 2007;318:987-990. PMID: 17962523.


24. Amodio DM, Frith CD. Meeting of minds: the medial frontal cortex and social cognition. Nat Rev Neurosci 2006;7:268-277. PMID: 16552413.


25. Inzlicht M, Bartholow BD, Hirsh JB. Emotional foundations of cognitive control. Trends Cogn Sci 2015;19:126-132. PMID: 25659515.



26. Phillips ML, Drevets WC, Rauch SL, Lane R. Neurobiology of emotion perception I: the neural basis of normal emotion perception. Biol Psychiatry 2003;54:504-514. PMID: 12946879.


27. Fair DA, Dosenbach NU, Church JA, Cohen AL, Brahmbhatt S, Miezin FM, et al. Development of distinct control networks through segregation and integration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2007;104:13507-13512. PMID: 17679691.



28. Beucke JC, Sepulcre J, Talukdar T, Linnman C, Zschenderlein K, Endrass T, et al. Abnormally high degree connectivity of the orbitofrontal cortex in obsessive-compulsive disorder. JAMA Psychiatry 2013;70:619-629. PMID: 23740050.


29. Harrison BJ, Soriano-Mas C, Pujol J, Ortiz H, Lopez-Sola M, Hernandez-Ribas R, et al. Altered corticostriatal functional connectivity in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2009;66:1189-1200. PMID: 19884607.


30. Posner J, Marsh R, Maia TV, Peterson BS, Gruber A, Simpson HB. Reduced functional connectivity within the limbic cortico-striato-thalamo-cortical loop in unmedicated adults with obsessive-compulsive disorder. Hum Brain Mapp 2014;35:2852-2860. PMID: 24123377.


31. Beucke JC, Sepulcre J, Eldaief MC, Sebold M, Kathmann N, Kaufmann C. Default mode network subsystem alterations in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Br J Psychiatry 2014;205:376-382. PMID: 25257066.


32. Jang JH, Kim JH, Jung WH, Choi JS, Jung MH, Lee JM, et al. Functional connectivity in fronto-subcortical circuitry during the resting state in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Neurosci Lett 2010;474:158-162. PMID: 20302914.


33. Seeley WW, Menon V, Schatzberg AF, Keller J, Glover GH, Kenna H, et al. Dissociable intrinsic connectivity networks for salience processing and executive control. J Neurosci 2007;27:2349-2356. PMID: 17329432.



34. Stern ER, Fitzgerald KD, Welsh RC, Abelson JL, Taylor SF. Resting-state functional connectivity between fronto-parietal and default mode networks in obsessive-compulsive disorder. PLoS One 2012;7:e36356PMID: 22570705.



35. Zhang T, Wang J, Yang Y, Wu Q, Li B, Chen L, et al. Abnormal small-world architecture of top-down control networks in obsessive-compulsive disorder. J Psychiatry Neurosci 2011;36:23-31. PMID: 20964957.



36. Andrews-Hanna JR, Reidler JS, Sepulcre J, Poulin R, Buckner RL. Functional-anatomic fractionation of the brain's default network. Neuron 2010;65:550-562. PMID: 20188659.



37. Liang X, Zou Q, He Y, Yang Y. Topologically reorganized connectivity architecture of default-mode, executive-control, and salience networks across working memory task loads. Cereb Cortex 2016;26:1501-1511. PMID: 25596593.



38. Spreng RN, Sepulcre J, Turner GR, Stevens WD, Schacter DL. Intrinsic architecture underlying the relations among the default, dorsal attention, and frontoparietal control networks of the human brain. J Cogn Neurosci 2013;25:74-86. PMID: 22905821.


39. Terada S, Sato S, Nagao S, Ikeda C, Shindo A, Hayashi S, et al. Trail making test B and brain perfusion imaging in mild cognitive impairment and mild Alzheimer's disease. Psychiatry Res 2013;213:249-255. PMID: 23830931.


40. McAnulty G, Duffy FH, Kosta S, Weisenfeld NI, Warfield SK, Butler SC, et al. School age effects of the newborn individualized developmental care and assessment program for medically low-risk preterm infants: preliminary findings. J Clin Neonatol 2012;1:184-194. PMID: 23951557.



41. Rosenbloom MJ, Sassoon SA, Pfefferbaum A, Sullivan EV. Contribution of regional white matter integrity to visuospatial construction accuracy, organizational strategy, and memory for a complex figure in abstinent alcoholics. Brain Imaging Behav 2009;3:379-390. PMID: 20161607.



42. Shin YW, Ha TH, Kim SY, Kwon JS. Association between EEG alpha power and visuospatial function in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 2004;58:16-20. PMID: 14678451.


43. Dempster K, Norman R, Theberge J, Densmore M, Schaefer B, Williamson P. Glutamatergic metabolite correlations with neuropsychological tests in first episode schizophrenia. Psychiatry Res 2015;233:180-185. PMID: 26163385.


44. Zheng H, Jia F, Guo G, Quan D, Li G, Wu H, et al. Abnormal anterior cingulate N-acetylaspartate and executive functioning in treatment-resistant depression after rTMS therapy. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 2015;18:pyv059PMID: 26025780.



45. Ohrmann P, Kugel H, Bauer J, Siegmund A, Kolkebeck K, Suslow T, et al. Learning potential on the WCST in schizophrenia is related to the neuronal integrity of the anterior cingulate cortex as measured by proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Schizophr Res 2008;106:156-163. PMID: 18799290.


46. Liu Y, Bengson J, Huang H, Mangun GR, Ding M. Top-down modulation of neural activity in anticipatory visual attention: control mechanisms revealed by simultaneous EEG-fMRI. Cereb Cortex 2016;26:517-529. PMID: 25205663.



47. Chang A, Chen CC, Li HH, Li CS. Perigenual anterior cingulate event-related potential precedes stop signal errors. Neuroimage 2015;111:179-185. PMID: 25700955.



48. Goodman WK, Price LH, Rasmussen SA, Mazure C, Fleischmann RL, Hill CL, et al. The Yale-Brown Obsessive Compulsive Scale. I. Development, use, and reliability. Arch Gen Psychiatry 1989;46:1006-1011. PMID: 2684084.


49. Beck AT, Ward CH, Mendelson M, Mock J, Erbaugh J. An inventory for measuring depression. Arch Psychol 1961;4:561-571.

50. Beck AT, Steer R. Manual for the Beck Anxiety Inventory. San Antonio: Psychological Corporation; 1990.
51. Yum TH, Park YS, Oh KJ, Kim JG, Lee HY. The Manual of Korean-Welchsler Adult-Intelligence Scale. Korean Guidance Press; 1992.
52. Osterrieth PA. Le test de copie d'une figure complexe. Arch Psychol 1944;30.
53. Rey A. Psychological examination in cases of traumatic encephalopathy. Arch Psychol 1941;28:215-285.
54. Somerville J, Tremont G, Stern RA. The Boston Qualitative Scoring System as a measure of executive functioning in Rey-Osterrieth Complex Figure performance. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol 2000;22:613-621. PMID: 11094396.


55. Stern RA, Javorsky DJ, Singer EA, Singer NG, Somerville JA, Duke LM. The Boston Qualitative Scoring System for the Rey-Osterrieth Complex Figure: Professional Manual. Odessa: Psychological Assessment Resources; 1999.
56. Lansbergen MM, Kenemans JL, van Engeland H. Stroop interference and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a review and meta-analysis. Neuropsychology 2007;21:251-262. PMID: 17402825.



57. Yun JY, Lee DY, Seo EH, Choo IH, Park SY, Kim SG, et al. Neural Correlates of Stroop Performance in Alzheimer's Disease: A FDG-PET Study. Dement Geriatr Cogn Dis Extra 2011;1:190-201. PMID: 22163244.



58. Heaton RK, Chelune GJ, Talley JL, Kay GG, Curtiss G. Wisconsin card sorting test manual: revised and expanded. Odessa, FL: Psychological Assessment Resources; 1993.
59. Eling P, Derckx K, Maes R. On the historical and conceptual background of the Wisconsin Card Sorting Test. Brain Cogn 2008;67:247-253. PMID: 18328609.


60. Greve KW. Can perseverative responses on the Wisconsin Card Sorting Test be scored accurately? Arch Clin Neuropsychol 1993;8:511-517. PMID: 14591990.


61. Tukel R, Gurvit H, Ertekin BA, Oflaz S, Ertekin E, Baran B, et al. Neuropsychological function in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Compr Psychiatry 2012;53:167-175. PMID: 21550029.


62. Reitan RM. Validity of the Trail Making Test as an indicator of organic brain damage. Percept Mot Skills 1958;8:271-276.

63. Penades R, Catalan R, Andres S, Salamero M, Gasto C. Executive function and nonverbal memory in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Psychiatry Res 2005;133:81-90. PMID: 15698680.


64. Song XW, Dong ZY, Long XY, Li SF, Zuo XN, Zhu CZ, et al. REST: a toolkit for resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging data processing. PLoS One 2011;6:e25031PMID: 21949842.



65. Margulies DS, Kelly AM, Uddin LQ, Biswal BB, Castellanos FX, Milham MP. Mapping the functional connectivity of anterior cingulate cortex. Neuroimage 2007;37:579-588. PMID: 17604651.


66. Rosen ML, Stern CE, Michalka SW, Devaney KJ, Somers DC. Cognitive control network contributions to memory-guided visual attention. Cereb Cortex 2016;26:2059-2073. PMID: 25750253.



67. Kuwabara M, Mansouri FA, Buckley MJ, Tanaka K. Cognitive control functions of anterior cingulate cortex in macaque monkeys performing a Wisconsin Card Sorting Test analog. J Neurosci 2014;34:7531-7547. PMID: 24872558.



68. Cavanagh JF, Grundler TO, Frank MJ, Allen JJ. Altered cingulate subregion activation accounts for task-related dissociation in ERN amplitude as a function of obsessive-compulsive symptoms. Neuropsychologia 2010;48:2098-2109. PMID: 20381506.



69. Marsh R, Stefan M, Bansal R, Hao X, Walsh BT, Peterson BS. Anatomical characteristics of the cerebral surface in bulimia nervosa. Biol Psychiatry 2015;77:616-623. PMID: 23978404.


70. Eickhoff SB, Stephan KE, Mohlberg H, Grefkes C, Fink GR, Amunts K, et al. A new SPM toolbox for combining probabilistic cytoarchitectonic maps and functional imaging data. Neuroimage 2005;25:1325-1335. PMID: 15850749.


71. Filippi M, van den Heuvel MP, Fornito A, He Y, Hulshoff Pol HE, Agosta F, et al. Assessment of system dysfunction in the brain through MRI-based connectomics. Lancet Neurol 2013;12:1189-1199. PMID: 24120645.


72. Gottlich M, Kramer UM, Kordon A, Hohagen F, Zurowski B. Decreased limbic and increased fronto-parietal connectivity in unmedicated patients with obsessive-compulsive disorder. Hum Brain Mapp 2014;35:5617-5632. PMID: 25044747.



73. Weissman DH, Prado J. Heightened activity in a key region of the ventral attention network is linked to reduced activity in a key region of the dorsal attention network during unexpected shifts of covert visual spatial attention. Neuroimage 2012;61:798-804. PMID: 22445785.


74. de Vries FE, de Wit SJ, Cath DC, van der Werf YD, van der Borden V, van Rossum TB, et al. Compensatory frontoparietal activity during working memory: an endophenotype of obsessive-compulsive disorder. Biol Psychiatry 2014;76:878-887. PMID: 24365484.


75. Kucyi A, Hove MJ, Esterman M, Hutchison RM, Valera EM. Dynamic brain network correlates of spontaneous fluctuations in attention. Cereb Cortex [Epub ahead of print].


76. van den Heuvel OA, Veltman DJ, Groenewegen HJ, Cath DC, van Balkom AJ, van Hartskamp J, et al. Frontal-striatal dysfunction during planning in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2005;62:301-309. PMID: 15753243.


77. Kalanthroff E, Anholt GE, Henik A. Always on guard: test of high vs. low control conditions in obsessive-compulsive disorder patients. Psychiatry Res 2014;219:322-328. PMID: 24947916.


78. Esterman M, Noonan SK, Rosenberg M, Degutis J. In the zone or zoning out? Tracking behavioral and neural fluctuations during sustained attention. Cereb Cortex 2013;23:2712-2723. PMID: 22941724.



79. Hellyer PJ, Shanahan M, Scott G, Wise RJ, Sharp DJ, Leech R. The control of global brain dynamics: opposing actions of frontoparietal control and default mode networks on attention. J Neurosci 2014;34:451-461. PMID: 24403145.



80. Shin NY, Kang DH, Choi JS, Jung MH, Jang JH, Kwon JS. Do organizational strategies mediate nonverbal memory impairment in drug-naive patients with obsessive-compulsive disorder? Neuropsychology 2010;24:527-533. PMID: 20604626.



81. Mayer AR, Teshiba TM, Franco AR, Ling J, Shane MS, Stephen JM, et al. Modeling conflict and error in the medial frontal cortex. Hum Brain Mapp 2012;33:2843-2855. PMID: 21976411.


82. Shin MS, Park SY, Park SR, Seol SH, Kwon JS. Clinical and empirical applications of the Rey-Osterrieth Complex Figure Test. Nat Protoc 2006;1:892-899. PMID: 17406322.


83. Chen Q, Marshall JC, Weidner R, Fink GR. Zooming in and zooming out of the attentional focus: an FMRI study. Cereb Cortex 2009;19:805-819. PMID: 18689860.



84. Ronconi L, Basso D, Gori S, Facoetti A. TMS on right frontal eye fields induces an inflexible focus of attention. Cereb Cortex 2014;24:396-402. PMID: 23048022.



85. Ostby Y, Tamnes CK, Fjell AM, Walhovd KB. Dissociating memory processes in the developing brain: the role of hippocampal volume and cortical thickness in recall after minutes versus days. Cereb Cortex 2012;22:381-390. PMID: 21666134.



86. Harrison BJ, Pujol J, Cardoner N, Deus J, Alonso P, Lopez-Sola M, et al. Brain corticostriatal systems and the major clinical symptom dimensions of obsessive-compulsive disorder. Biol Psychiatry 2013;73:321-328. PMID: 23200527.


87. Jhung K, Ku J, Kim SJ, Lee H, Kim KR, An SK, et al. Distinct functional connectivity of limbic network in the washing type obsessive-compulsive disorder. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 2014;53:149-155. PMID: 24768985.


Figure 1
Resting state functional connectivity of the five seed regions of anterior cingulate for subjects with obsessive-compulsive disorder and for healthy controls [p<0.001 and k (cluster size) ≥10].

Figure 2
Between-group differences in five sub-regions of anterior cingulate cortex (ACC)-based resting state functional connectivity network (rs-FCN); displayed at p<0.001 and k (cluster size ≥10), including the seed S1-based (connections between the red circles), S3-based (between the yellow circles), S5-based (between the green circles), S7-based (between the light blue circles), and the I9-based (the purple circle) rs-FCN. Lines connecting different circles demonstrate the weaker (grey line) or stronger (red line) strength of ACC-based rs-FCN in subjects with obsessivecompulsive disorder relative to healthy controls. BA: Brodmann area, dACC: dorsal anterior cingulate cortex, DLPFC: dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, HC: healthy control, IFG: inferior frontal gyrus, Lt: left, MCC: middle cingulate cortex, OCD: obsessive-compulsive disorder, PO: pars opercularis, Rt: right, vACC: ventral anterior cingulate cortex.
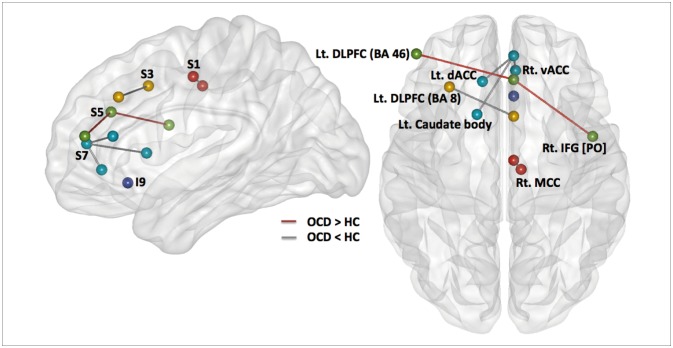
Figure 3
Area of significant interaction between the diagnosis and the strength of anterior cingulate cortex (ACC)-based resting state functional connectivity network (rs-FCN) in the correlation between executive functioning versus ACC-based rs-FCN (p<0.001, k≥10; general linear modeling using SPM8 while covarying for age and sex). Specifically, increment of ACC seed S3 (dorsal)-based rs-FCN in the right dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC) correlated inversely with Rey-Osterrieth Complex Figure Test (RCFT) organization score in healthy controls [HC; r (partial correlation coefficient while covarying for age and sex)=-0.466, p=0.007] but not in obsessive-compulsive disorder [OCD; r=0.479, p=0.024>0.013 (=0.05/4)]. In addition, reductions of ACC seed S7 (perigenual)-based rs-FCN in left prefrontal eye field (FEF) correlated inversely with the Stroop Color-Word Test (SCWT) interference score in HC (r=-0.595, p=0.0004) but not in OCD (r=0.425, p=0.049>0.013). ACC: anterior cingulate cortex, BA: Broadmann area, DLPFC: dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, FEF: frontal eye field, HC: healthy control, Lt: left, OCD: obsessive-compulsive disorder, rRCFT: Rey-Osterrieth Complex Figure Test, s-FCN: resting state functional connectivity network, Rt: right, SCWT: stroop color-word test.
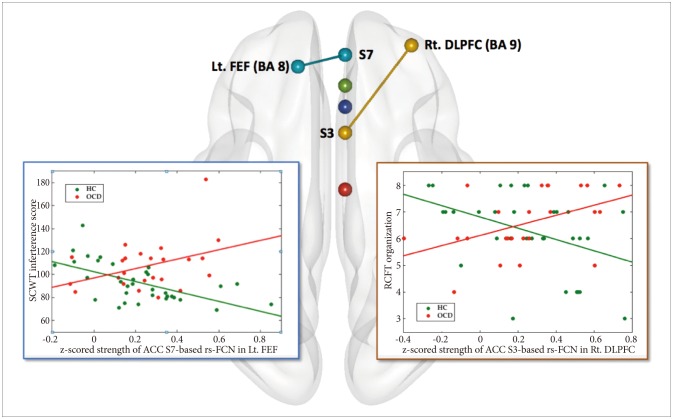
Table 1
Demographic and clinical characteristics of subjects with obsessive-compulsive disorder and healthy controls*
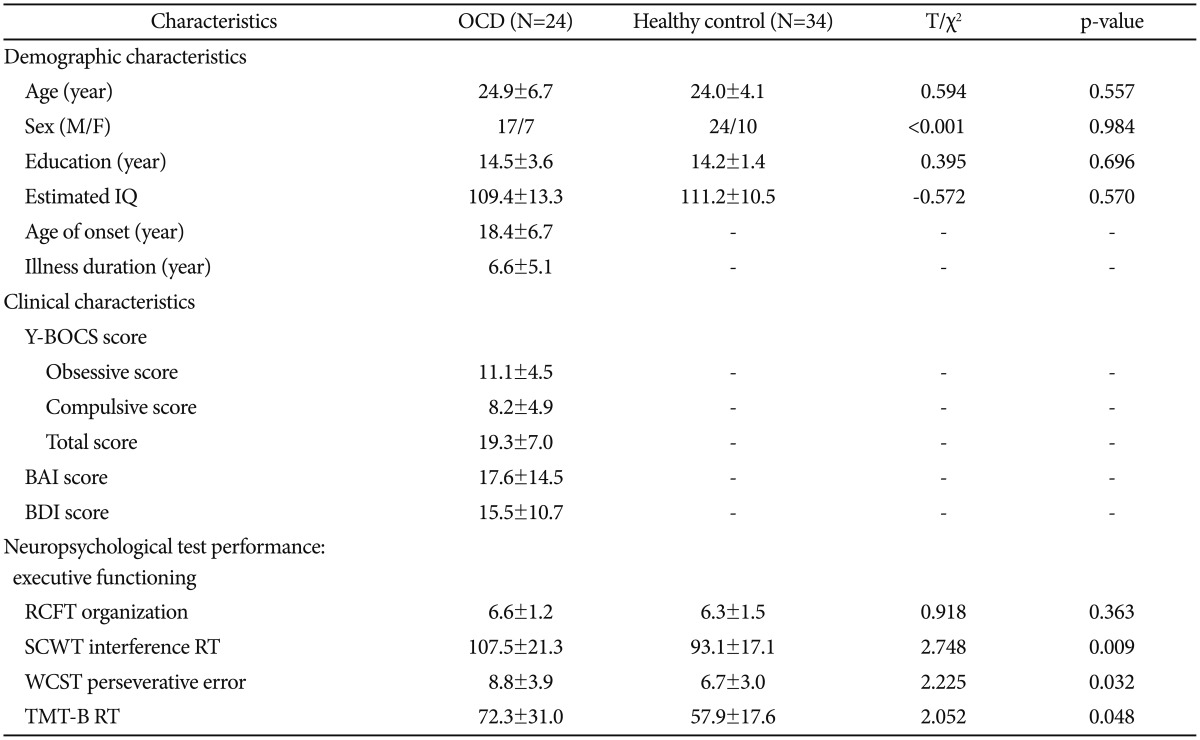
*data are given as mean±standard deviation. BAI: Beck Anxiety Inventory, BDI: Beck Depression Inventory, OCD: obsessive-compulsive disorder, RCFT: Rey-Osterrieth Complex Figure Test, RT: reaction time, SCWT: Stroop Color-Word Test, TMT: Trail Making Test, Y-BOCS: Yale-Brown Obsessive Compulsive Scale, WCST: Wisconsin Card Sorting Test







